JVM-13
Cat.No.: CSC-C3406
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
Source: Blood; Peripheral Blood
Morphology: lymphoblastoid cells growing in clusters in suspension
Culture Properties: suspension
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
- Documents
Immunology: CD3 -, CD10 -, CD13 -, CD19 +, CD20 +, CD34 -, CD37 +, CD80 +, CD138 -, HLA-DR +, sm/cyIgM +, sm/cyIgG -, sm/cykappa -, sm/cylambda +
Viruses: ELISA: reverse
The JVM-13 cell line is a well-known cell line derived from the peripheral blood of a male patient diagnosed with B-lymphocytic leukemia (PLL). The cell line was established by the transformation of B-PLL cells using Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) during treatment with the phorbol ester TPA (12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol 13-acetate).
B-PLL is a rare and aggressive subtype of B-cell leukemia characterized by the proliferation of immature B lymphocytes with a prominent prolymphocytic morphology. It is considered a variant of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) with distinct clinical and pathological features. PLL typically presents with a high white blood cell count, splenomegaly (enlarged spleen), lymphadenopathy (enlarged lymph nodes), and bone marrow involvement. The establishment of the JVM-13 cell line has provided researchers with a valuable tool for studying the biology, pathogenesis, and therapeutic responses of B-PLL.
The transformation of the JVM-13 cells using EBV allows for their immortalization and long-term maintenance in cell culture. This provides researchers with a continuous and reliable supply of cells for experimental purposes. The use of TPA during the establishment of the cell line helps in promoting the growth and expansion of the transformed cells.
Shikonin Exert Antitumor Activity in JVM-13 Cells
Shikonin is a well-known antitumor substance that induces apoptosis, inhibits proliferation of cancer cells, and inhibits angiogenesis. The antitumor activity of shikonins in JVM-13, human B-PLL cells was explored. As shown in Fig. 1, derivatives of shikonin isobutyrylshikonin (IBS) and α-methylbutyrylshikonin (MBS) decreased the viability of JVM-13 cells in a dose-dependent manner. From a concentration of 110 μg/mL, both IBS and MBS reduced the viability of JVM-13 cells to 100% (Fig. 1).
As illustrated in Fig. 2, IBS- and MBS-induced apoptosis and the majority of JVM-13 cells were in or occurred during late apoptosis. Quantitative analysis of Bcl-2, Bax, Mcl-1, and Noxa molecules in JVM-13 cells strongly indicated apoptotic death of JVM-13 cells after treatment with MBS and IBS. Treatment of JVM-13 cells with IBS and MBS at a concentration of 2 µg/mL significantly attenuated the percentage of Mcl-1-expressing cells and significantly enhanced the percentage of cells that expressed the pro-apoptotic molecule Noxa, even at a lower concentration of 1 µg/mL (Fig. 2c). Analysis of Bax and Bcl-2 expression at mRNA levels also showed significant attenuation of Bcl-2 and enhancement of Bax mRNA levels after treatment of JVM-13 cells with IBS and MBS (Fig. 2d). The antiproliferative effects of testing molecules were evaluated by assessment of the Ki67 expression level in treated cells using flow cytometry. The percentage of Ki67-positive JVM-13 cells (Fig. 3) treated with IBS and MBS was significantly lower compared to untreated cells.
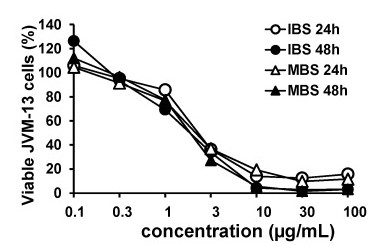 Fig. 1 Dose- and time-dependent cytotoxicity of IBS and MBS on the JVM-13 cell line. (Todorovic Z, et al., 2021)
Fig. 1 Dose- and time-dependent cytotoxicity of IBS and MBS on the JVM-13 cell line. (Todorovic Z, et al., 2021)
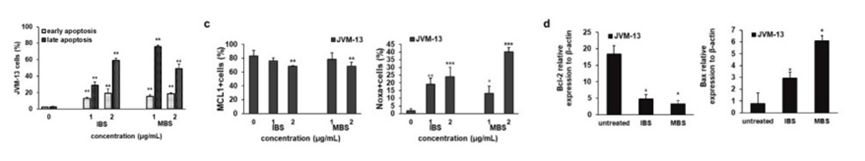 Fig. 2 IBS and MBS induce apoptotic death of JVM-13 cells. (Todorovic Z, et al., 2021)
Fig. 2 IBS and MBS induce apoptotic death of JVM-13 cells. (Todorovic Z, et al., 2021)
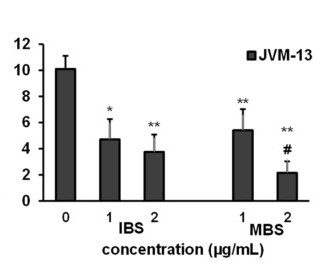 Fig. 3 IBS and MBS attenuate the expression of Ki67 in JVM-13 cells. (Todorovic Z, et al., 2021)
Fig. 3 IBS and MBS attenuate the expression of Ki67 in JVM-13 cells. (Todorovic Z, et al., 2021)
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- You May Also Need
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells





