T3M-4
Cat.No.: CSC-C6425J
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
Source: Lymph Node Metastasis
Morphology: epithelial-like
Culture Properties: Adherent cells
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
Store in liquid nitrogen.
The T3M-4 cell line was established in 1986 from a lymph node metastasis of a patient with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), the most common and aggressive type of pancreatic cancer. The cell line has a typical epithelial morphology and carries key genetic mutations commonly seen in PDAC, including mutations in KRAS (G12V) and TP53. T3M-4 cells are characterized by their high tumorigenicity and metastatic potential in immunodeficient mice, consistent with their metastatic origin. They also express relevant biomarkers, such as CA19-9, and retain the ability to interact with the desmoplastic stroma, a hallmark feature of pancreatic tumors.
T3M-4 has been widely used to study key aspects of PDAC, particularly invasion, metastasis, and therapeutic resistance. Its high clinical relevance, robust in vivo growth and metastasis formation, retention of desmoplastic reaction capabilities in co-culture or xenograft models, and its utility as a model for intrinsic and acquired chemoresistance, provide a representative platform for investigating this lethal cancer. Researchers leverage T3M-4 to test novel therapeutics, including chemotherapy combinations, targeted agents (especially against KRAS downstream pathways, EGFR, and MEK), and drugs aimed at disrupting the tumor-stroma interactions (e.g., Hedgehog inhibitors or FAK inhibitors). The availability of T3M-4 cells allows for reproducible and consistent experimental results, contributing to the advancement of pancreatic cancer research and the development of more effective treatment options.
LAT1 is Expressed on Exosomes Isolated from Cell Culture Supernatant of T3M-4 Cells
L-type amino acid transporter 1 (LAT1) is upregulated in various cancers and contributes to the growth and proliferation of cancer cells. Previous clinicopathological studies have revealed associations between the high expression of LAT1 and the poor prognosis in multiple cancer types. However, in those studies, LAT1 expression was assessed only by immunohistochemistry on resected tumors or tissue biopsies. Cancer cell-derived exosomes are gaining increasing attention as a resource of diagnostic, prognostic, and therapeutic biomarkers. In this study, we revealed the expression of LAT1 on exosomes from pancreatic cancer T3M-4 cells by western blotting, immunoprecipitation, and immuno-transmission electron microscopy. The results showed that LAT1 was expressed on exosomes secreted by T3M-4 cells into the cell culture supernatant.
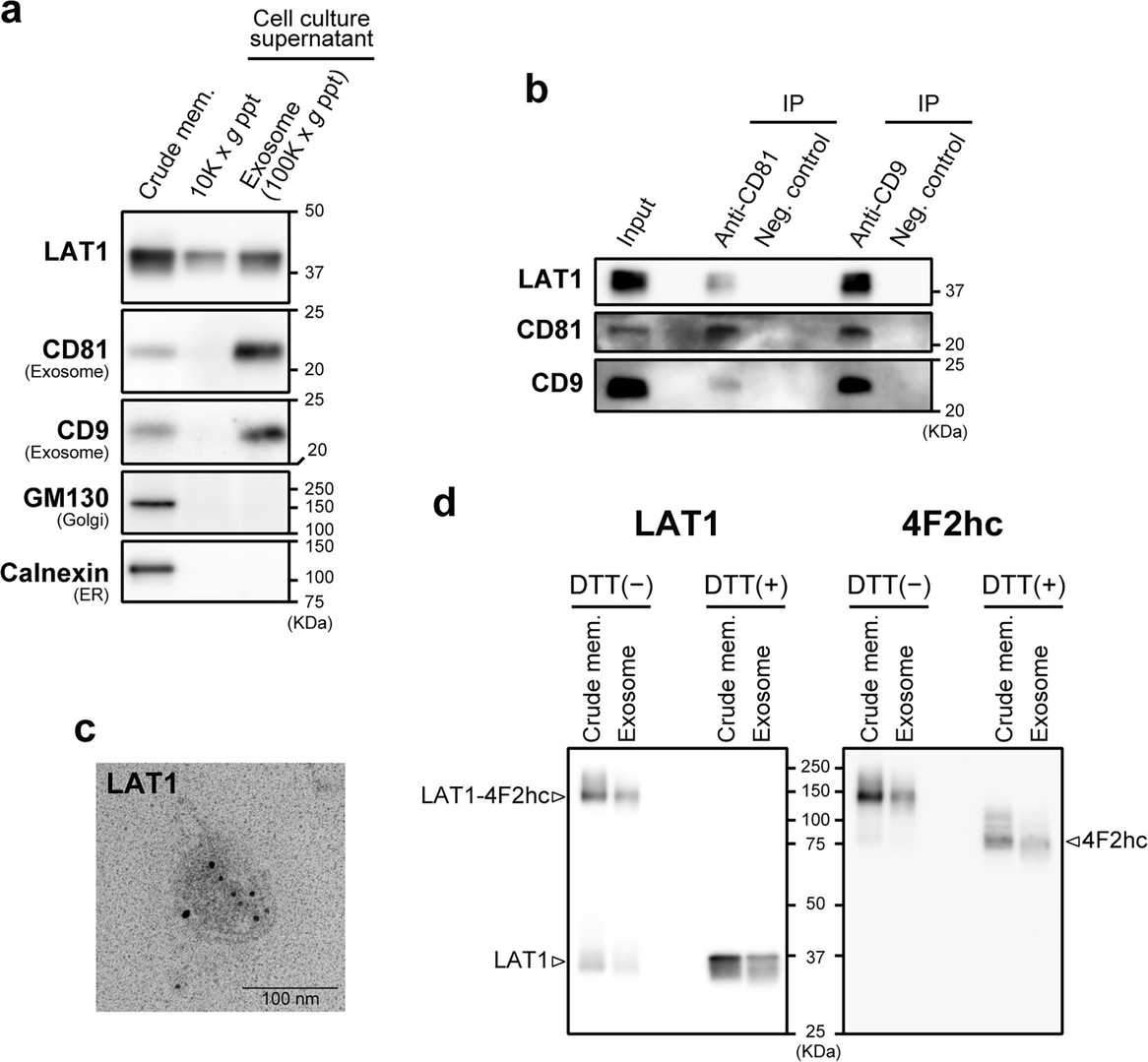 Fig. 1. Detection of LAT1 in exosome fraction isolated from T3M-4 cell culture supernatant (Liu, Yumiao, et al. 2024).
Fig. 1. Detection of LAT1 in exosome fraction isolated from T3M-4 cell culture supernatant (Liu, Yumiao, et al. 2024).
Gemcitabine Increases HLA-I Expression by Pancreatic Cancer Cells
Pancreatic cancer is a deadly disease with a five-year overall survival rate of only 13%. Therefore, the existing treatment methods needs to be adjusted, with attention shifting towards liberating the stalled efficacy of immunotherapies. Select chemotherapeutic agents with inherent immune-modifying behaviors could revitalize immune activity against pancreatic tumors and potentiate immunotherapeutic success. In this study, Larson, Alaina C., et al. characterized the influence of gemcitabine, a chemotherapeutic agent approved for the treatment of pancreatic cancer, on tumor antigen presentation by human leukocyte antigen class I (HLA-I). Gemcitabine increased pancreatic cancer cells' HLA-I mRNA transcripts, total protein, surface expression, and surface stability. These data support further exploration of immunotherapies, including peptide-based vaccines, to be used with gemcitabine as new combination treatment modalities for pancreatic cancer.
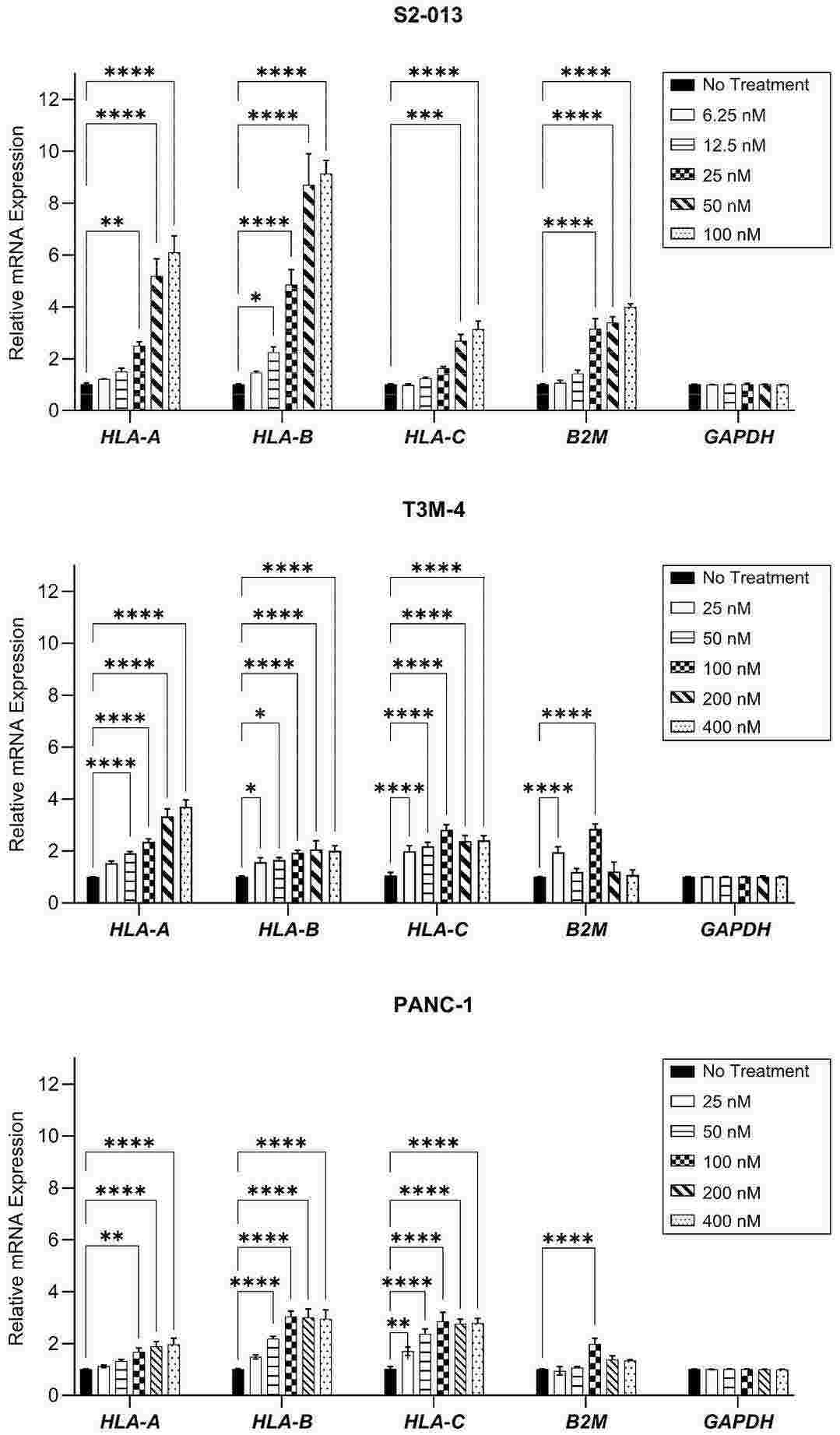 Fig. 2. HLA-I mRNA transcripts are enhanced by gemcitabine (Larson, Alaina C., et al. 2024)
Fig. 2. HLA-I mRNA transcripts are enhanced by gemcitabine (Larson, Alaina C., et al. 2024)
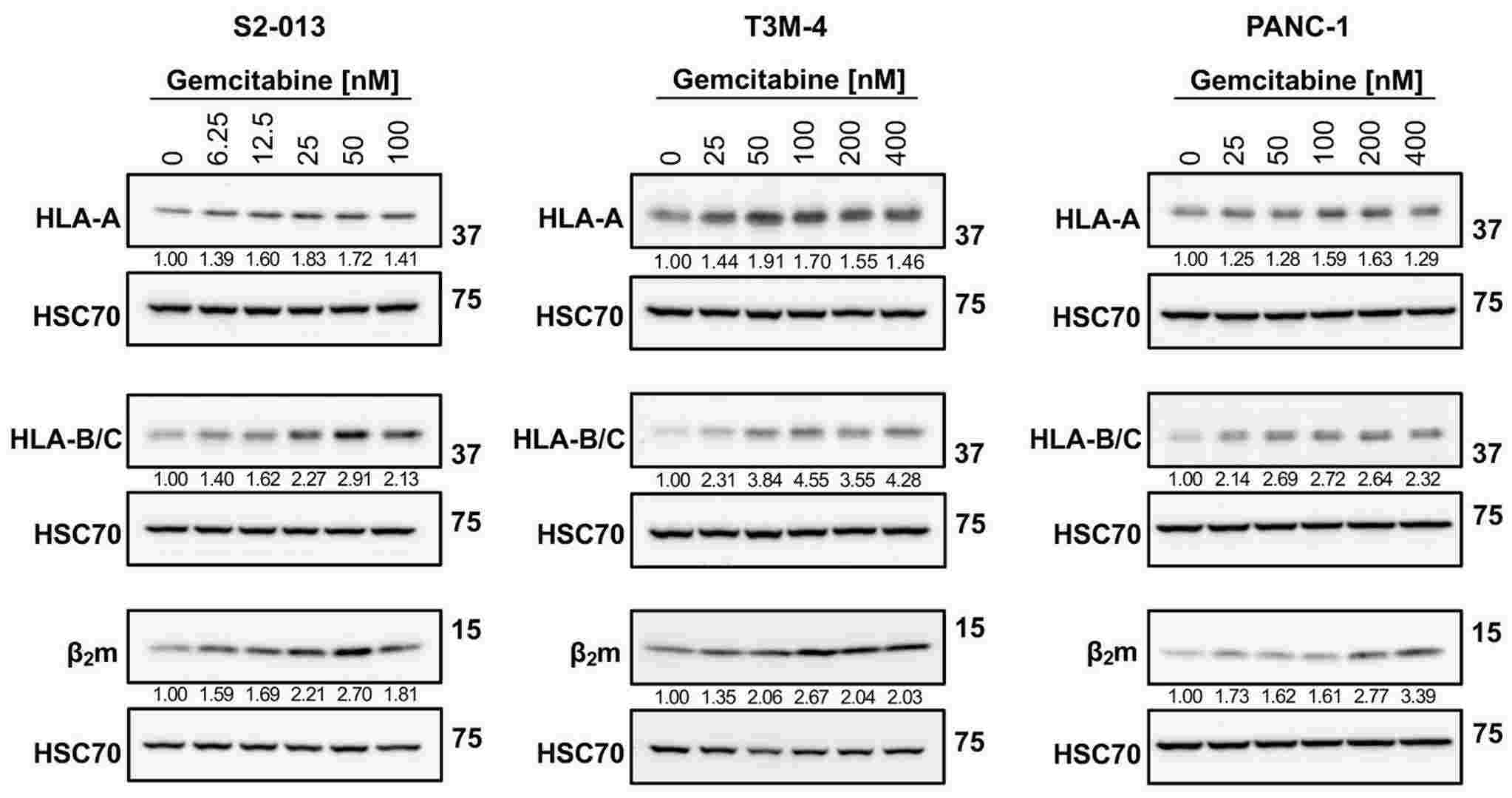 Fig. 3. Gemcitabine augments protein expression of HLA-I (Larson, Alaina C., et al. 2024).
Fig. 3. Gemcitabine augments protein expression of HLA-I (Larson, Alaina C., et al. 2024).
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- You May Also Need
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells