EFM-19
Cat.No.: CSC-C0338
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
Source: Pleural Effusion Metastasis
Morphology: epitheloid, growing in clusters at first, then as monolayer
Culture Properties: monolayer
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
Immunology: cytokeratin +, cytokeratin-7 +, cytokeratin-8 +, cytokeratin-17 +, cytokeratin-18 +, cytokeratin-19 +, desmin -, endothel -, EpCAM -, GFAP -, neurofilament -,
The EFM-19 cell line was established from the malignant pleural effusion of a postmenopausal patient with metastatic invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC). It is an important in vitro model for estrogen receptor-positive (ER+), progesterone receptor-positive (PR+), HER2-negative (HER2-) luminal breast cancer. Its key characteristics include slow proliferation, strong dependence on estrogen for growth, expression of functional ERα, and the ability to form complex structures in 3D culture. Current research applications heavily focus on studying mechanisms of endocrine therapy resistance (particularly resistance to tamoxifen and fulvestrant), exploring metastatic processes (e.g., roles of CXCR4 signaling), investigating novel therapeutic targets within luminal biology (like JAK/STAT pathways or CDK inhibitors beyond CDK4/6), and developing more physiologically relevant 3D organoid or co-culture models for drug screening.
EFM-19's significant advantages lie in its faithful representation of the clinically common, often treatment-resistant luminal A subtype. Unlike many ER+ lines (e.g., MCF-7, T47D) that may lose functional ER or exhibit genetic drift, EFM-19 maintains robust ER expression and responsiveness, providing a more robust model for studying acquired endocrine resistance mechanisms associated with patient relapse. Its origin from metastatic disease also makes it particularly valuable for investigating late-stage luminal breast cancer biology and testing therapies aimed at overcoming resistance in advanced settings.
PLK1 Inhibitor Onvansertib Enhances the Efficacy of Alpelisib in PIK3CA-Mutated HR-Positive Breast Cancer
Endocrine therapy (ET) combined with cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitors (CDK4/6i) is the preferred first-line treatment for hormone receptor-positive (HR+)/HER2- metastatic breast cancer. Although this is beneficial, acquired resistance leads to disease progression, and patients harboring PIK3CA mutations are treated with targeted therapies such as the PI3Kα inhibitor, alpelisib, alongside ET. Drug-related resistance mechanisms limit the efficacy of alpelisib, highlighting the need for better combination therapies. This study aimed to evaluate the efficacy of combining alpelisib with a highly specific PLK1 inhibitor, onvansertib, in PIK3CA-mutant HR+ breast cancer preclinical models.
The combination synergistically inhibited cell viability, suppressed PI3K signaling, induced G2/M arrest and apoptosis in PI3K-activated cell lines. Pharmacodynamic studies confirmed the inhibition of both PLK1 and PI3K activity and pronounced apoptosis in the combination-treated tumors. These findings support that targeting PLK1 and PI3Kα with onvansertib and alpelisib, respectively, may be a promising strategy for patients with PIK3CA-mutant HR+ breast cancer failing ET + CDK4/6i therapies and warrant clinical evaluation.
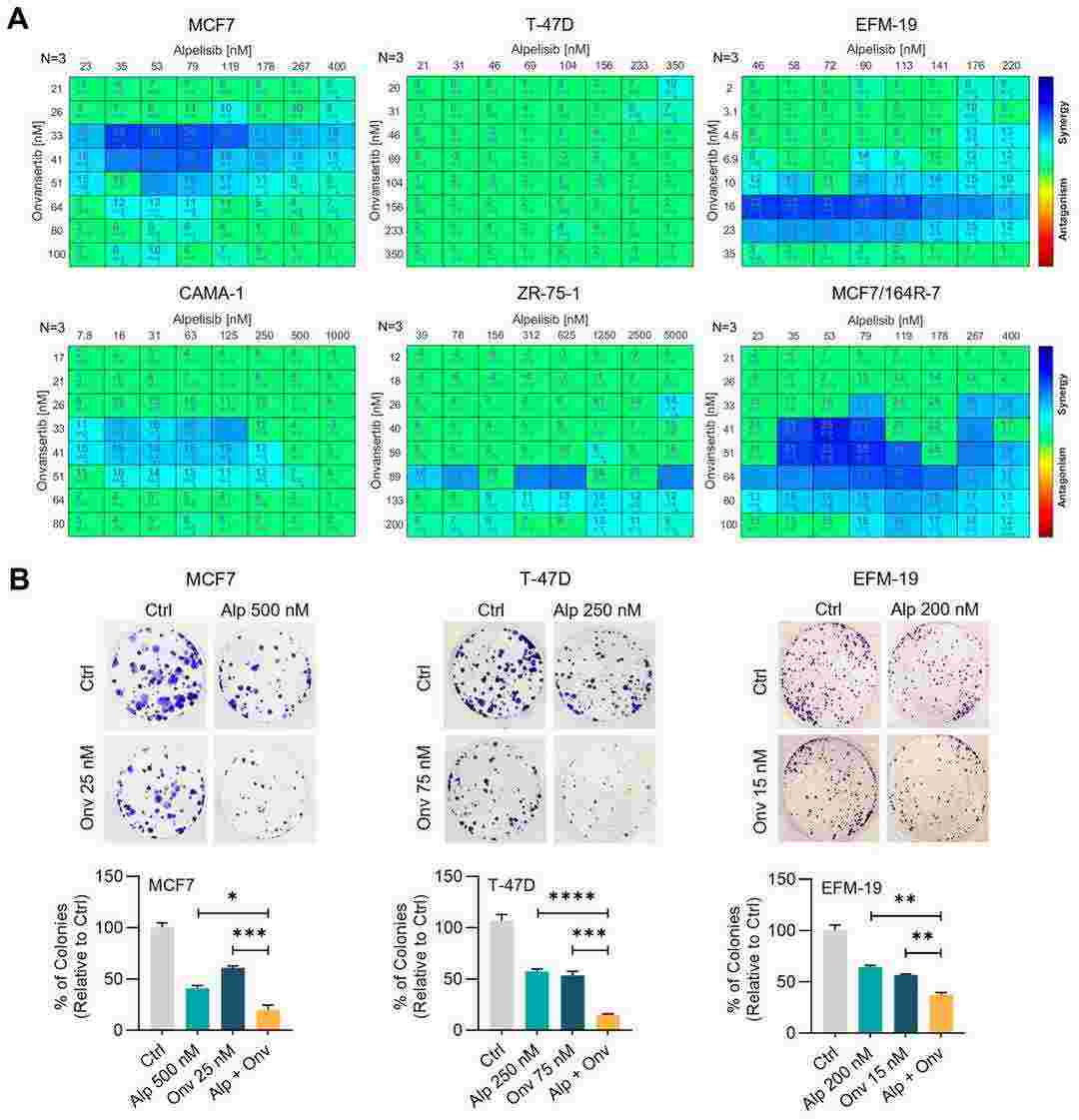 Fig. 1. Combination of alpelisib and onvansertib displays a synergistic effect in HR+ breast cancer cell lines (Sreekumar, Sreeja, et al. 2024).
Fig. 1. Combination of alpelisib and onvansertib displays a synergistic effect in HR+ breast cancer cell lines (Sreekumar, Sreeja, et al. 2024).
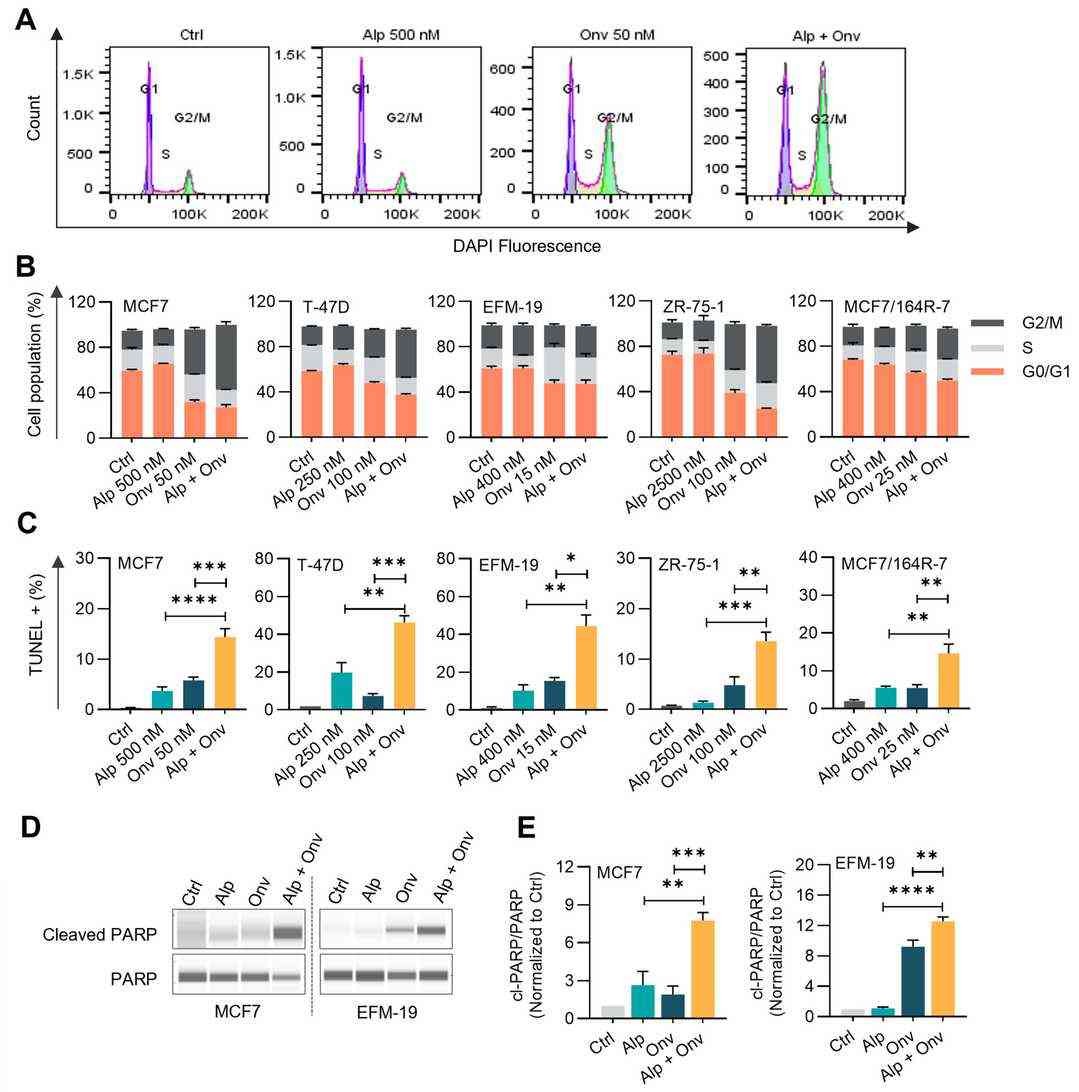 Fig. 2. Alpelisib and onvansertib combination induces G2/M arrest and apoptosis in ER+ breast cancer cell lines (Sreekumar, Sreeja, et al. 2024).
Fig. 2. Alpelisib and onvansertib combination induces G2/M arrest and apoptosis in ER+ breast cancer cell lines (Sreekumar, Sreeja, et al. 2024).
The Role of ER Promoter Methylation in Fulvestrant-Resistant Cell Line Models
Oestrogen receptor alpha (ER; gene symbol ESR1) is the most important prognostic and treatment-predictive biomarker in breast cancer. Drugs targeting oestrogen and ER for endocrine therapy of breast cancer include aromatase inhibitors, the selective ER modulator tamoxifen and the selective ER degrader fulvestrant. Tumors can develop resistance to endocrine therapy through several mechanisms, which is often linked to altered expression of ER. To investigate the role of promoter methylation in the regulation of ESR1 expression, we used bisulfite sequencing to measure methylation at CpG sites in alternative ER promoter regions for six cell line models of fulvestrant resistance. Both CpG methylation and expression of alternative first exons changed dynamically, with striking differences between cell lines that had stable or unstable resistance upon fulvestrant withdrawal. Methylation at some CpG sites was strongly negatively correlated with expression of specific first exons.
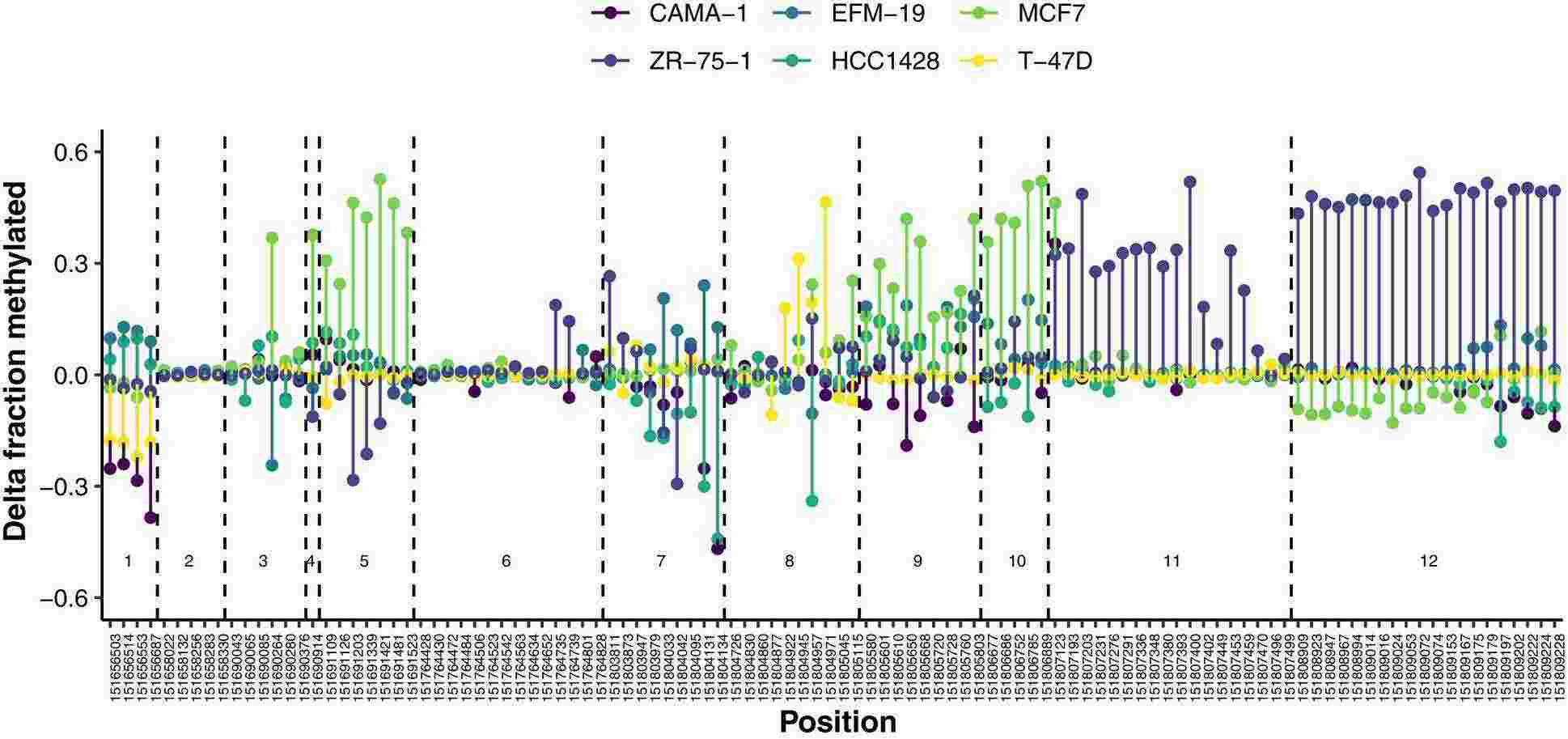 Fig. 3. Differences in the fraction of methylated reads at CpG sites between fulvestrant-resistant sublines and their respective parental cell line (Albrecht, Juliane, et al. 2025).
Fig. 3. Differences in the fraction of methylated reads at CpG sites between fulvestrant-resistant sublines and their respective parental cell line (Albrecht, Juliane, et al. 2025).
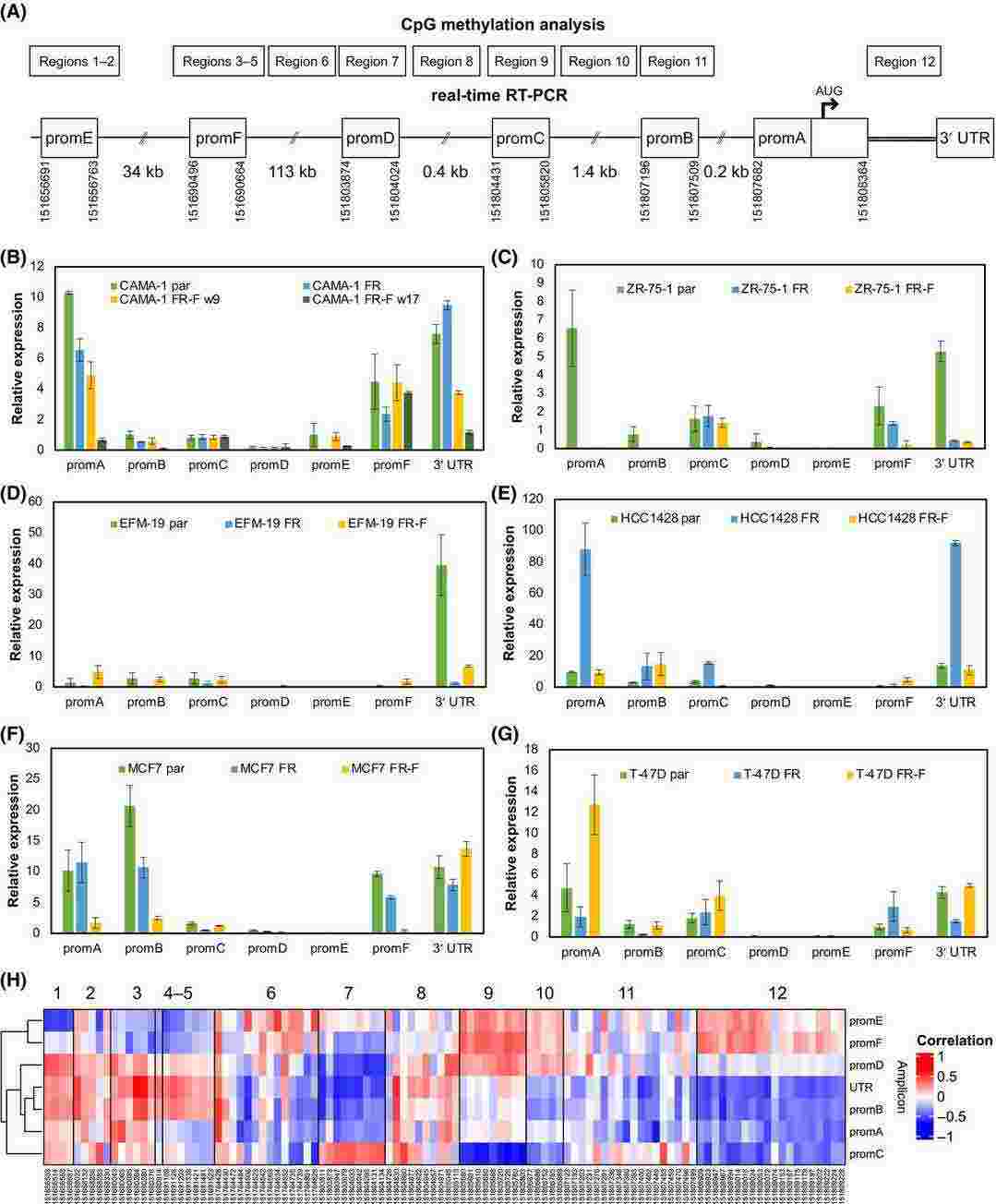 Fig. 4. Alternative first exon expression and correlation with CpG site methylation (Albrecht, Juliane, et al. 2025).
Fig. 4. Alternative first exon expression and correlation with CpG site methylation (Albrecht, Juliane, et al. 2025).
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- You May Also Need
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells