
KYO-1
Cat.No.: CSC-C0602
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
Source: Blood; Peripheral Blood
Morphology: round cells growing singly or in clumps in suspension
Culture Properties: suspension
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
Immunology: CD3 -, CD13 -, CD14 -, CD19 -, CD33 +, CD34 -, CD41 -, CD42b -, CD71 +, CD235a +
Viruses: PCR: EBV -, HBV -, HCV -, HIV -, HTLV-I/II -, SMRV -
KYO-1 is a myeloid blast crisis-derived cell line of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML). It was developed in 1981 from the peripheral blood of a 22-year-old male patient. KYO-1 cells have the Philadelphia chromosome translocation (t(9;22)(q34;q11)), which is a typical genetic abnormality of CML. The cells are round and proliferate mainly in suspension as single cells or occasionally in small clusters. Some cells may be double-sized.
The KYO-1 cell line is mainly used for the study of pathological mechanisms of CML and the biological characteristics of the blast crisis phase of CML. In addition, because it has the Philadelphia chromosome translocation, it is also valuable for the study of the genetic and molecular mechanism of leukemia and drug resistance, as well as the development of targeted therapy.
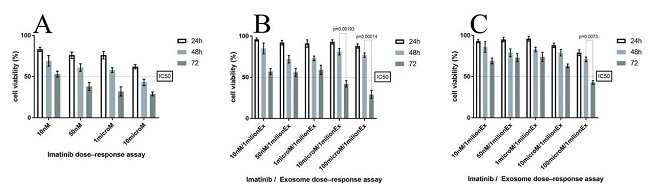
A Microchip for Exosome Isolation that can be Impregnated with Imatinib Simultaneously: an In Vitro Analysis
In this study, Monfaredan et al. have created microfluidic devices to separate exosomes from various sources by utilizing magnetic beads that are coupled with CD68. The MTT assay was used for cytotoxicity of imatinib-loaded CD63-Mag caught exosome with chip against KYO-1 cell line. As shown in Fig. 1A to 1C, the free imatinib, imatinib-loaded CD63-Mag caught exosome with chip, and available kits' toxicity on KYO-1 cells are dose dependent. In addition, as cells are treated with the exosome which were extracted by an available kit, the dose was normalized to 100 μmol. It should be mentioned that this compensation could be done by chip, because it can keep the shape and morphology of the caught exosome for longer time. This effective dose was similar to the direct injection of cells with imatinib.
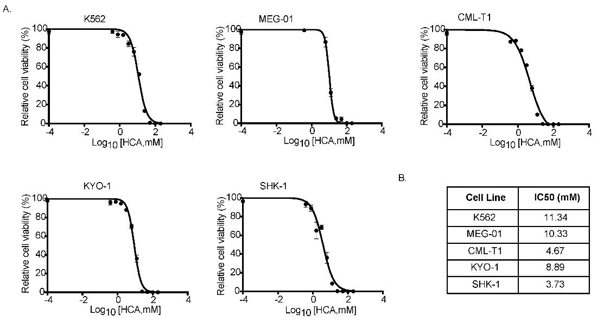
HCA Inhibited Tumor Cell Growth In Vitro
Chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) is a type of cancer that has been targeted for metabolic regulation via AMPK activation. This study investigates hydroxycitric acid (HCA), a natural bioactive compound from Garcinia gummi-gutta, for its ability to inhibit CML growth by activating AMPK and mTOR pathways.
To test HCA's therapeutic potential on CML, they first examined its effect on CML cell growth in vitro. K562 cells were treated with HCA at concentrations from 1 mM to 100 mM for up to 72 h. Cell viability results showed that HCA inhibited K562 cell proliferation in a concentration-dependent manner, with an IC50 of 11.34 mM (Fig. 2A). Similarly, HCA inhibited the growth of other human CML cell lines (MEG-01, CML-T1, SKH-1, and KYO-1) with IC50 values ranging from 3 to 12 mM (SKH-1, 3.73 mM; CML-T1, 4.67 mM; KYO-1, 8.89 mM; MEG-01, 10.33 mM) (Fig. 2A). However, HCA did not affect the proliferation of normal mouse embryo fibroblasts, even at 100 mM.
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- You May Also Need
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells





