SUP-HD1
Cat.No.: CSC-C0579
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
Source: Pleural Effusion
Morphology: round cells growing singly or in small clumps in suspension
Culture Properties: suspension
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
Immunology: CD2 -, CD3 -, CD13 -, CD14 -, CD15 +, CD19 -, CD25 +, CD30 -, CD34 -
Viruses: PCR: EBV -, HBV -, HCV -, HIV -, H
The SUP-HD1 cell line originates from pleural effusion obtained from a patient who had nodular sclerosis Hodgkin lymphoma (NSHD). This disease represents a distinctive form of Hodgkin lymphoma which manifests through tumor cells that display Reed-Sternberg cell morphology and include acid phosphatase and non-specific esterase activity. Research demonstrates that chromosomal copy number abnormalities exist in the SUP-HD1 cell line which includes deletions at multiple regions: 2q, 5q, 6q, 7q, 9q, 10q, 15q, and 19q. The 1q23 chromosomal region shows PBX1 gene amplification which frequently appears as a genomic abnormality in Hodgkin lymphoma.
Researchers use the SUP-HD1 cell line and other HL cell lines such as KM-H2 and L-428 to investigate Hodgkin lymphoma molecular mechanisms. For instance, the interaction between PBX1 and NFIB functions as a critical factor in the development of cHL. The suppression of either PBX1 or TLX2 genes leads to major changes in cell proliferation and apoptosis rates. Researchers also use the SUP-HD1 cell line to test potential drug treatments for classic Hodgkin lymphoma. For example, the HGF signaling pathway activation leads to a decrease in PBX1 expression which results in reduced TLX2 expression. Additionally, SUP-HD1 cells show low expression of the S1P receptor S1PR1 which indicates its possible use as a therapeutic target.
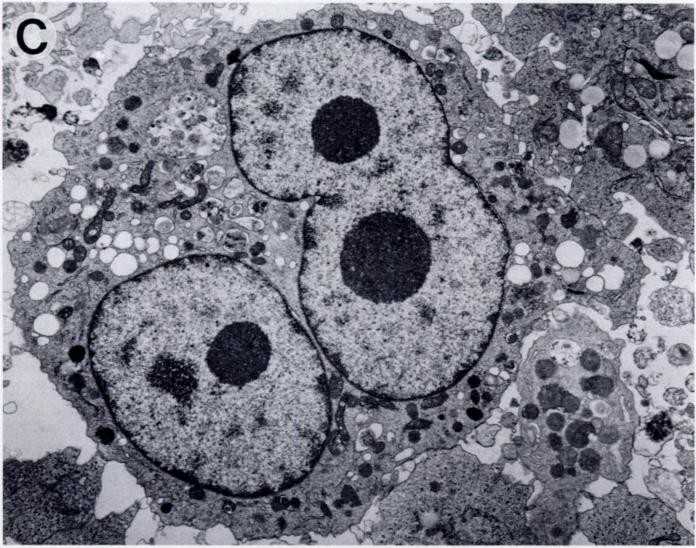 Fig. 1. Morphology of theSUP- HD1 cell line (Naumovski L, Utz P, et al., 1990).
Fig. 1. Morphology of theSUP- HD1 cell line (Naumovski L, Utz P, et al., 1990).
The Functional Impact of ETV3 on Gene Regulation in Hodgkin Lymphoma Cells SUP-HD1
ETS transcription factors are vital for blood and immune cell development, with dysregulation linked to hematologic malignancies. The human genome encodes numerous TFs, including ETS factors, that dictate cell differentiation in hematopoiesis. Nagel et al. utilized public datasets to chart ETS gene activities in hematopoiesis and lymphopoiesis, defining the lymphoid ETS-code.
They investigated ETV3's role in gene regulation within HL cells using the SUP-HD1 model and performed siRNA-mediated knockdown, confirmed by Western blot and RQ-PCR (Fig. 1A and B). ETV3 did not affect EBF1 and PAX5, but it suppressed CD19 and activated GATA3, showing mutual activation with GATA3 (Fig. 1B). They found an ETS-binding site upstream of CD19, indicating direct regulation by ETV3. Gene expression profiling of ETV3-knockdown in SUP-HD1 revealed other targets, including repression of miR155-repressor CELF2, with ETS-binding sites in CELF2 supporting this regulation. Analysis using DAVID showed ETV3 activates developmental processes and suppresses BMP-signaling via BMP1 and BMP2. RQ-PCR analysis further confirmed ETV3's suppression of CELF2, BMP1, and BMP2 (Fig. 1C). The LL-100 dataset corroborated reduced CELF2 and elevated MIR155 in HL cell lines (Fig. 1D and E), with HDLM-2 showing a genomic deletion near MIR155. BMP4 treatment and BMP-pathway inhibitor dorsomorphin demonstrated that BMP-signaling inhibits ETV3, hinting at a feedback loop (Fig. 1F). This analysis identified ETV3's involvement in differentiation, miR155 activation, and BMP-signaling suppression.
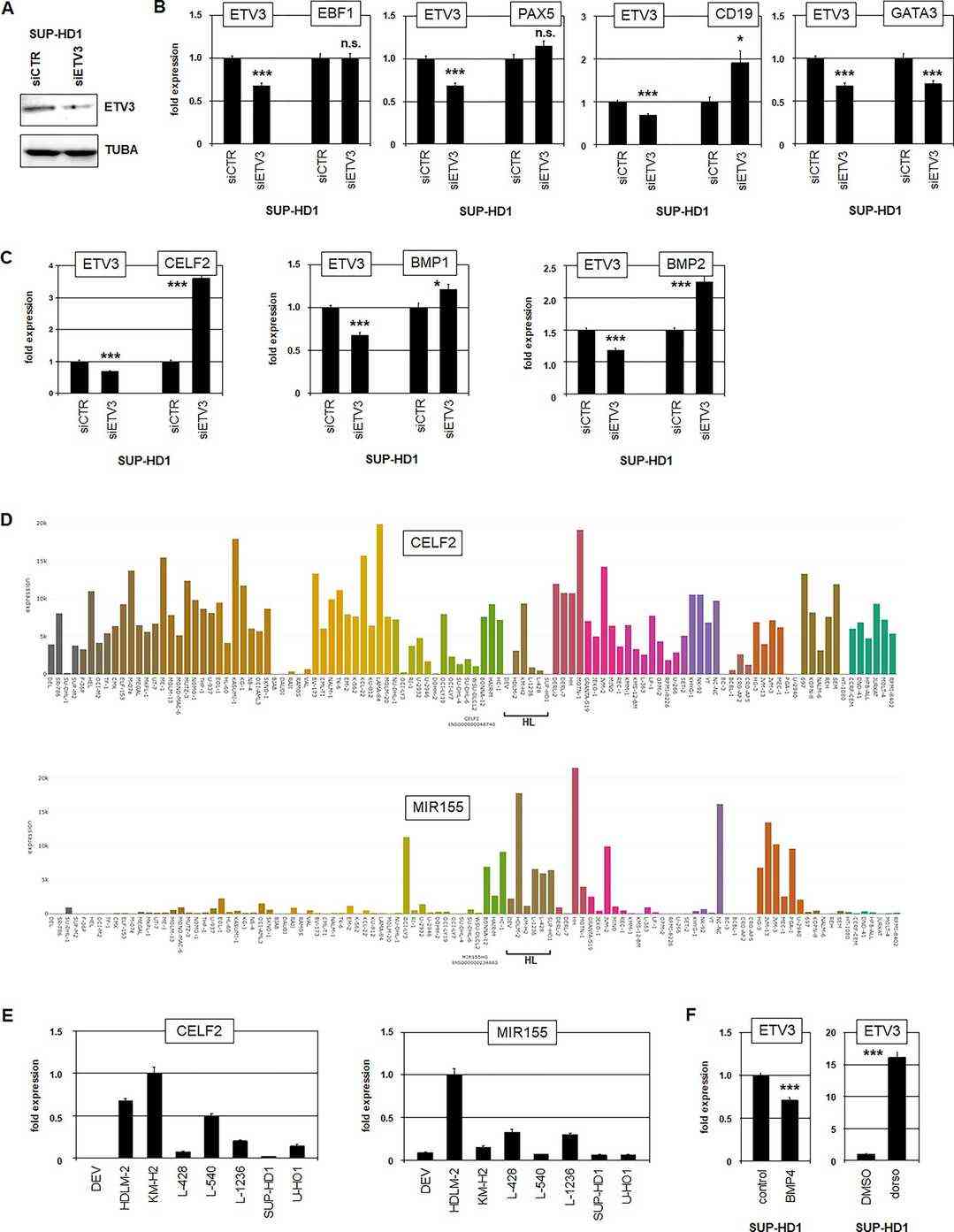 Fig. 1. Target gene analyses of ETV3 (Nagel S, Meyer C, et al., 2023).
Fig. 1. Target gene analyses of ETV3 (Nagel S, Meyer C, et al., 2023).
PBX1 is activated by genomic aberration in HL cell lines
Homeobox genes are transcription factors vital for cell differentiation, organized into classes by sequence similarity. TALE homeobox genes are ancient regulators with critical roles in hematopoiesis. Aberrant expression of these genes, such as PBX1, can lead to lymphoid malignancies like Hodgkin lymphoma (HL). Utilizing expression analysis, Nagel et al. developed the TALE-code to map homeobox gene activity in hematopoiesis and lymphopoiesis. Public datasets of HL patients and cell lines like SUP-HD1 helped identify deregulated TALE genes.
Chromosomal and genomic aberrations significantly contribute to gene deregulation in cancers, including HL. To determine if the PBX1 locus at 1q23 is altered in KM-H2 and SUP-HD1, they conducted cytogenetic analysis and genomic profiling. Both cell lines showed several rearrangements, but none at 1q23. RT-PCR found the TCF3-PBX1 fusion gene in B-cell line 697, but not in KM-H2 or SUP-HD1, ruling out chromosomal aberration t(1;19)(q23;p13), aligning with cytogenetic results (Fig. 2A). Nevertheless, genomic profiling revealed a gain at position 1q23 unique to these HL cell lines (Fig. 2B and C). RQ-PCR confirmed these gains at PBX1 (Fig. 2D), explaining increased PBX1 transcript levels in KM-H2 and SUP-HD1.
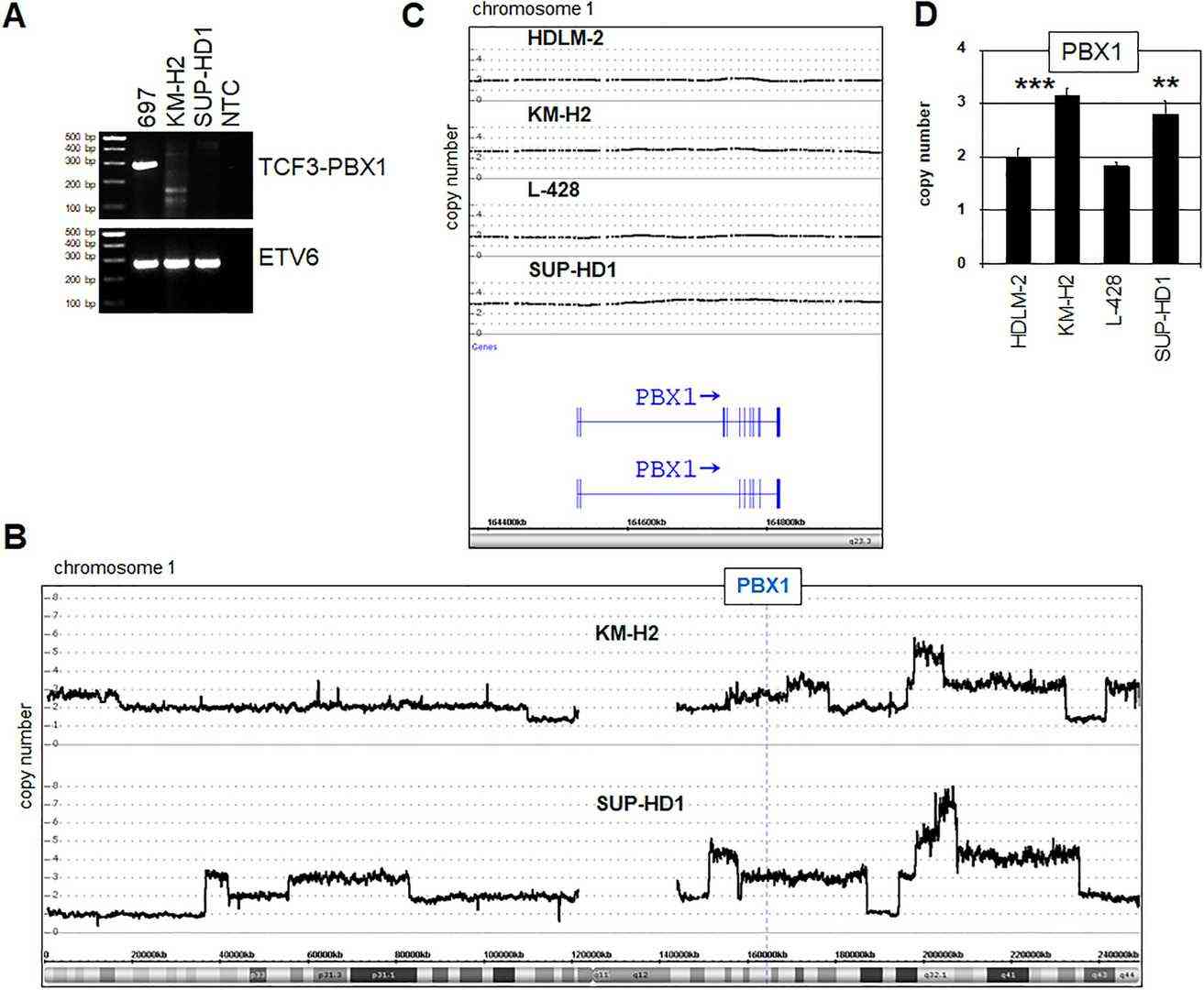 Fig. 2. Genomic analyses of the PBX1 locus (Nagel S, Pommerenke C, et al., 2021).
Fig. 2. Genomic analyses of the PBX1 locus (Nagel S, Pommerenke C, et al., 2021).
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- You May Also Need
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells