
SHI-1
Cat.No.: CSC-C0630
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
Source: Bone Marrow
Morphology: round cells growing singly in suspension
Culture Properties: suspension
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
Immunology: CD3 -, CD13 +, CD15 +, CD19 -, CD33 +, CD34 -, CD41 +, CD235a -
Viruses: PCR: EBV -, HBV -, HCV -, HIV -, HTLV-I/II -, SMRV -
SHI-1 is a human acute monocytic leukemia (AML-M5b) cell line, created from the peripheral blood mononuclear cells of a male patient. The line harbors the classic t(6;11)(q27;q23) translocation that results in the oncogenic MLL- AF6 fusion transcript as well as a p53 mutation and a FLT3-ITD allele. These genetic alterations result in constitutive activation of STAT5, PI3K/AKT and MAPK pathways. Morphologically, SHI-1 cells are in suspension, round to slightly irregular in shape, 12-15 µm in diameter, with finely dispersed chromatin and prominent nucleoli and often contain Auer rods; by immunophenotyping, they show strong expression of myeloid/monocytic markers CD13, CD33, CD14, CD15 and moderate expression of CD11b, but are negative for CD34 and CD117. They can be grown autonomously in RPMI-1640 (or IMDM) medium containing 10-15 % fetal bovine serum, doubling every 30-36 hours with a stable karyotype even after many years in culture.
The line is functionally characterized by high tumorigenicity in nude mice, high levels of MMP-2/-9 secretion and multidrug-resistant phenotypes (high levels of LRP and GST-π and low P-gp). This makes it a useful model for research into leukemogenesis, particularly the roles of MLL-AF6 and FLT3-ITD, as well as pre-clinical testing of FLT3 inhibitors (midostaurin, gilteritinib), epigenetic drugs (azacitidine, decitabine) and new MDR-reversing agents (artesunate, curcumin). The line is also amenable to differentiation studies. PMA or 1,25-(OH)₂-vitamin D₃ treatment induces macrophage-like adhesion and up-regulation of CD14, CD86 and HLA-DR.
Suchilactone Inhibited Proliferation and Promoted Apoptosis of AML Cells In Vitro
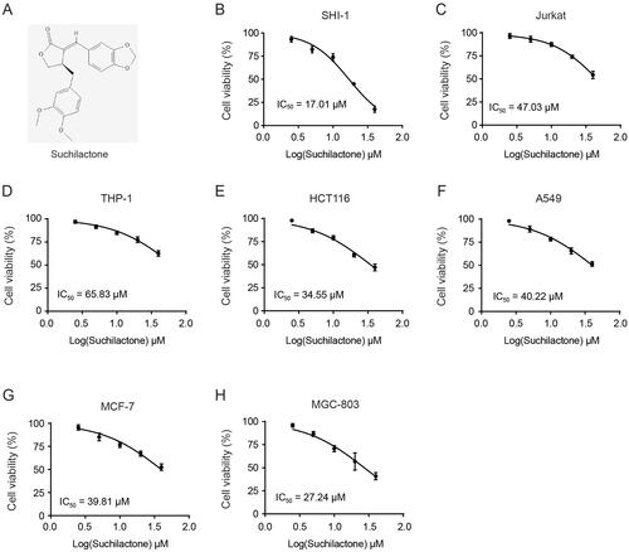
Suchilactone, a lignan compound from Monsonia angustifolia, has limited research on its pharmacological activity, particularly regarding its potential inhibitory effect on acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Wu's team aims to investigate suchilactone's antitumor effects and its underlying mechanism in AML.
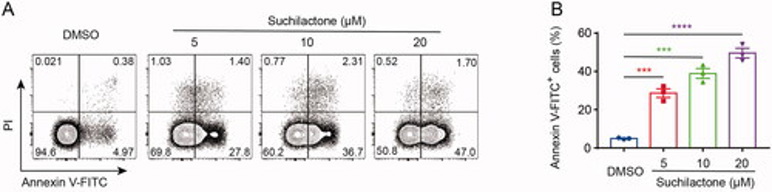
To assess antitumor activity, they screened suchilactone against multiple cancer lines. It most potently blocked proliferation of the AML line SHI-1 (IC₅₀ = 17 µM), outperforming Jurkat, THP-1, and solid-tumor lines (Fig. 1B-H). From these results, they found that suchilactone has a better inhibitory effect on the proliferation of AML cell line SHI-1, then they will continue to explore its mechanism. They treated SHI-1 cell with suchilactone for 24 h, flow cytometry showed that suchilactone induced apoptosis of SHI-1 cell, and that 20 µM suchilactone induced apoptosis in nearly 50% of the SHI-1 cells (Fig. 2A, B). These results showed that suchilactone inhibited growth of AML cells by suppressing cell proliferation and inducing apoptosis.
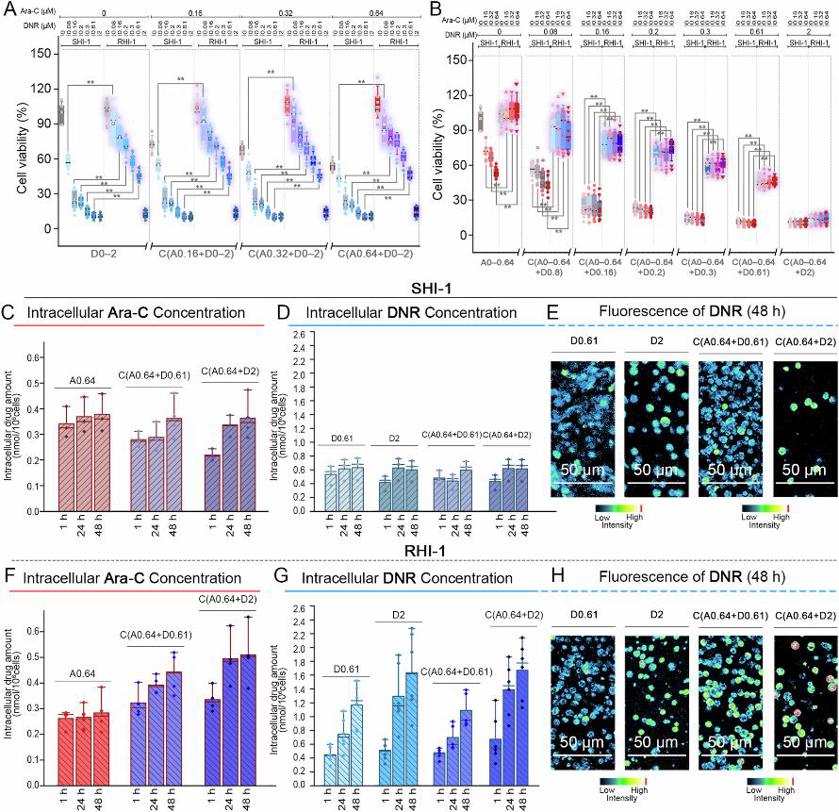
Drug Tolerance of Ara-C-resistant AML Cells
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is highly aggressive; FLT3-wild-type relapsed/refractory (R/R) patients lack effective therapies. Using FLT3-wild-type AML line SHI-1 and its Ara-C-resistant derivative RHI-1, Chae et al. explored mechanisms of resistance to cytarabine (Ara-C) and daunorubicin (DNR).
Cell viability assay was conducted to elucidate the responses of SHI-1 and RHI-1 cells to Ara-C (0-0.64 μM) and DNR (0-2 μM) either alone or as a combination after 24 and 48 h of treatment. Ara-C and DNR treatments significantly decreased the viability of SHI-1 cells in a concentration-dependent manner within 48 h (Fig. 3A, B). The cell viability results for the combination treatments followed a similar pattern to that of the single treatments with DNR. Although the combination treatment decreased cell viability to the same extent as DNR monotherapy, combination added no synergy. RHI-1 cells exhibited resistance to Ara-C and DNR treatments (Fig. 3A, B). Although DNR treatment was cytotoxic to RHI-1 cells, its effect was 1.3-4 times lower than that in SHI-1 cells. Despite the different mechanisms of action of DNR and Ara-C, RHI-1 cells exhibited significant tolerance to DNR, regardless of the presence or absence of Ara-C. Collectively, RHI-1 cells were resistant to both Ara-C and DNR and the combined treatments.
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- You May Also Need
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells





