IPC-298
Cat.No.: CSC-C0352
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
Morphology: adherent, spindle-like cells (a few epitheliod cells) growing as confluent monolayer
Culture Properties: monolayer
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
Immunology: cytokeratin -, desmin -, endothel -, GFAP -, HMB-45 +, neurofilament +, vimentin +
Viruses: ELISA: reverse transcriptase negative; PCR: EBV -, HBV -, HCV -, HHV-8
IPC-298 cell line was established from the primary tumor of a 64-year-old woman. Melanoma is a type of tumor derived from melanocytes, the pigment cells in the skin, and may occur in other parts of the body including the mouth, nose, and genitals. This cell line exhibits several notable biological characteristics: it is a BRAF-mutant melanoma cell line with a Q61L mutation, closely associated with abnormal activation of the MAPK signaling pathway. Additionally, IPC-298 cells show a high expression level of the ERBB4 (HER3) receptor, a receptor tyrosine kinase that promotes cell proliferation and survival through the PI3K/AKT and MAPK pathways. IPC-298 cells also display sensitivity to certain drugs such as the non-degrading molecular glue NST-628, which targets the RAS-MEK pathway.
IPC-298 cell line is useful for melanoma research as it helps understand BRAF mutations, ERBB4 signaling pathways, and the PMEL protein. In addition, IPC-298 cell line is frequently used to evaluate different anti-melanoma drugs, and showed good sensitivity to the RAS-MEK pathway inhibitor NST-628. IPC-298 cells were shown to be highly invasive and highly metastatic when transplanted in vivo, and have been utilized as a model for understanding the mechanism of melanoma metastasis.
Anti-Melanoma Effects of Ni/Cu-NCPs
Bimetallic nanoparticles (NPs) offer enhanced properties for cancer therapy. Huang's team synthesized nickel/copper NPs using the aqueous extract of Artemisia absinthium, a medicinal plant with known antioxidant and anticancer properties. The NPs were characterized using FT-IR, XRD, and FE-SEM. Their antioxidant activity was tested against DPPH, and their anti-melanoma efficacy was evaluated using an MTT assay on HT144, IPC-298, and SKMEL24 cell lines.
In cytotoxicity tests, introducing Ni/Cu-NCPs to melanoma cells (HT144, IPC-298, and SKMEL24) notably reduced ATP levels, causing mitochondrial damage. Ni/Cu-NCPs can produce substantial ROS, enhancing cytotoxicity. They applied Ni/CuNPs@ A. absinthium to cells at 0-1000 μg/mL. Using the MTT test, formazan crystal formation indicated cell viability. Figure 1 shows cytotoxic effects on HT144, IPC-298, and SKMEL24 cell lines, revealing decreased viability with increased Ni/CuNPs loads. Normal cell line HUVEC showed no significant viability drop. Figure 1 illustrates IC50 values for cancer studies as 150, 170, and 147 μg/mL against HT144, IPC-298, and SKMEL24, respectively, highlighting Ni/CuNPs@ A. absinthium's strong antiproliferative effect on melanoma cells, especially in SKMEL24 cells with the lowest IC50 value.
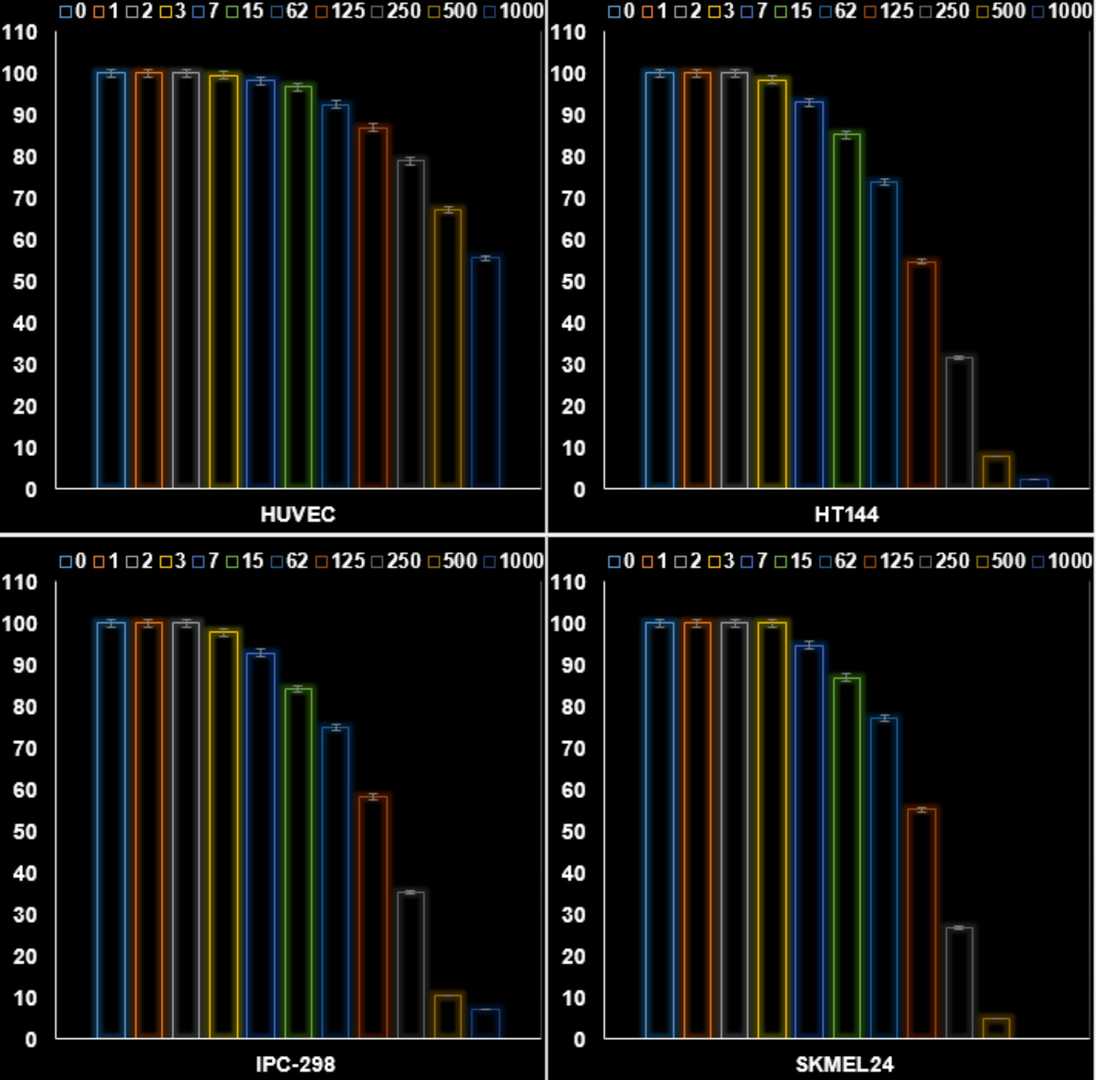 Fig. 1. The efficacy of Ni/CuNPs@ A. absinthium on the cell viability (%) of HUVEC, HT144, IPC-298, and SKMEL24 cell lines (Huang A, Zhang L, et al., 2025).
Fig. 1. The efficacy of Ni/CuNPs@ A. absinthium on the cell viability (%) of HUVEC, HT144, IPC-298, and SKMEL24 cell lines (Huang A, Zhang L, et al., 2025).
Anti-Human Melanoma and Antioxidant Properties of Fe3O4@CML/Au NPs
Gold nanoparticles (Au NPs) are particularly important for catalysis and medical therapies due to their stability and biocompatibility. However, their small size often leads to aggregation, reducing their potential. This study synthesizes Au NPs immobilized on Fe3O4 nanoparticles using carboxymethyl lignin (CML) as a green reducing and stabilizing agent. The nanocomposite was characterized using various physicochemical methods and tested for catalytic reduction of nitroaromatics and anti-human melanoma efficacy.
To measure the anti-human melanoma efficacy of Fe3O4@CML/Au NPs nanocomposite, MTT assay was applied on HT144, MUM2C, IPC-298 and SKMEL24 cell lines. Fe3O4@CML/Au NPs nanocomposite had high anti-human melanoma efficacy on above tumor cells. The IC50 of Fe3O4@CML/Au NPs nanocomposite was 137, 145, 185, and 125 μg/mL against HT144, MUM2C, IPC-298 and SKMEL24 cells, respectively. The best finding of anti-human melanoma properties of Fe3O4@CML/Au NPs nanocomposite was seen in the case of the SKMEL24 cell line (Fig. 2). The Fe3O4@CML/Au NPs nanocomposite increased significantly the apoptosis and ROS levels in the HT144, MUM2C, IPC-298 and SKMEL24 cells. The data of Fig. 2, Fig. 3 protects the anti-melanoma effects of the Fe3O4@CML/Au NPs nanocomposite.
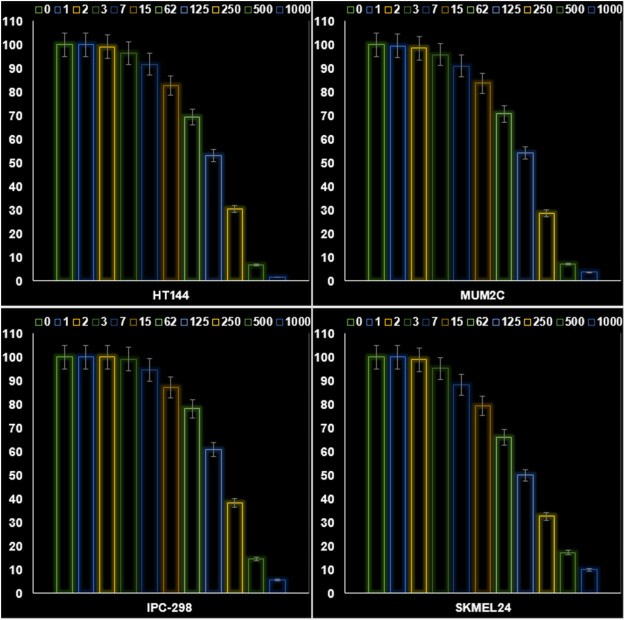 Fig. 2. The properties of Fe3O4@CML/Au NPs nanocomposite on the cell viability (%) of HT144, MUM2C, IPC-298 and SKMEL24 cells (Zhao Z J, Wu D J, et al., 2024).
Fig. 2. The properties of Fe3O4@CML/Au NPs nanocomposite on the cell viability (%) of HT144, MUM2C, IPC-298 and SKMEL24 cells (Zhao Z J, Wu D J, et al., 2024).
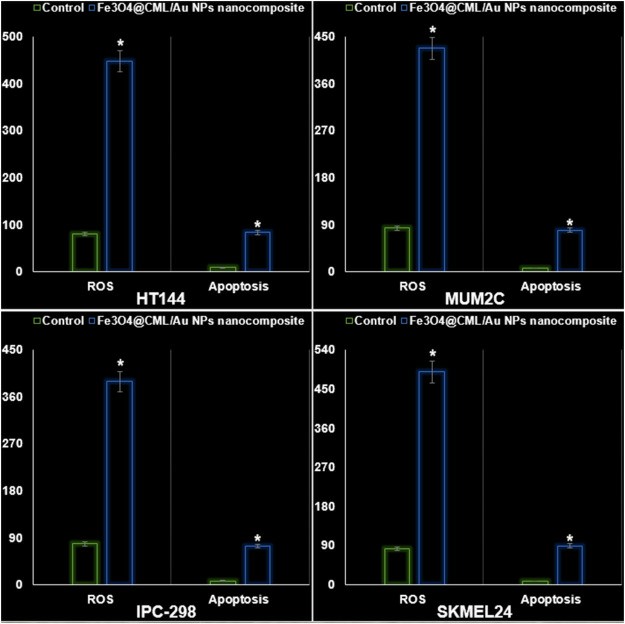 Fig. 3. The properties of Fe3O4@CML/Au NPs nanocomposite on the ROS (a.u.) and apoptosis (%) of HT144, MUM2C, IPC-298 and SKMEL24 cells (Zhao Z J, Wu D J, et al., 2024).
Fig. 3. The properties of Fe3O4@CML/Au NPs nanocomposite on the ROS (a.u.) and apoptosis (%) of HT144, MUM2C, IPC-298 and SKMEL24 cells (Zhao Z J, Wu D J, et al., 2024).
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- You May Also Need
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells