
SIG-M5
Cat.No.: CSC-C0495
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
Source: Bone Marrow
Morphology: large round cells growing singly in suspension
Culture Properties: suspension
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
Immunology: CD3 -, CD13 (+), CD14 (+), CD15 +, CD19 -, CD33 +, CD34 -, cyCD68 +, HLA-DR -
Viruses: PCR: EBV -, HBV -, HCV -, HIV -, HTLV-I/II -, SMRV -
The human bone marrow stromal cell line, SIG-M5, is connected to myeloid neoplasia as it was collected from a patient with the myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS). This cell line is used as a model for myeloid tumors studies. For example, it has been used for the analysis of TET2, which is responsible for DNA demethylation and loss of TET2 results in defects in gene expression, and differentiation. SIG-M5 has also been used for the study of the mutual exclusivity of IDH1/2 and TET2. This relationship is where IDH1/2 mutations accumulate 2-HG which inhibits the activity of TET2, and causes synthetic lethality. DNMT1 has also been analyzed in SIG-M5 cells to determine how mutations in this gene impact AML and whether mutations in DNMT3A have synergistic effects on cell proliferation and differentiation. The cell line has been used to screen for drugs such as TET inhibitors and the effects of the inhibitor, TETi76, on cell growth.
Knockout Mutations Spanning DNMT1 Confer Sensitivity in Isogenic AML Cell Line Pairs with Clinically Relevant DNMT3A Mutations
Aberrant DNA methylation is a feature of cancer and is controlled by a family of DNMT proteins including DNMT1 (maintenance methylation) and DNMT3A/3B (de novo methylation). Mutations in DNMT3A are found in ~22% of acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Bhogal et al. sought to investigate whether DNMT1 or DNMT3B may be a synthetic lethal target for DNMT3A mutant AML.
Their data from DNMT3A wild-type and mutant cell lines is inconclusive as to whether DNMT1 is synthetically lethal with DNMT3A mutation. The shRNA data shows that AML cell lines are sensitive to DNMT1 knockdown whether or not they are DNMT3A mutant. Similarly, their published and internal screens demonstrate sensitivity to DNMT1 knockout mutations in both DNMT3A wild-type and mutant AML cell lines. However, AML cell lines are genetically diverse, making genetic interaction conclusions difficult. They generated isogenic AML cell line pairs that only differ by DNMT3A mutation status to more precisely define this relationship. They knocked in an R882C mutation into OCI-M1 and NOMO-1 cells (both of which are normally DNMT3A wild-type) and reverted the DNMT3A mutation back to wild-type in OCI-AML2 and SIG-M5 cells (Fig. 1a, b). Sanger sequencing confirmed successful knock-in of the relevant sequences into the DNMT3A locus (Fig. 1c–f).
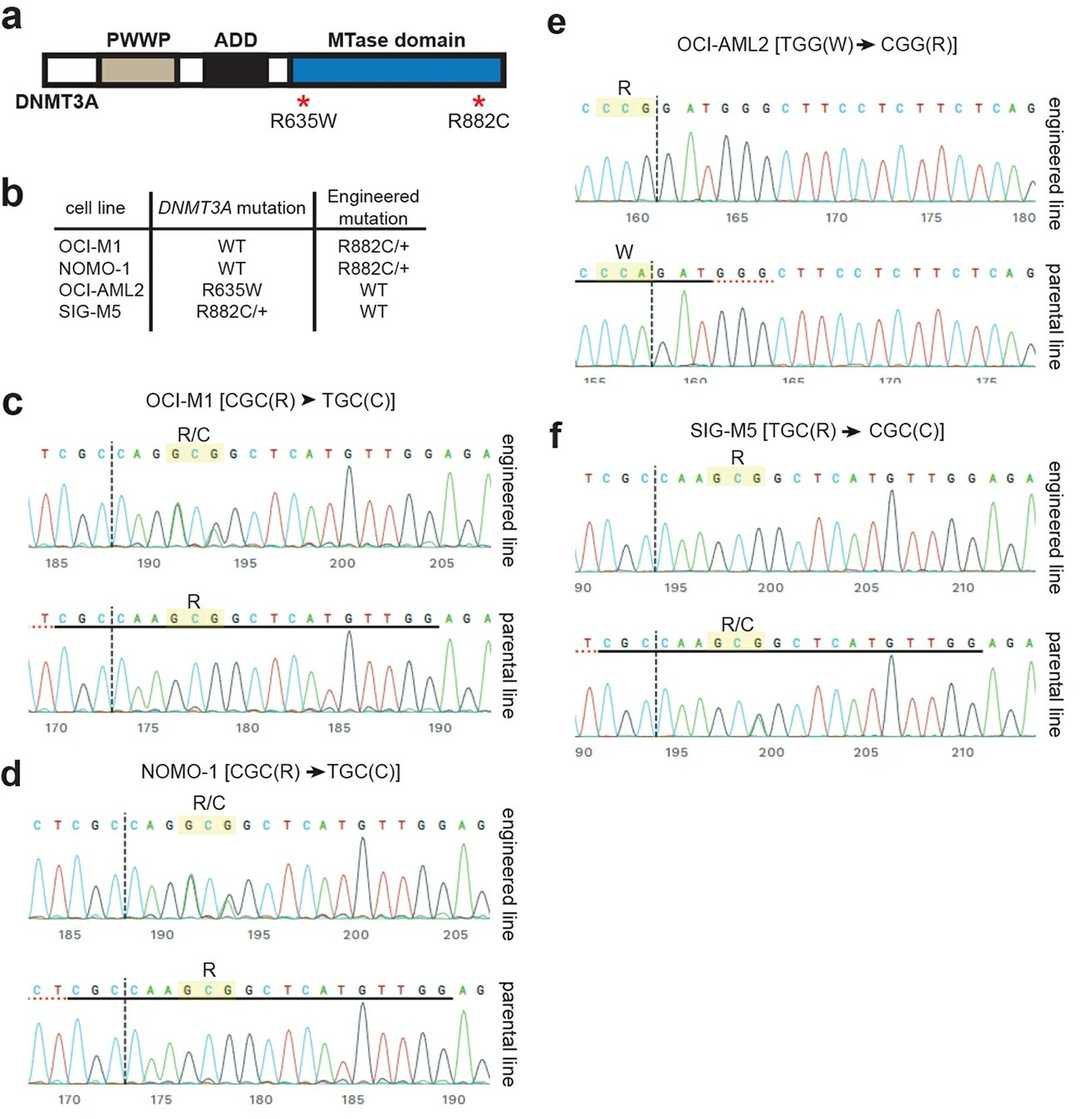 Fig. 1. Engineering DNMT3A Mutations in AML Cell Lines and Verification by Sanger Sequencing (Bhogal B, Weir B A, et al., 2022).
Fig. 1. Engineering DNMT3A Mutations in AML Cell Lines and Verification by Sanger Sequencing (Bhogal B, Weir B A, et al., 2022).
TET Dioxygenase Inhibition as a Therapeutic Strategy in TET2 Mutant Myeloid Neoplasia
TET2 is a commonly mutated gene in myeloid neoplasia that leads to loss of enzymatic function. TET2 and TET1/3 are DNA-dioxygenases that convert 5mC to 5hmC, 5fC, and 5caC, to prevent maintenance methylation and to promote demethylation. Guan's team explored TET dioxygenase inhibition as a treatment for TET2 mutant myeloid neoplasia. They used biochemical assays and cell-based models to study the impact of TET inhibition on DNA methylation and cell proliferation.
They showed that TET2 mutations (TET2MT) and IDH1/2 mutations (IDH1/2MT) are mutually exclusive in myeloid neoplasia, and that IDH1/2MT strongly inhibits growth of TET2MT cells by producing 2-HG (Fig. 2A-E). They therefore proposed a model of synthetic lethality, rather than functional redundancy. In TET2-mutant (TET2MT) cells, 2-HG inhibits residual TET activity (TET1/3), and could also lead to synthetic lethality. SIG-M5 cells have robust expression of TET3, but almost no TET1. Their dependence on residual TET3 activity was validated by inducible TET3 knockdown. They therefore hypothesized that transient inhibition of this residual DNA dioxygenase activity by selective inhibitors could specifically target and kill TET2-deficient cells. Known TET inhibitors like 2-HG, N-oxalylglycine (NOG), and dimethyl methyl fumarate (DMF) are non-specific and lack potency. They designed and synthesized 16 aKG derivatives and TETi76 inhibited TET activity and cell growth most potently in TET2-low cells. TETi76 binds to the α-KG site of TET2, and a co-crystal structure revealed the involvement of several highly conserved amino acids (H1801, H1381, S1898). TETi76 was tested in human myeloid cell lines with TET2 mutations or low TET2 expression and bone marrow from Tet2+/+, Tet2+/-, and Tet2-/- mice (Fig. 2F-G). They found that cells with low 5hmC levels were more sensitive to TETi76, and its specificity was validated by RNAseq analyses. They also found that TETi76 did not affect α-KG-dependent histone dioxygenases.
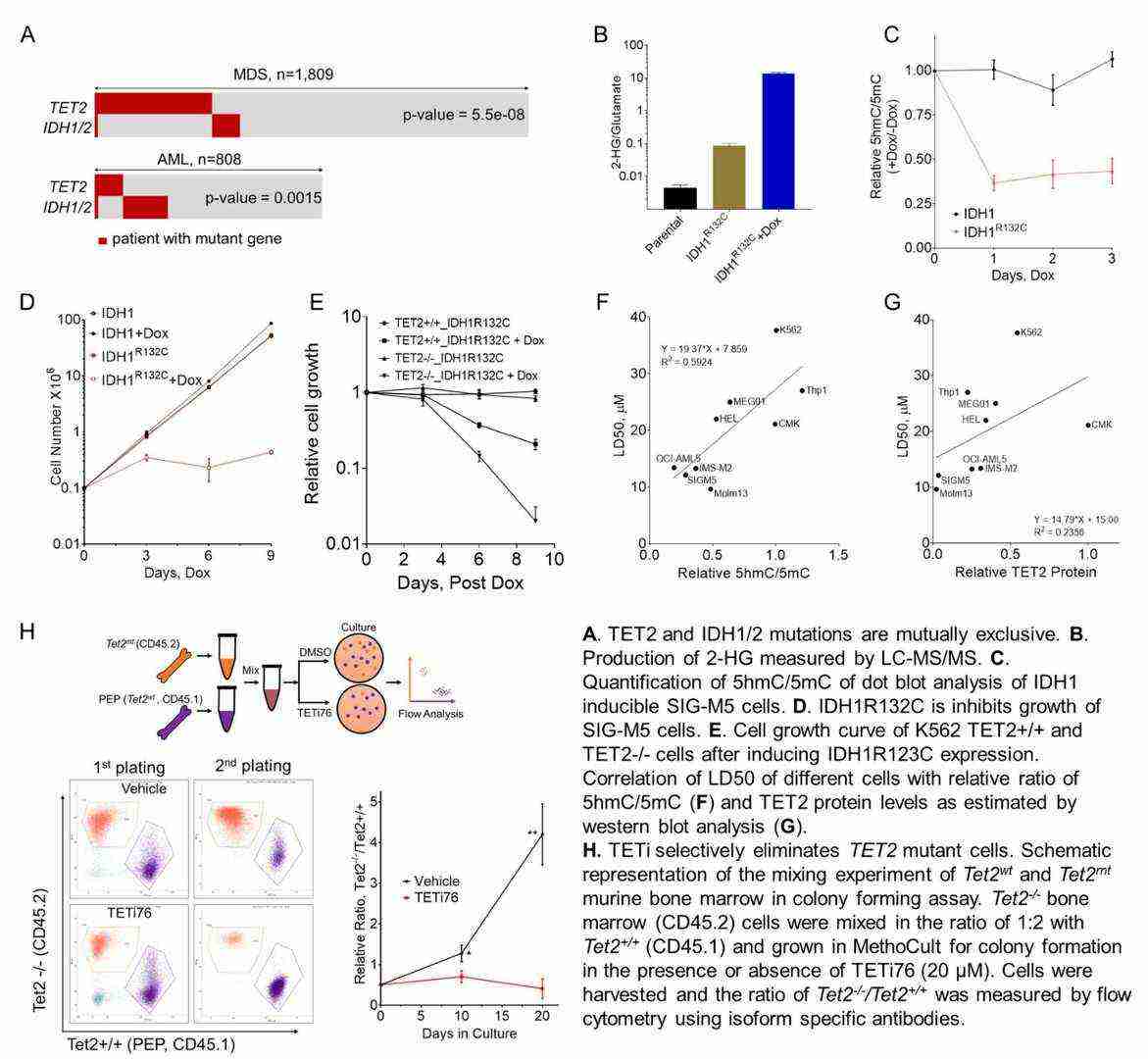 Fig. 2. TET Dioxygenase Inhibition as a Therapeutic Strategy in TET2 Mutant Myeloid Neoplasia (Guan Y H, Tiwari A, et al., 2019).
Fig. 2. TET Dioxygenase Inhibition as a Therapeutic Strategy in TET2 Mutant Myeloid Neoplasia (Guan Y H, Tiwari A, et al., 2019).
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- You May Also Need
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells





