CAL-78
Cat.No.: CSC-C0481
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
Source: Muscle; Skeletal Muscle
Morphology: adherent fibroblast-like cells growing as monolayer; the culture contains a large amount of cellular debris
Culture Properties: monolayer
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
Immunology: cytokeratin +, desmin -, endothel -, GFAP +, neurofilament -, vimentin +
Viruses: PCR: EBV -, HBV -, HCV -, HIV -, HTLV-I/II -, SMRV -
CAL-78 is a human chondrosarcoma cell line derived from a malignant tumor of cartilage, presumably of long bone or axial skeleton origin. This adherent cell line has a spindle-shaped to polygonal morphology, expected for a mesenchymal cell line, and grows well in standard culture media. It partially retains the expression of chondrogenic differentiation markers such as COL2A1 but has undergone genomic changes typical of high-grade sarcomas, including genomic instability and aggressive growth characteristics.
Functionally, CAL-78 exhibits dysregulated pathways such as IGF signaling and hypoxia-inducible factors (HIFs), among others, which are relevant to its tumorigenic properties. This cell line is known for its resistance to apoptosis and certain conventional treatments, mirroring the therapeutic challenges often encountered with chondrosarcomas in clinical settings. Consequently, it serves as a model to explore the efficacy of targeted therapies and the mechanisms of therapeutic resistance in cartilage-derived sarcomas.
Research studies common utilize CAL-78 to examine metastasis processes and cartilage cancer biology while testing drug efficacy. It is not as widely used as some other sarcoma cell lines but offers unique insights into chondrosarcoma due to its genetic and phenotypic characteristics. The cell line's applications extend to molecular oncology, skeletal disease modeling, and preclinical studies, addressing gaps in understanding cartilage-derived cancers.
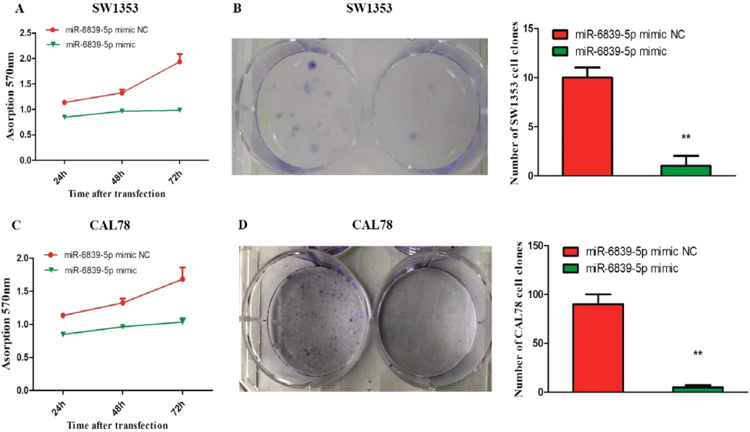
miR-6839-5p Inhibits the Proliferation and Migration of Human Chondrosarcoma Cells
MicroRNAs are key in cancer cell proliferation, invasion, and metastasis. Prior studies showed that miR-6839-5p levels rose significantly in SW1353 cells after 125I seed 6 Gy irradiation, suggesting it may suppress tumor growth in chondrosarcoma cells. Li's team explored miR-6839-5p's effects on human chondrosarcoma cells and its potential target genes.
Using MTT and colony formation assays, they found that miR-6839-5p mimic-transfected cells had significantly lower proliferation rates than controls (Fig. 1). At 24 hours post-transfection, SW1353 experimental cells had 10% and CAL78 experimental cells had 5.56% of the clone formation capacity of their respective controls. Wound healing assays showed that miR-6839-5p reduced cell migration. Experimental SW1353 cells migrated 15% and CAL78 cells migrated 23% after 24 hours, compared to 60% for SW1353 and 82% for CAL78 control cells (Fig. 2).

Ask a Question
Write your own review
- You May Also Need
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells