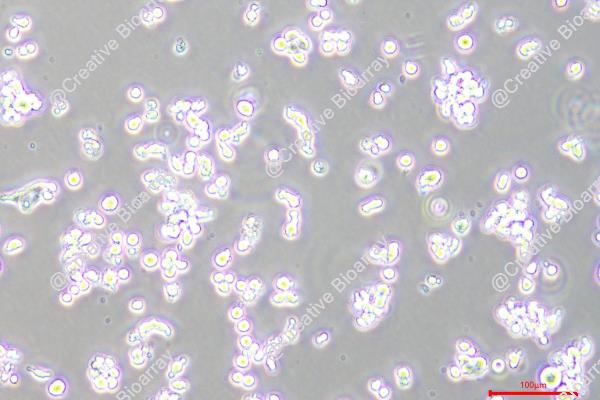
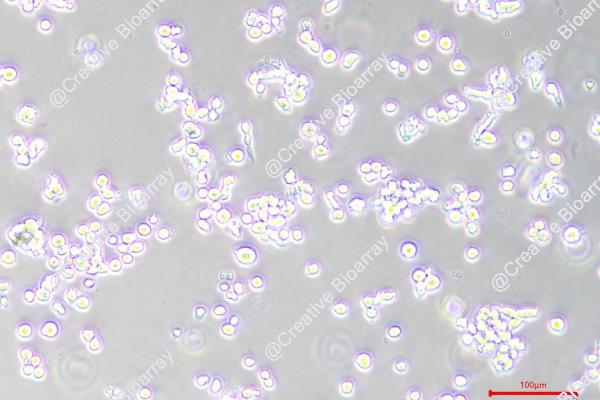
EJM
Cat.No.: CSC-C0566
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
Source: Ascites
Morphology: round to polymorph, single or clustered cells growing either in suspension or adherent
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
Immunology: CD3 -, CD10 -, CD13 -, CD19 -, CD20 -, CD34 -, CD37 +, CD38 +, CD80 -, CD138 +, cyIgG +, cyIgM -, cykappa -, cylambda +
Viruses: PCR: EBV -, HBV -, HCV -, HIV -, HTLV-I/II -, SMRV -
An IgG lambda myeloma plasma cell line, EJM, was established from the peritoneal effusion of a patient with extramedullary myeloma. EJM cells exhibited a plasmablastic morphology with abundant rough endoplasmic reticulum and grow in liquid culture with a doubling time of 72 h and a labelling index of 36%. In addition to cytoplasmic IgG lambda, the cells are positive for CD9, 20, 32, 38, 44, 54, 71, 78, MHC Class II DR, DP and DQ. With their ability to secrete immunoglobulins and typical myeloma features, EJM cells exhibits multiple genetic alterations and aberrant signaling pathways that mimic disease progression in vivo and are a key resource for the ongoing pursuit of effective treatments and a deeper understanding of the biology of multiple myeloma.
BSO-Radiosensitized Human Cancer Cell Lines to 177Lu-DOTATATE
Peptide receptor radionuclide therapy with 177Lu-DOTATATE is an efficient treatment for patients suffering from metastasized neuroendocrine tumors. Lu-177 induces oxidative stress, eventually leading to tumor cell death. Inhibition of the antioxidant defence mechanisms, using buthionine sulfoximine (BSO), represents an attractive strategy to increase 177Lu-DOTATATE efficacy. In cells and an animal model, the combination of 177Lu-DOTATATE and BSO was more effective than 177Lu-DOTATATE alone. In addition, it did not result in additional toxicity. Targeting the antioxidant defence system opens new safe treatment combination opportunities with 177Lu-DOTATATE.
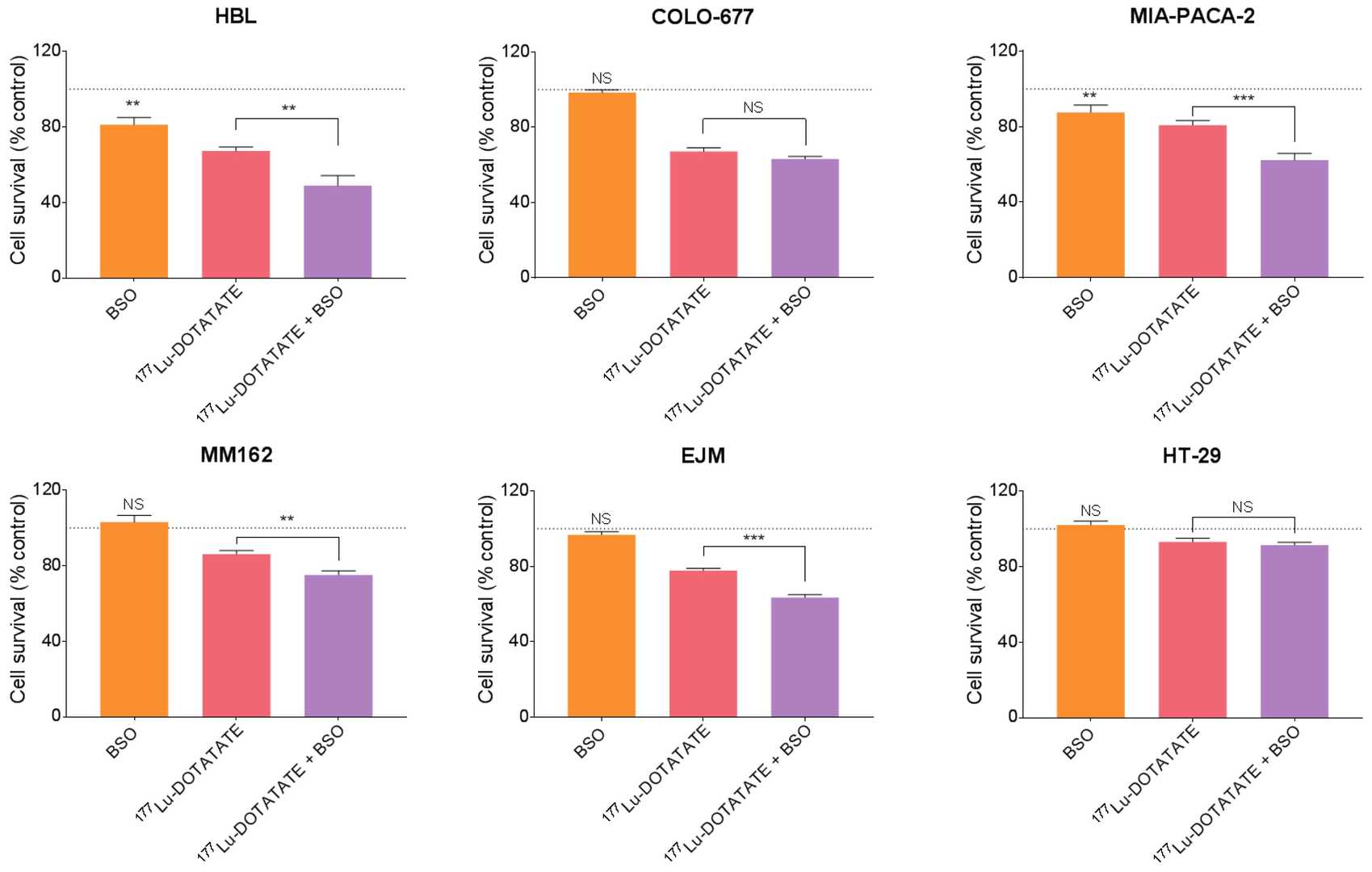 Fig. 1. Effect of BSO and its combination with 177Lu-DOTATATE on the survival of melanoma (HBL and MM162), multiple myeloma (COLO-677 and EJM) and GEP (MIA-PACA-2 and HT-29) cell lines (Delbart, Wendy, et al. 2023).
Fig. 1. Effect of BSO and its combination with 177Lu-DOTATATE on the survival of melanoma (HBL and MM162), multiple myeloma (COLO-677 and EJM) and GEP (MIA-PACA-2 and HT-29) cell lines (Delbart, Wendy, et al. 2023).
Ad35K++ and CD59 Inhibitor (rILYD4) Additively Enhance CDC by Daratumumab and Isatuximab in MM Cells
Remarkable progress has been made in the treatment of Multiple myeloma (MM) with anti-CD38 monoclonal antibodies such as daratumumab and isatuximab, which can kill MM cells by inducing complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC). We showed that the CDC efficacy of daratumumab and isatuximab is limited by membrane complement inhibitors, including CD46 and CD59, which are upregulated in MM cells. We recently developed a small recombinant protein, Ad35K++, which is capable of transiently removing CD46 from the cell surface. We also produced a peptide inhibitor of CD59 (rILYd4). In this study, we tested Ad35K++ and rILYd4 in combination with daratumumab and isatuximab in MM cells as well as in cells from two other B-cell malignancies. We showed that Ad35K++ and rILYd4 increased CDC triggered by daratumumab and isatuximab. The combination of both inhibitors had an additive effect in vitro in primary MM cells as well as in vivo in a mouse xenograft model of MM.
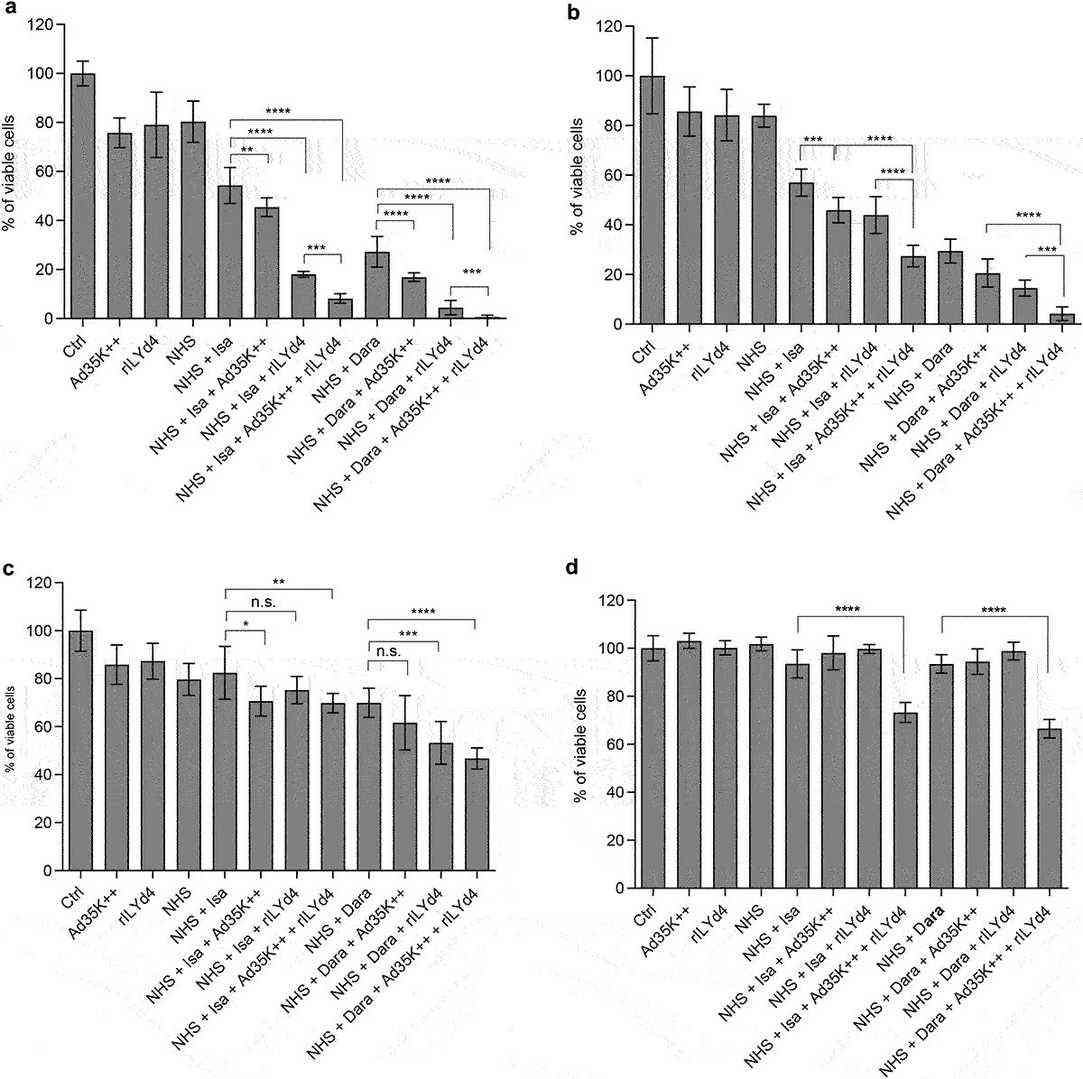 Fig. 2. The combination of Ad35K++ and rIYd4 additively enhanced the CDC effect of daratumumab and isatuximab. MOLP8 (a), SU-DHL-8 (b), EJM (c) and MM.1?R (d) (Wang, Hongjie, et al. 2024).
Fig. 2. The combination of Ad35K++ and rIYd4 additively enhanced the CDC effect of daratumumab and isatuximab. MOLP8 (a), SU-DHL-8 (b), EJM (c) and MM.1?R (d) (Wang, Hongjie, et al. 2024).
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- You May Also Need
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells