
UCSD-AML1
Cat.No.: CSC-C0672
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
Source: Bone Marrow
Morphology: single cells in suspension, a few cells are lightly adherent
Culture Properties: suspension
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
Immunology: CD3 -, CD4 +, CD13 +, CD14 -, CD15 -, CD19 -, CD33 +, CD34 +, cyCD68 +, HLA-DR +
Viruses: PCR: EBV -, HBV -, HCV -, HIV -, HTLV-I/-II -
UCSD-AML1 is a human acute myeloid leukemia (AML) cell line that was derived from the bone marrow of a 73-year-old woman with relapsed AML. First established in 1989, the UCSD-AML1 cell line is characterized by the chromosomal translocations t(3;3)(q21;q26) and t(12;22)(p13;q12), which result in the overexpression of MECOM (EVI1) and the ETV6-MN1 (TEL-MN1) fusion gene, respectively. The UCSD-AML1 cell line is composed of single cells that are round to polygonal in shape and of varying sizes. The cells are in suspension culture, with a few cells adhering to the culture vessel. UCSD-AML1 cells are cytokine-dependent for growth, requiring the presence of GM-CSF, IL-6, or M-CSF for proliferation. The doubling time for UCSD-AML1 cells is approximately 50-60 hours. The UCSD-AML1 cell line expresses CD34, CD7, TdT, and antigens that are associated with myeloid and megakaryocytic/platelet lineages. Researchers utilize the UCSD-AML1 cell line as a central model for acute myeloid leukemia cell biology research as well as for molecular mechanism investigations and drug testing.
MK0974 alone Suppressed the Proliferation of CRLR-Expressing AML Cell Lines
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) with high expression of the oncogenic transcription factor ecotropic viral integration site-1 (EVI1) is refractory and has a poor prognosis. Previous studies have shown that calcitonin receptor-like receptor (CRLR) and receptor activity modifying protein 1 (RAMP1) are highly expressed in EVI1high AML and participate in CGRP-induced stress hematopoiesis. Suekane et al. examined whether MK0974, a CGRP antagonist, can act as a therapeutic agent in CRLR/RAMP1high AML cell lines by disrupting ERK signaling and inducing apoptosis.
First, they analyzed the expression of CRLR and RAMP proteins in various AML cell lines using RT–PCR. Four EVI1high AML cell lines (UCSD/AML1, HNT-34, Kasumi-3, and MOLM-1) showed high CRLR and RAMP1 expression but low RAMP2 or RAMP3 expression. Most of the 11 EVI1low AML cell lines had low CRLR and RAMP family expression, except for high CRLR in KG-1 and high RAMP1 in NH cell lines (Fig. 1A). Next, they tested if CGRP stimulates CRLR/RAMP1high AML cell growth. CGRP significantly enhanced the growth of two CRLR/RAMP1high AML cell lines (UCSD/AML1 and MOLM1) but not a CRLR/RAMP1low AML cell line (U937). MK0974, a CGRP receptor antagonist, inhibited the proliferation of CRLR/RAMP1high AML cells, even without CGRP. In CRLR/RAMP1low U937 cells, CGRP, MK0974, or both had no effect on proliferation (Fig. 1B and 1C). Thus, MK0974 can inhibit the growth of CRLR/RAMP1high AML cells.
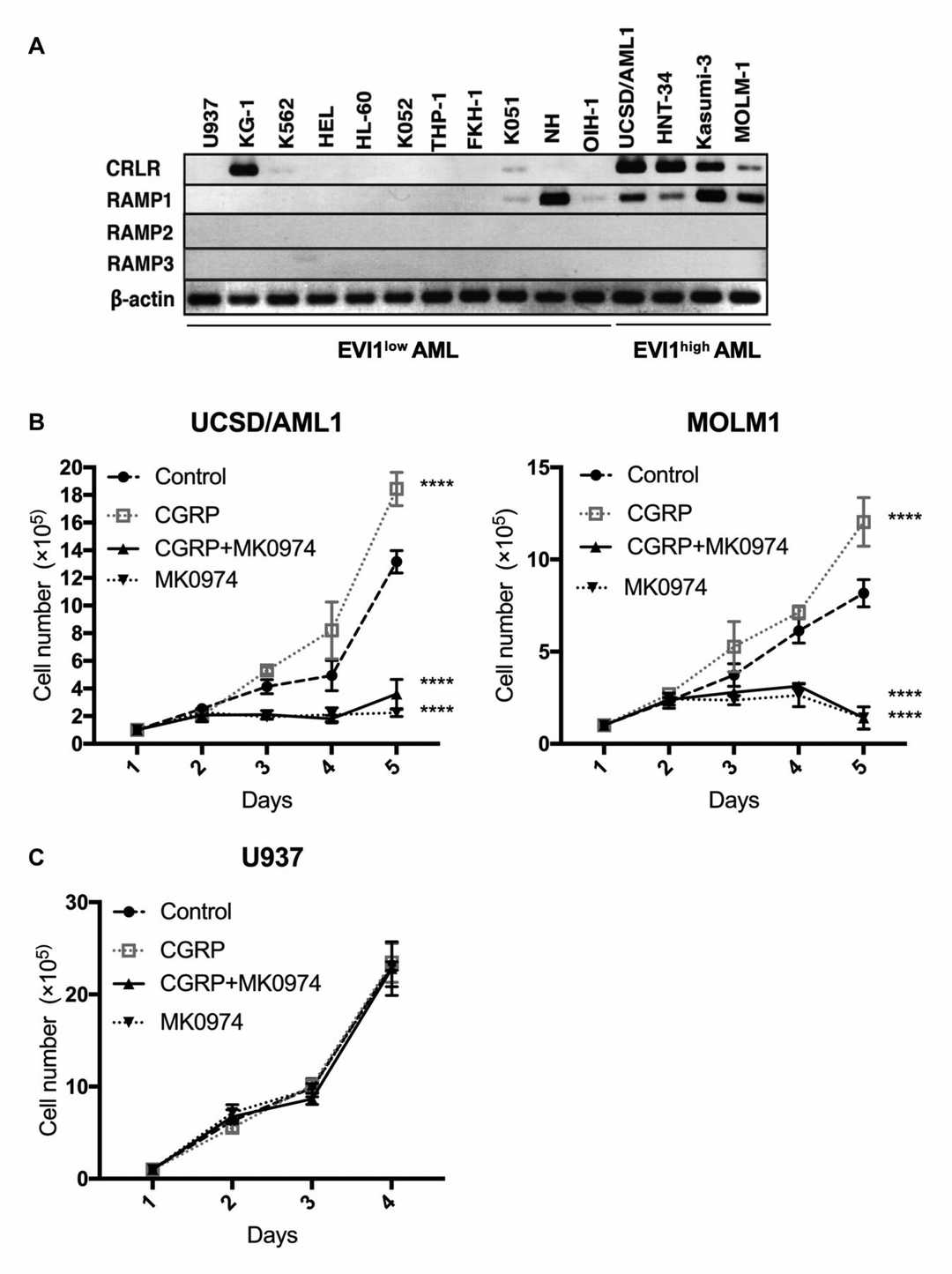 Fig. 1. Expression of calcitonin receptor-like receptor (CRLR) and RAMP family members and the effects of CGRP and/or CRLR inhibitors on AML cell lines (Suekane A, Ichikawa T, et al., 2022).
Fig. 1. Expression of calcitonin receptor-like receptor (CRLR) and RAMP family members and the effects of CGRP and/or CRLR inhibitors on AML cell lines (Suekane A, Ichikawa T, et al., 2022).
BET Inhibitor and TV Treatment Induces Loss of Viability of AML Cells Harboring inv(3)/t(3;3)
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) with chromosomal alterations involving 3q26 overexpresses the transcription factor EVI1, which is associated with poor prognosis and therapy resistance. Previous studies have shown that AML cells with 3q26 lesions are dependent on BRD4, and BET inhibitors can repress EVI1 and induce apoptosis. Birdwell et al. investigated the preclinical efficacy of targeting epigenetic mechanisms in AML with 3q26 lesions and EVI1 overexpression using BET inhibitors and Tegavivint (TV) to induce apoptosis and improve survival in AML models.
They confirmed that the pan-BET protein inhibitor OTX015 induced lethality in AML cell lines (MUTZ3, UCSD-AML1, OCI-AML20, HNT-34, AML191, AML194, and AML219) and PD AML cells with inv(3q26) or t(3;3) and EVI1 overexpression. FISH and cytogenetics analyses of AML191, AML194, and AML219 cells are shown in Fig. 2A, and the oncoplot of genetic alterations in PD AML cells is in Fig. 2B. OTX015 dose-dependently reduced viability in AML cell lines, with varying sensitivity (Fig. 3A). It repressed mRNA and protein expressions of MECOM, LEF1, KIT, MYB, and MYC, while increasing HEXIM1 expression (Fig. 3B-C). OTX015 also reduced viability in PD AML cells with inv(3q26) or t(3;3) compared to those without (Fig. 3D). They then tested TV, known to reduce nuclear β-catenin levels, on AML cells. TV dose-dependently induced apoptosis in AML cell lines and reduced viability in PD AML cells with inv(3q26) or t(3;3) (Fig. 3E, F), but had less lethality in normal progenitor cells. TV treatment reduced mRNA and protein levels of MECOM, LEF1, MYB, MYC, and KIT, and increased Axin-2 and cleaved PARP levels (Fig. 3G-H). TV-induced lethality was not due to ROS increase or proteosomal degradation of EVI1. Low concentrations of TV induced myeloid differentiation in AML191 cells. These results highlight the in vitro efficacy of TV and BET inhibitors in AML cells with inv(3q26) or t(3;3).
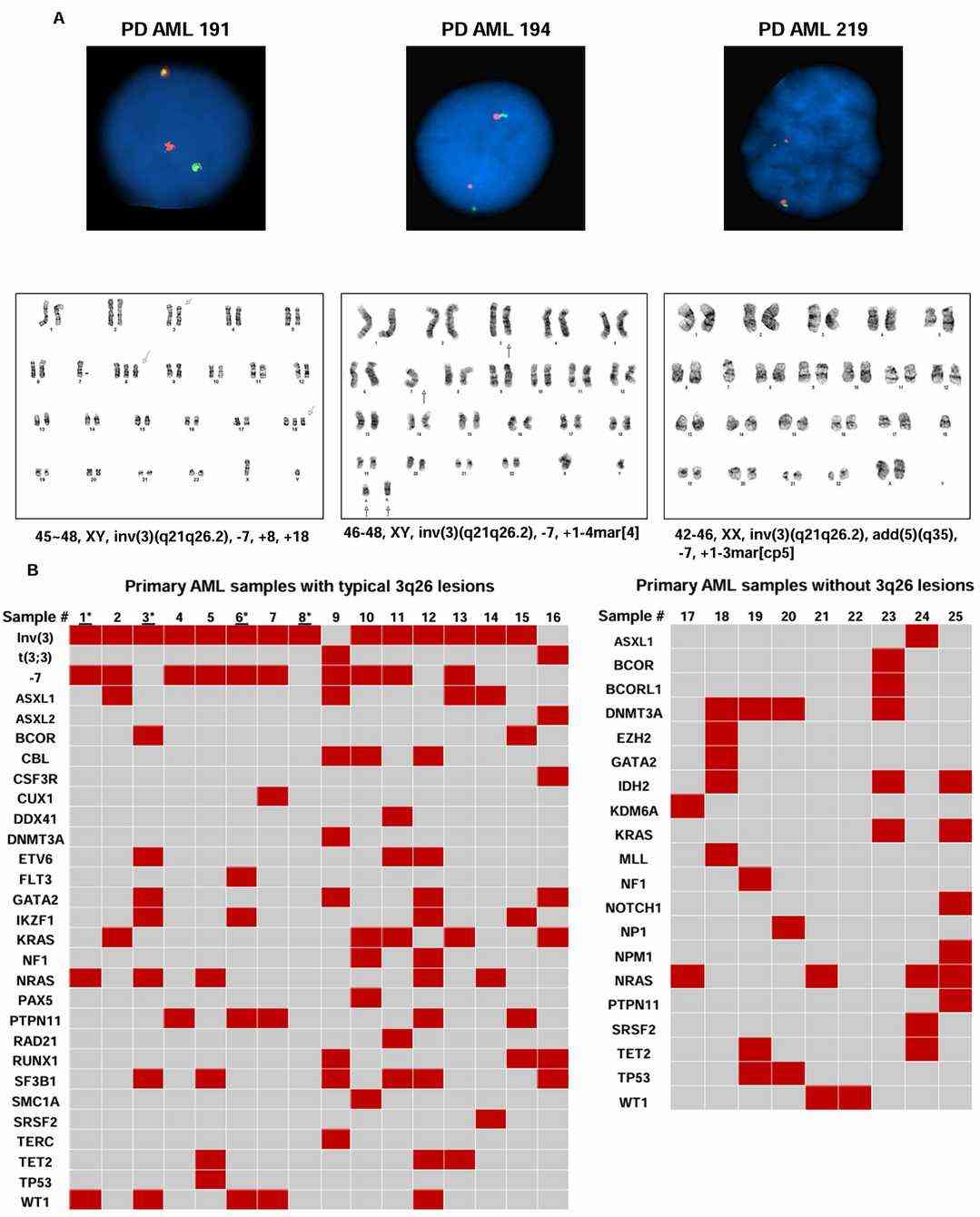 Fig. 2. Treatment with BET inhibitor or tegavivint depletes MECOM (EVI1) expression with concomitant induction of p21 in 3q26.2-rearranged AML cells (Birdwell E C, Fiskus W, et al., 2024).
Fig. 2. Treatment with BET inhibitor or tegavivint depletes MECOM (EVI1) expression with concomitant induction of p21 in 3q26.2-rearranged AML cells (Birdwell E C, Fiskus W, et al., 2024).
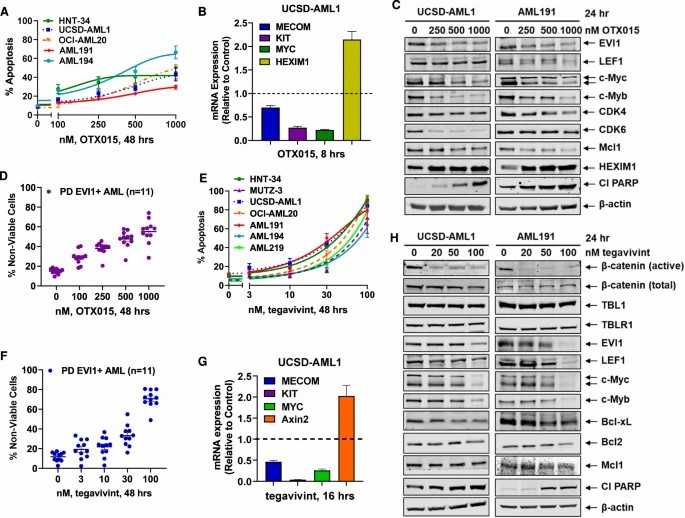 Fig. 3. Treatment with BET inhibitor OTX015 or β-catenin antagonist TV depletes EVI1 and c-Myc expression and dose-dependently induces lethality in 3q26.2-rearranged EVI1-expressing AML cells (Birdwell E C, Fiskus W, et al., 2024).
Fig. 3. Treatment with BET inhibitor OTX015 or β-catenin antagonist TV depletes EVI1 and c-Myc expression and dose-dependently induces lethality in 3q26.2-rearranged EVI1-expressing AML cells (Birdwell E C, Fiskus W, et al., 2024).
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- You May Also Need
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells





