HDLM-2
Cat.No.: CSC-C0201
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
Source: Pleural Effusion
Morphology: single, round to polygonal cells in suspension; heterogeneity in cell size, 15-100 μm or larger; many bi- and polynucleated cells
Culture Properties: suspension
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
- Documents
b. Cell-Based assay
c. In vivo efficacy study
Viruses: ELISA: reverse transcriptase negative; PCR: EBV +, HBV -, HCV -, HHV-8 -, HIV-1 -, HIV-2 -, HTLV-I/II -, MLV -, SMRV -
Store in liquid nitrogen.
Biosafety classification is based on U.S. Public Health Service Guidelines, it is the responsibility of the customer to ensure that their facilities comply with biosafety regulations for their own country.,
The HDLM-2 cell line is a widely used and well-characterized cell line that was established from the pleural effusion of a 74-year-old man diagnosed with Hodgkin lymphoma (HL, nodular sclerosing subtype, stage IV) in 1982. The HDLM-2 cell line represents a specific subtype of HL known as nodular sclerosing, which is one of the most common subtypes of the disease. Nodular sclerosing HL is characterized by the presence of large, tumor-like masses called nodules within the lymph nodes, along with fibrosis or scarring in the surrounding tissues.
The establishment of the HDLM-2 cell line has provided researchers with a valuable tool for studying the biology, pathogenesis, and therapeutic responses of HL. The cell line has been extensively studied and characterized, allowing for in vitro and in vivo investigations of various aspects of the disease. Researchers have used HDLM-2 cells to explore the genetic and molecular alterations present in HL, the signaling pathways involved in its development and progression, and the mechanisms of resistance to treatment.
Effect of ECP on Hodgkin Lymphoma Cell Lines
In HL, tumor eosinophilia indicates poor prognosis, probably caused by eosinophil-induced stimulation of tumor cells. The study was to investigate the effects of eosinophil cationic protein (ECP) on HL tumor cells in vitro. All cell lines were sensitive to ECP but to various degrees. At low concentrations of ECP, HDLM-2 was more sensitive than the L428 and particularly the KMH2 cell lines (Fig. 1). At higher concentrations the opposite was seen, with a more pronounced reduction in SI for L428 and KMH2 as compared to HDLM-2, where a plateau effect was seen.
For HDLM-2 (Fig. 1), a reduction in SI was evident at the lowest ECP concentration tested, 0.004 μM (p < 0.01). At a concentration of 0.018 μM, a plateau in SI of about 70% was reached. No statistically significant difference was determined from the concentration of 0.018 μM ECP and the higher ECP concentrations (ECP up to 1.14 μM) added, thus showing a true plateau.
In an additional experiment, HDLM-2 cells were incubated with or without ECP (LMW-ECP II at 0.07 μM) for 72 hours, after which a new serum-containing medium without ECP was added. Figure 2 shows HDLM-2 cells first after 72 hours of incubation with ECP, and then after an additional 72 hours of culture with serum. The cells continued to grow exponentially after the serum was added; this indicated that ECP caused no injury to the surviving HDLM-2 cells that affected their proliferation.
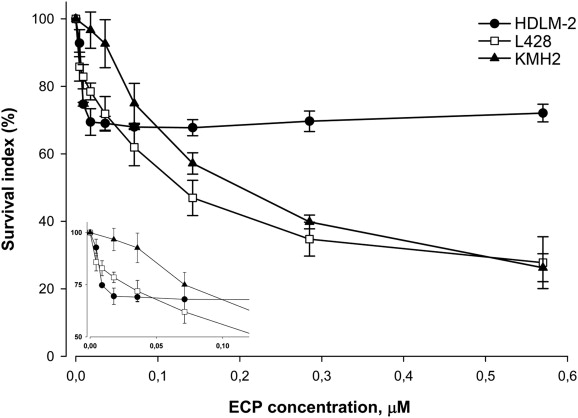 Fig. 1 The cytotoxic effect of LMW-ECP II on the cell lines HDLM-2 (filled circles), L428 (white squares), and KMH2 (filled triangles). (Glimelius I, et al., 2011)
Fig. 1 The cytotoxic effect of LMW-ECP II on the cell lines HDLM-2 (filled circles), L428 (white squares), and KMH2 (filled triangles). (Glimelius I, et al., 2011)
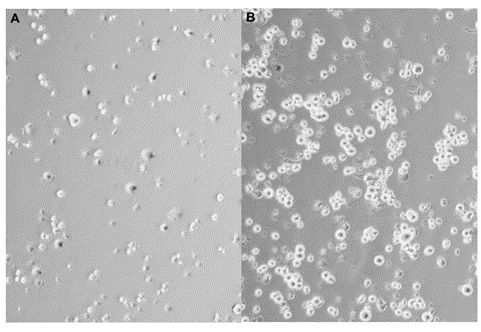 Fig. 2 HDLM-2 cells cultured in 24-well plates with LMW-ECP II at a concentration of 0.07 μM for 72 hours. (Glimelius I, et al., 2011)
Fig. 2 HDLM-2 cells cultured in 24-well plates with LMW-ECP II at a concentration of 0.07 μM for 72 hours. (Glimelius I, et al., 2011)
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- You May Also Need
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells





