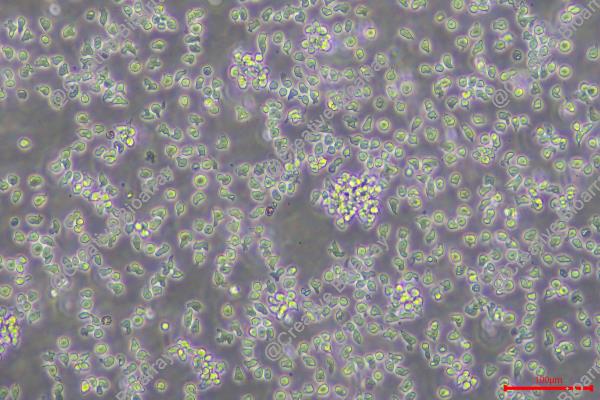
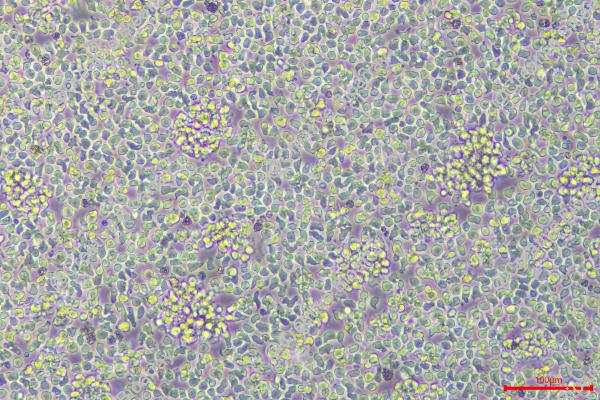
REH
Cat.No.: CSC-C0205
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
Source: Blood; Peripheral Blood
Morphology: Lymphoblast
Culture Properties: suspension
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
- Documents
Cell type: B cell precursor leukemia
Origin: established from the peripheral blood of a 15-year-old North African girl with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL at first relapse) in 1973; carries t(12;21) leading to ETV6-RUNX1 (TEL-AML1) fusion gene
According to our STR-Analysis and comparison with various databanks, the DNA results are ambiguous.
CSF1PO: 12,13
D13S317: 11,12,13
D16S539: 9,10,13
D5S818: 11,12,13
D7S820: 9,12
THO1: 7
TPOX: 8
vWA: 14,15
D3S1358: 18
D21S11: 27,28,29,30,31
D18S51: 10,13,14
Penta E: 10,11
Penta D: 9,10,12
D8S1179: 13,16
FGA: 22,23,24
The REH cell line is a well-known and widely used cell line in cancer research, specifically in the study of acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). These cells were established from the peripheral blood of a 15-year-old North African girl with ALL during her first relapse in 1973. The REH cell line is characterized by a specific genetic abnormality known as the t(12;21) translocation, resulting in the formation of the ETV6-RUNX1 fusion gene, also referred to as the TEL-AML1 fusion gene.
The t(12;21) translocation, leading to the ETV6-RUNX1 fusion gene, is a common genetic alteration observed in pediatric B-cell precursor ALL. This fusion gene arises from the fusion of the ETV6 (TEL) gene on chromosome 12 with the RUNX1 (AML1) gene on chromosome 21. The resulting fusion protein disrupts the normal functions of both ETV6 and RUNX1, contributing to leukemogenesis and ALL development.
The REH cell line has been extensively characterized and utilized as a research tool for investigating various aspects of ALL biology, focusing on understanding the molecular mechanisms underlying the formation and function of the ETV6-RUNX1 fusion gene. Researchers have utilized REH cells to study the impact of the fusion gene on cellular processes, such as cell proliferation, differentiation, and signaling pathways.
Genomic, Transcriptomic, and Epigenomic Sequencing Data of REH Cell Lines
This data paper aims to describe a collection of 33 genomic, transcriptomic, and epigenomic sequencing datasets of the B-cell ALL cell line REH. REH is one of the most frequently used cell lines for functional studies of pediatric ALL, and these data provide a multi-faceted characterization of its molecular features.
The cell line’s authenticity was confirmed by karyotyping and STR analysis. The datasets are divided into nine library types. Of the seven library types using DNA as input, five are whole genome sequencing (WGS) methods producing genomic data, one is a method producing chromatin accessibility data (single-cell ATAC-seq), and one is a whole genome methylome sequencing method producing epigenomic data (EM-seq). The WGS methods include Illumina TruSeq DNA PCR-Free, PacBio SMRT, Oxford Nanopore (ONT), MGISEQ stLFR, and linked-read WGS (10 × Genomics), while RNA was used as input to two RNA-seq methods, Illumina TruSeq Stranded Total RNA and PacBio IsoSeq. The datasets include raw sequencing reads in FASTA and FASTQ formats, reference-mapped BAM files, and de-novo assemblies (Table 1).
Table. 1 Overview of the data file. (Lysenkova Wiklander M, et al., 2023)
| Data file | File types | Accession |
| Overview of REH sequencing datasets | PNG | Figshare: 10.6084/m9.figshare.23966340 |
| Supplemental Methods | Figshare: 10.6084/M9.FIGSHARE.22643065 | |
| Short Tandem Repeat Analysis of the REH cell line | Figshare: 10.6084/m9.figshare.24131670 |
Cathepsin B Is Not Intrinsic to Reh Cell Line Asparaginase Resistance
L-asparaginase (ASNase) is a biopharmaceutical used as an essential drug in the treatment of ALL. The REH ALL cell line, used as a model for studying the most common subtype of ALL, is considered resistant to treatment with ASNase. Cathepsin B (CTSB) is one of the proteases involved in the regulation of in vivo ASNase serum half-life and it has also been associated with the progression and resistance to treatment of several solid tumors.
CTSB REH (Fig. 1) and CTSB KO cells were generated utilizing the clustered regularly interspaced repeats with associated protein 9 (CRISPR/Cas9) system. REHcas9 cells were monitored for 27 days via quantification of GFP levels across all conditions (Fig. 2A). The GFP levels of REH cells bearing CTSB sgRNAs, and those from the non-targeting control Rosa 26 condition remained steady through the analysis. These results were supported by the GFP level monitoring analysis of FACS-isolated CTSB KO cells and Rosa26-targeted cells, which remained unchanged over time (Fig. 2B). These results support that REH ALL cells do not depend on the expression of CTSB for overall survival and proliferation.
REHcas9 and REHcas9 + sgRNA-1 cells were treated with different concentrations of ASNases for 72 h, and then cell viability was determined. In all the conditions tested, the cell viability profile was the same between REHcas9 and REHcas9 + sgRNA1 cells (Fig. 3). Thus, deletion of CTSB in REH ALL cells did not confer ASNase treatment sensitivity, thus suggesting that intrinsic expression of CTSB is not a mechanism that drives the resistant nature of these ALL cells to enzymes used as the first-line treatment against leukemia.
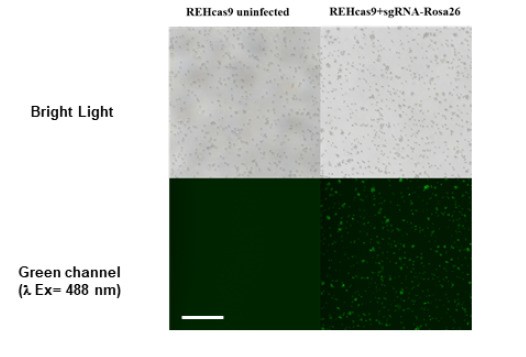 Fig. 1 Representative image of REHcas9 infection. (Costa IM, et al., 2023)
Fig. 1 Representative image of REHcas9 infection. (Costa IM, et al., 2023)
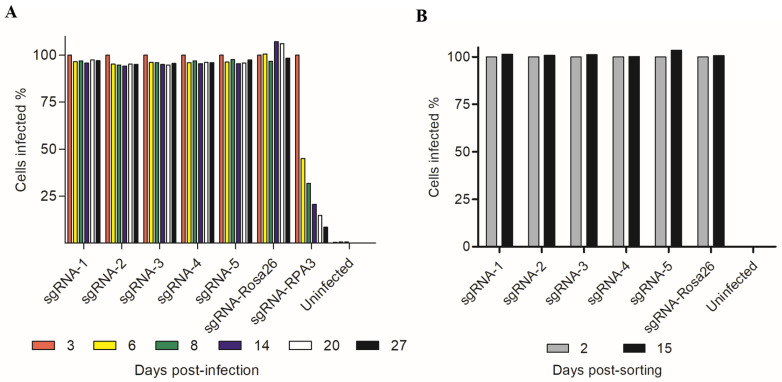 Fig. 2 Monitoring of REHcas9-sgRNA cell proliferation by flow cytometry. (Costa IM, et al., 2023)
Fig. 2 Monitoring of REHcas9-sgRNA cell proliferation by flow cytometry. (Costa IM, et al., 2023)
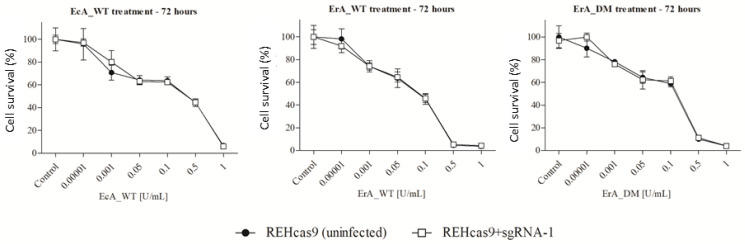 Fig. 3 In vitro cytotoxicity assay of CTSB KO cells in the presence of ASNase. (Costa IM, et al., 2023)
Fig. 3 In vitro cytotoxicity assay of CTSB KO cells in the presence of ASNase. (Costa IM, et al., 2023)
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- You May Also Need
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells