SU-DHL-4
Cat.No.: CSC-C0506
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
Source: Peritoneal Effusion
Morphology: single round cells growing in suspension
Culture Properties: suspension
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
Cell type: B cell lymphoma
Origin: established from the peritoneal effusion of a 38-year-old man with B-NHL (diffuse large cell, cleaved cell type; originally described as "diffuse histiocytic lymphoma") in 1975; cell line carries EZH2 Y641S mutation; assigned to GCB-like lymphoma subtype (germinal center B-cell)
D13S317: 11, 12
D7S820: 8, 11
D16S539: 11, 13
vWA: 18, 19
THO1: 6, 9.3
Amelogenin: X Y
TPOX: 9, 11
CSF1PO: 12
SU-DHL-4 is a lymphoblast-like cell that was isolated from the peritoneal effusion of a White, 38-year-old, male patient. This cell line represents a model of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), one of the most common types of non-Hodgkin lymphoma in adults. The establishment of this cell line has provided valuable insights into the biology of DLBCL, especially concerning the cellular and molecular mechanisms underlying lymphomagenesis and tumor progression.
SU-DHL-4 cells have been widely used to study the efficacy and mechanism of action of various chemotherapeutic and targeted therapeutic agents, reflecting their importance in lymphoma treatment research. The cells express several key immunophenotypic markers associated with the B-cell lineage such as CD19 and CD20, which are essential for the development and function of B-lymphocytes. These markers also make SU-DHL-4 an excellent target for testing B-cell-specific therapies, including monoclonal antibodies and small molecule inhibitors that disrupt key signaling pathways involved in lymphoma cell survival and proliferation.
APOC1 Knockdown Induces Apoptosis and Decreases Angiogenesis in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Cells
Apolipoprotein C1 (APOC1) plays a significant role in the proliferation and metastasis of various malignant tumors; however, its role in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL)—particularly its effects on angiogenesis—remains largely unexplored. This study investigates the functional role of APOC1 in DLBCL development and its potential molecular mechanisms through in vitro and in vivo experiments. Results showed that APOC1 is overexpressed in DLBCL tissues and cells, with high APOC1 levels associated with poor patient prognosis. In vitro experiments revealed that APOC1 knockdown increased apoptosis and inhibited cell proliferation, migration, invasion, HUVEC angiogenesis, and PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway protein expression in DLBCL cells.
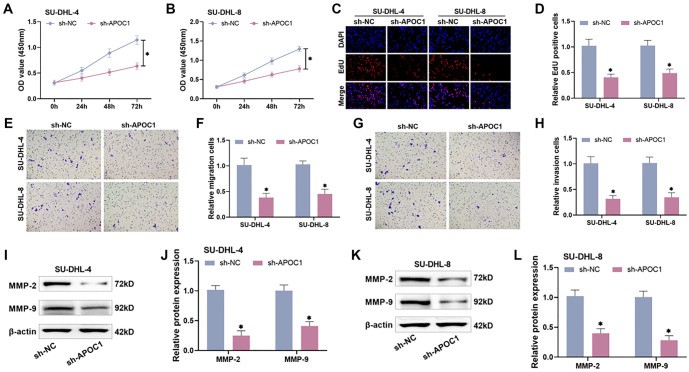 Fig. 1. Knockdown of APOC1 decreases DLBCL cellular carcinogenic activities (Gao, Jing, et al. 2025).
Fig. 1. Knockdown of APOC1 decreases DLBCL cellular carcinogenic activities (Gao, Jing, et al. 2025).
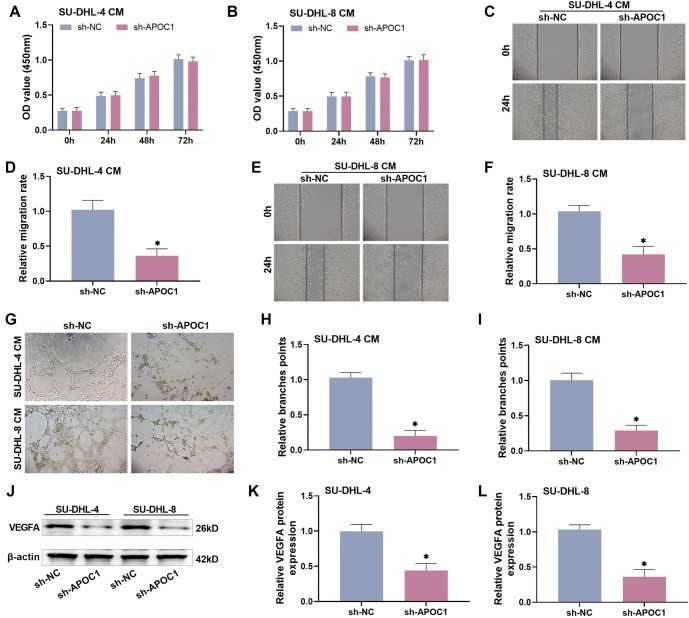 Fig. 2. Knockdown of APOC1 reduces angiogenesis in HUVECs (Gao, Jing, et al. 2025).
Fig. 2. Knockdown of APOC1 reduces angiogenesis in HUVECs (Gao, Jing, et al. 2025).
Chidamide and Orelabrutinib Synergistically Induce Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma
In vitro experiments were conducted using DB and SU-DHL-4 cells treated with chidamide, orelabrutinib, and a combination of both. Cell viability was assessed by cell counting kit-8. Cell apoptosis and the cell cycle were determined using flow cytometry. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) production and mitochondrial function were assessed through ROS and JC-1 staining. RNA sequencing and western blot analyses were conducted to elucidate the molecular mechanisms underlying the combined action of chidamide and orelabrutinib in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) cells.
This investigation revealed markedly enhanced antiproliferative effects when chidamide was combined with orelabrutinib. The findings of this study provide a compelling justification for the clinical utilization of chidamide and orelabrutinib to treat relapsed/refractory DLBCL.
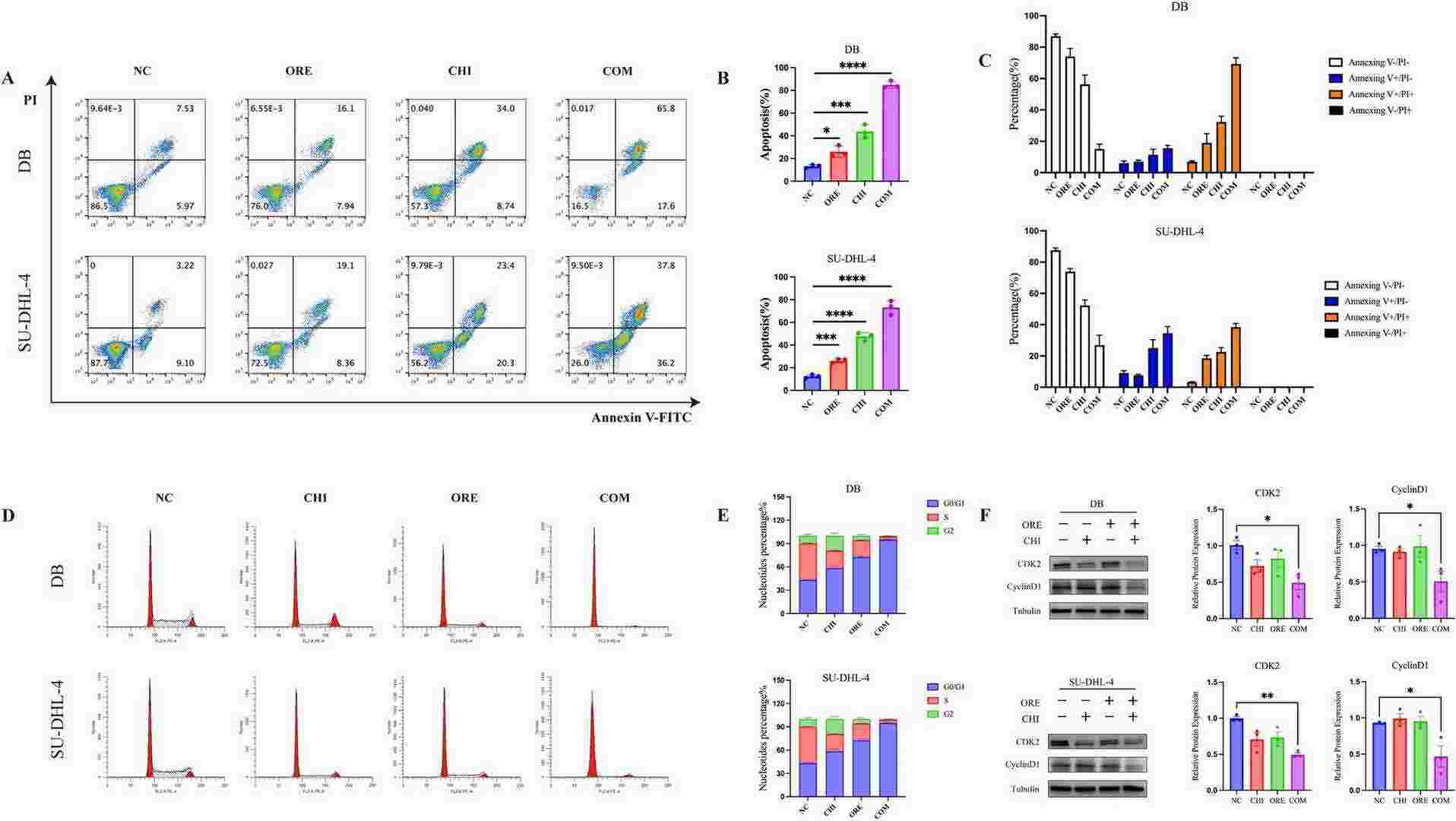 Fig. 3. Effect of chidamide and orelabrutinib in DLBCL cell line apoptosis (Wu, Chunyan, et al. 2024).
Fig. 3. Effect of chidamide and orelabrutinib in DLBCL cell line apoptosis (Wu, Chunyan, et al. 2024).
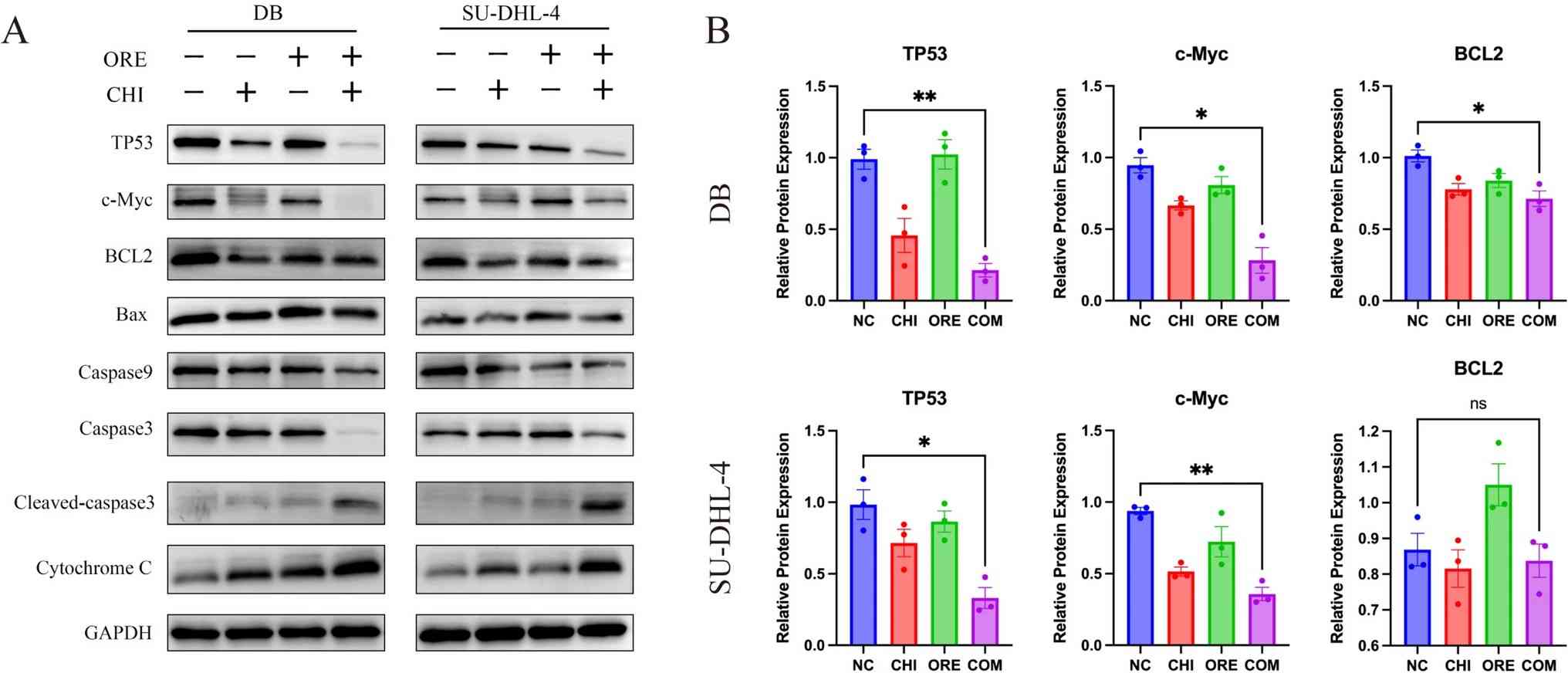 Fig. 4. Effects of chidamide and orelabrutinib on c-Myc, BCL2, TP53, and other apoptosis proteins in DLBCL cells (Wu, Chunyan, et al. 2024).
Fig. 4. Effects of chidamide and orelabrutinib on c-Myc, BCL2, TP53, and other apoptosis proteins in DLBCL cells (Wu, Chunyan, et al. 2024).
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- You May Also Need
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells