RBL-2H3
Cat.No.: CSC-C9588L
Species: Rattus norvegicus (Rat)
Source: Blood; Peripheral Blood
Morphology: fibroblast
Culture Properties: Monolayer
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
The RBL-2H3 cell line was initially isolated and cloned from basophilic leukemia cells in Wistar rats in 1978 by scientists. The cell line has the capability to mimic mast cell degranulation which is critical for allergic reactions. Following activation of the IgE-mediated signaling pathway RBL-2H3 cells emit histamine and leukotrienes together with other inflammatory mediators which initiate inflammatory processes. Calcium signaling activates the degranulation process by controlling the activity of intracellular enzymes phospholipase C and protein kinase C in RBL-2H3 cells.
The RBL-2H3 cell line has been widely used to study the mechanisms of allergic reactions, including the degranulation of mast cells and the release of histamine. By simulating IgE-mediated allergic reactions, this cell line provides an important tool for the study of allergen recognition and the detection of antigen-specific IgE. The RBL-2H3 cell line has also played a significant role in the study of interactions between immune cells and immune responses. For example, by analyzing the secretory properties of these cells after binding to fibronectin, it has been possible to reveal the mechanisms of intercellular signaling.
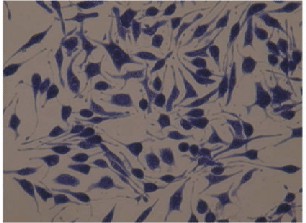 Fig. 1. Normal RBL-2H3 cells (Tang JM, Liu J, et al., 2012).
Fig. 1. Normal RBL-2H3 cells (Tang JM, Liu J, et al., 2012).
Effect of Isoscopoletin on the Viability of HaCaT and RBL-2H3 Cells
Atopic dermatitis (AD) represents a chronic skin condition that shows rising occurrence rates and features both skin inflammation and allergic responses. Isoscopoletin, a plant-derived compound, has shown potential in treating skin diseases but its effects on AD are unknown.
To evaluate the physiological activity of isoscopoletin, first, the range that does not affect cell viability was determined. MTT assay was used to examine the range's effects on HaCaT and RBL-2H3 cells. HaCaT cell viability decreased significantly compared to the control group when treated with 80 μM and 160 μM isoscopoletin which showed values of 96.49 ± 0.29% and 89.87 ± 0.01% respectively (Fig. 1A). The viability of RBL-2H3 cells decreased significantly to 91.82 ± 1.03% at 80 μM and 85.19 ± 0.44% at 160 μM when compared to the untreated control group according to Fig. 1B). Cell viability remained consistent between both cell lines at concentrations under 40 μM. Therefore, isoscopoletin was applied in the following experiments at a concentration of 5–40 μM.
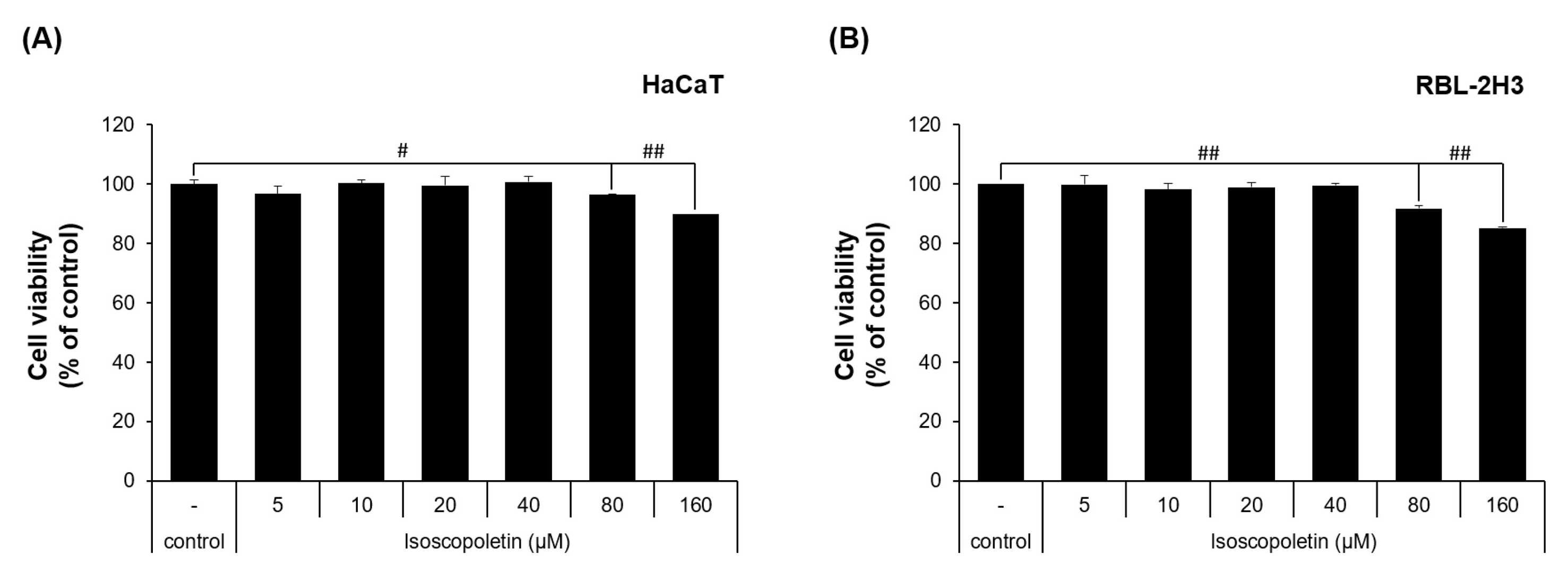 Fig. 1. Viability of HaCaT and RBL-2H3 cells treated with isoscopoletin (Seo D-Y, Park J-W, et al., 2024).
Fig. 1. Viability of HaCaT and RBL-2H3 cells treated with isoscopoletin (Seo D-Y, Park J-W, et al., 2024).
Effect of Polymethoxyflavonoids and Milk Proteins on Degranulation of Rat Basophilic Leukemia Cells (RBL-2H3)
Allergies are rising in developed countries, with type-I allergies causing significant reductions in quality of life. Degranulation of mast cells and basophils, triggered by IgE antibodies, is a key process in type-I allergies.
Miyake et al. investigated the combined anti-allergic effects of nobiletin and lactoferrin on degranulation in RBL-2H3 cells. To evaluate IgE-mediated degranulation, they employed a β-hexosaminidase release assay. The release of β-hexosaminidase from RBL-2H3 cells decreased significantly with PMF treatment, starting at 5 μM NOB and 10 μM TNG, but not with SNT (Fig. 2a). For milk proteins, significant inhibition began at 2 μg/mL LF and 170 μg/mL β-LG (Fig. 2b). NOB had the strongest inhibitory effect among PMF, followed by TNG and SNT. LF was more effective than β-LG among milk proteins. Therefore, NOB and LF were chosen to study the combined inhibitory effects on degranulation. At 50 μM NOB and 15 μg/mL LF, the β-hexosaminidase release rate was inhibited by 27% and 41%, respectively. When combined, NOB and LF inhibited release by 82% (Fig. 3).
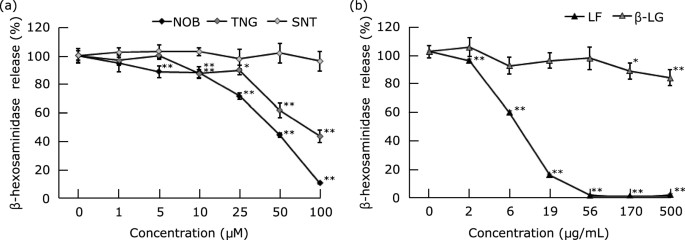 Fig. 2. Effect of polymethoxyflavonoids and milk proteins on degranulation of RBL-2H3 cells (Miyake K, Tanaka M, et al., 2024).
Fig. 2. Effect of polymethoxyflavonoids and milk proteins on degranulation of RBL-2H3 cells (Miyake K, Tanaka M, et al., 2024).
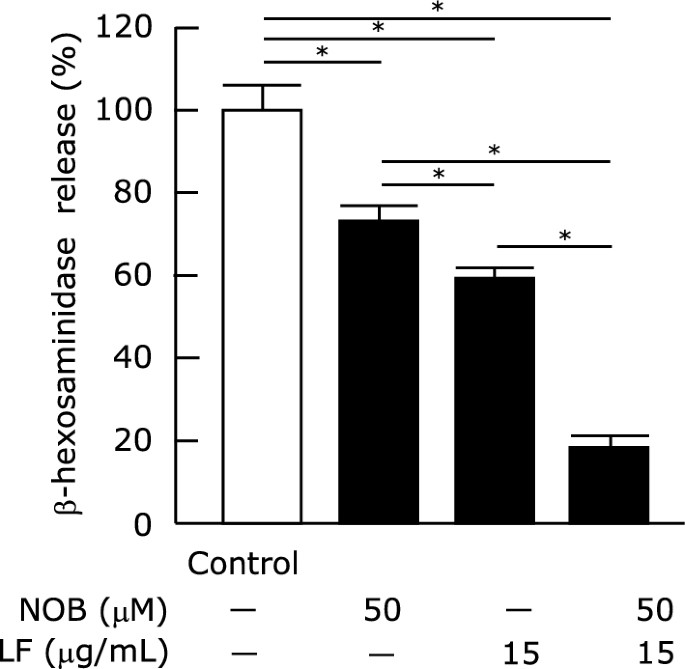 Fig. 3. Effect of nobiletin and lactoferrin on degranulation of RBL-2H3 cells (Miyake K, Tanaka M, et al., 2024).
Fig. 3. Effect of nobiletin and lactoferrin on degranulation of RBL-2H3 cells (Miyake K, Tanaka M, et al., 2024).
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- You May Also Need
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells