G-361
Cat.No.: CSC-C9382L
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
Source: Skin
Morphology: epithelial
Culture Properties: monolayer
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
Isoenzyme: G6PD, B
Production: melanin
Histopathology: melanoma
vWA: 15,17
FGA: 19,21
Amelogenin: X
TH01: 7,9
TPOX: 8,10
CSF1P0: 10
D5S818: 11
D13S317: 11
D7S820: 8,11
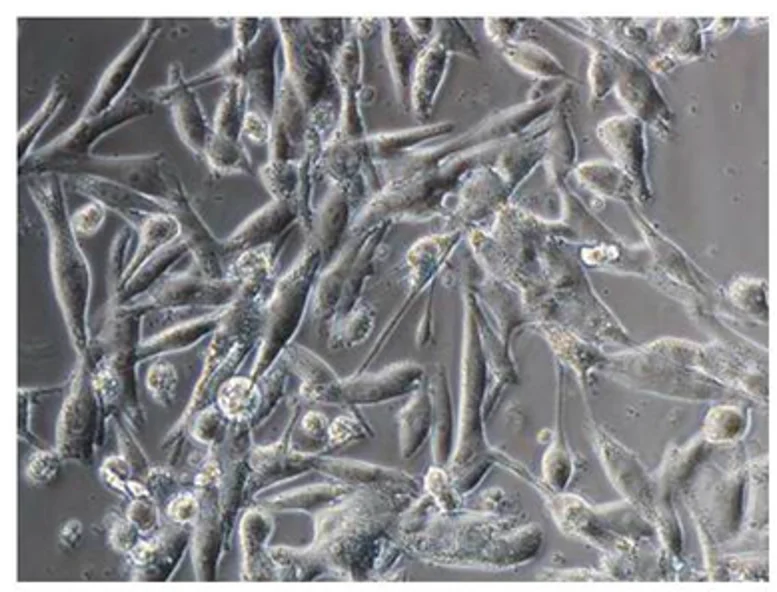
The G-361 cell line was isolated from a metastatic skin lesion of a 31-year-old man with malignant melanoma. Morphologically, these are epithelioid, adherent cells with a highly malignant aspect, with irregular growth with proliferation under usual culture conditions. The G-361 cells are thought to have developed from melanocytes, which are epidermal pigment cells. In addition to a malignant appearance, they have the same oncogenic BRAF/NRAS mutations and melanoma-associated antigenic markers (e.g., S100, HMB-45). The G-361 cells have a high level of tyrosinase activity.
The cell line is commonly used in cancer biology to model and study the mechanisms of cancer progression, drug resistance, and metastasis. They can also be used to study the genetic and molecular basis of melanoma and its response to different targeted therapies, such as BRAF inhibitors and immunotherapies, as they also express melanoma-associated antigenic markers. In addition, the cells' consistent growth and phenotypic characteristics ensure reproducibility and reliability in experiments. The G-361 cell line is a frequently used in vitro model for many applications in basic and translational research to understand the biology of malignant melanoma, mechanisms of resistance to therapies, and the development of new therapeutic strategies.
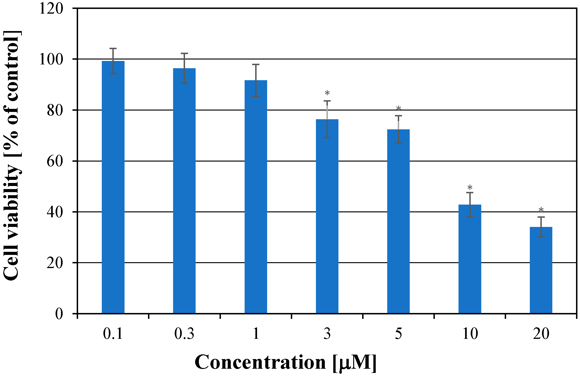
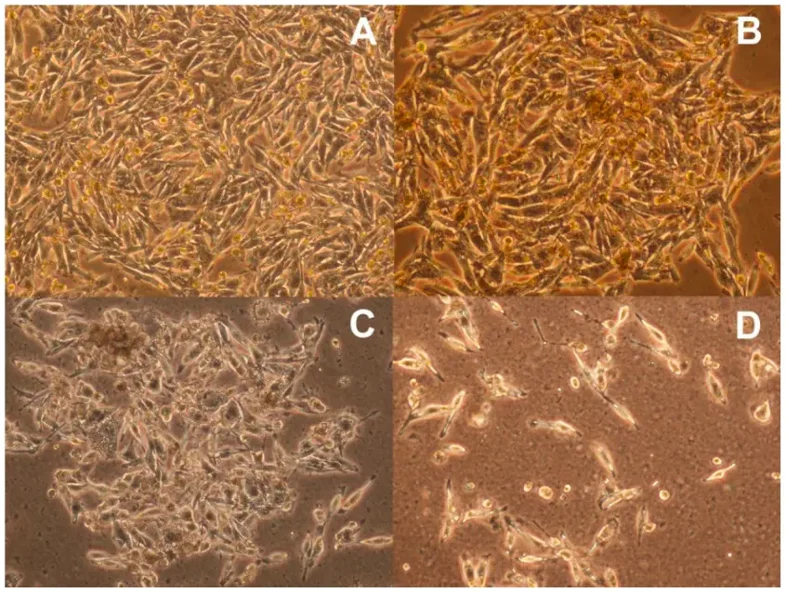
Cytotoxicity Effect of Simvastatin in G-361 Human Melanoma Cells
Free radicals in cancer cells can influence cancer processes and are affected by therapeutic substances. Chodurek et al. examined the influence of simvastatin at different concentrations on free radicals in G-361 human melanoma cells using EPR spectroscopy, aiming to correlate free radical changes with cell proliferation and find the optimal simvastatin concentration for cancer cell destruction.
To evaluate the cytotoxic activity of simvastatin, different concentrations of simvastatin (0.1-20 μM) were added to the medium and then the cells were cultured for 72 hours (Fig. 1). Simvastatin at a concentration of 0.1 μM, 0.3 μM, and 1 μM had no significant effect on the growth of cells compared to control cells. Treatment of G361 cells with 3 μM and 5 μM reduced cell growth, with similar cytotoxic activity. Cell growth inhibition was significant at 10 μM and 20 μM. IC50 value for G361 cells treated with simvastatin for 72 hours was 6.72 μM. In A-2058 melanoma cells, similar results were observed. Simvastatin had a more significant effect on the proliferation of A-375 cells. The morphological changes of G361 melanoma cells cultured with various simvastatin concentrations are presented in Fig. 2A-D. The cells cultured for 72 hours in medium with 1 μM simvastatin (Fig. 2B) did not show morphological changes in contrast to the controls (Fig. 2A), so they have good viability. On the other hand, the cells cultured in a medium with 20 μM simvastatin (Fig. 2D) have severe damage.
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- You May Also Need
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells