CAL-148
Cat.No.: CSC-C0489
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
Source: Pleural Effusion Metastasis
Morphology: epitheloid cells growing as single cells or as clumps either in suspension or, if supplemented with EGF, in monolayers
Culture Properties: monolayer
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
Immunology: cytokeratin +, cytokeratin-7 +, cytokeratin-8 +, cytokeratin-17 -, cytokeratin-18 +, cytokeratin-19 +, desmin -, endothel -, EpCAM +, GFAP -, neurofilament -, vimen
Derived from the malignant pleural effusion of a patient with metastatic triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC), the CAL-148 cell line serves as a critical in vitro and in vivo model for studying this aggressive subtype of breast cancer characterized by the lack of estrogen receptor (ER), progesterone receptor (PR), and HER2 overexpression. Its key features include an epithelial morphology, high tumorigenicity in immunodeficient mice, and harboring common TNBC-associated genetic alterations, such as TP53 mutation and PIK3CA amplification. Current researches heavily leverage CAL-148 to investigate novel therapeutic strategies for TNBC, particularly evaluating the efficacy of chemotherapy combinations, PARP inhibitors (despite being BRCA wild-type), targeted agents against pathways like PI3K/AKT/mTOR, and immunotherapies (notably as it expresses PD-L1). Its main advantages lie in its direct clinical origin from metastatic TNBC, ensuring high relevance; its stability and availability; and its utility as a representative "hard-to-treat" model for screening drug responses and deciphering mechanisms of therapy resistance and metastasis inherent to TNBC.
Xiaochaihu Decoction Inhibits the Proliferation of Breast Cancer Cells In Vitro
Xiaochaihu (XCH) decoction is a traditional Chinese prescription that has been recorded in the pharmacopeia of the People's Republic of China. In China, the XCH decoction is used clinically to treat a variety of tumors, including breast cancer. However, its potential mechanism of action is still undefined.
To confirm the inhibitory effect of the XCH decoction on breast tumor cells, different concentrations of the XCH decoction (0, 2.5, 5, 10, 20, 40, 80 or 160 μg/mL) were used to treat different breast cancer cell lines. After 48 hours, cell viability was determined by a CCK-8 assay. The results showed that the XCH decoction inhibited the proliferation of breast cancer cells, especially CAL-148 and MCF-7 cells (Fig. 1A). Subsequently, to further verify the effectiveness of the XCH decoction, CAL-148 and MCF-7 cells were treated with different concentrations of the XCH decoction for 24 h, 48 h or 72 h. The data demonstrated that the XCH decoction significantly curbed the growth of CAL-148 and MCF-7 cells in a dose- and time-dependent manner (Fig. 1B, 1C). In addition, after treatment with the XCH decoction for 48 hours, cell survival decreased, as determined by 40-fold light microscopy (Fig. 1D). A colony formation assay was used to evaluate the effect of the XCH decoction on proliferation, and the results showed that the number of cell clones in the XCH decoction group was dramatically less than that in the control group (Fig. 1E, 1F).
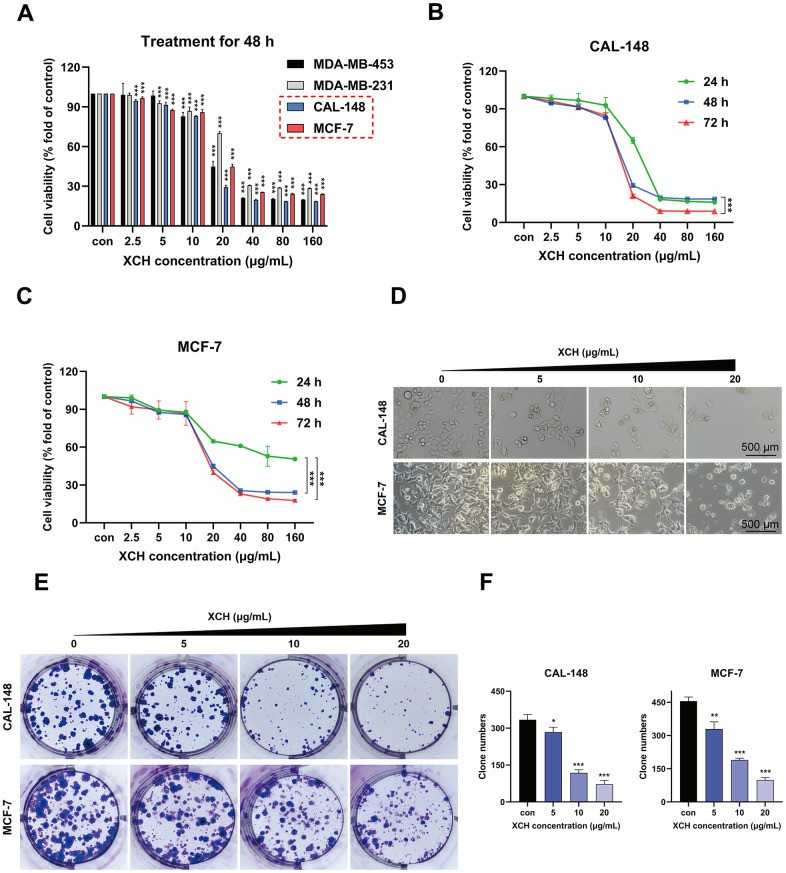 Fig. 1. Xiaochaihu decoction restrains breast cancer cell proliferation in vitro (Liu, Qinglong, et al. 2024).
Fig. 1. Xiaochaihu decoction restrains breast cancer cell proliferation in vitro (Liu, Qinglong, et al. 2024).
Synergistic Effect of Chidamide Combined with Enzalutamide In Vitro
In this study, we chose chidamide, a selective histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitor targeting HDAC 1/2/3/10 subtypes. As a candidate drug compatible with the anti-androgen receptor (AR) agent enzalutamide, for the treatment of luminal androgen receptor (LAR) subtype of triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC). It is worth noting that chemotherapy is the main strategy for TNBC, and LAR TNBCs are characterized by a high frequency of PI3K mutations. Therefore, we selected the PI3Ki alpelisib and paclitaxel as controls.
We conducted growth inhibition assays to investigate the drug sensitivity of MDA-MB-453 and CAL-148 cell lines, both categorized as the LAR subtype. Our findings indicate that MDA-MB-453 cells were significantly inhibited by chidamide and showed overall sensitivity to all tested drugs (Fig. 2A). CAL-148 cells exhibited increased sensitivity to chidamide, paclitaxel, and alpelisib but demonstrated resistance to enzalutamide (Fig. 2B). This study confirmed that the combination of HDAC inhibitors and AR antagonists possessed greater therapeutic efficacy than monotherapy in LAR TNBC.
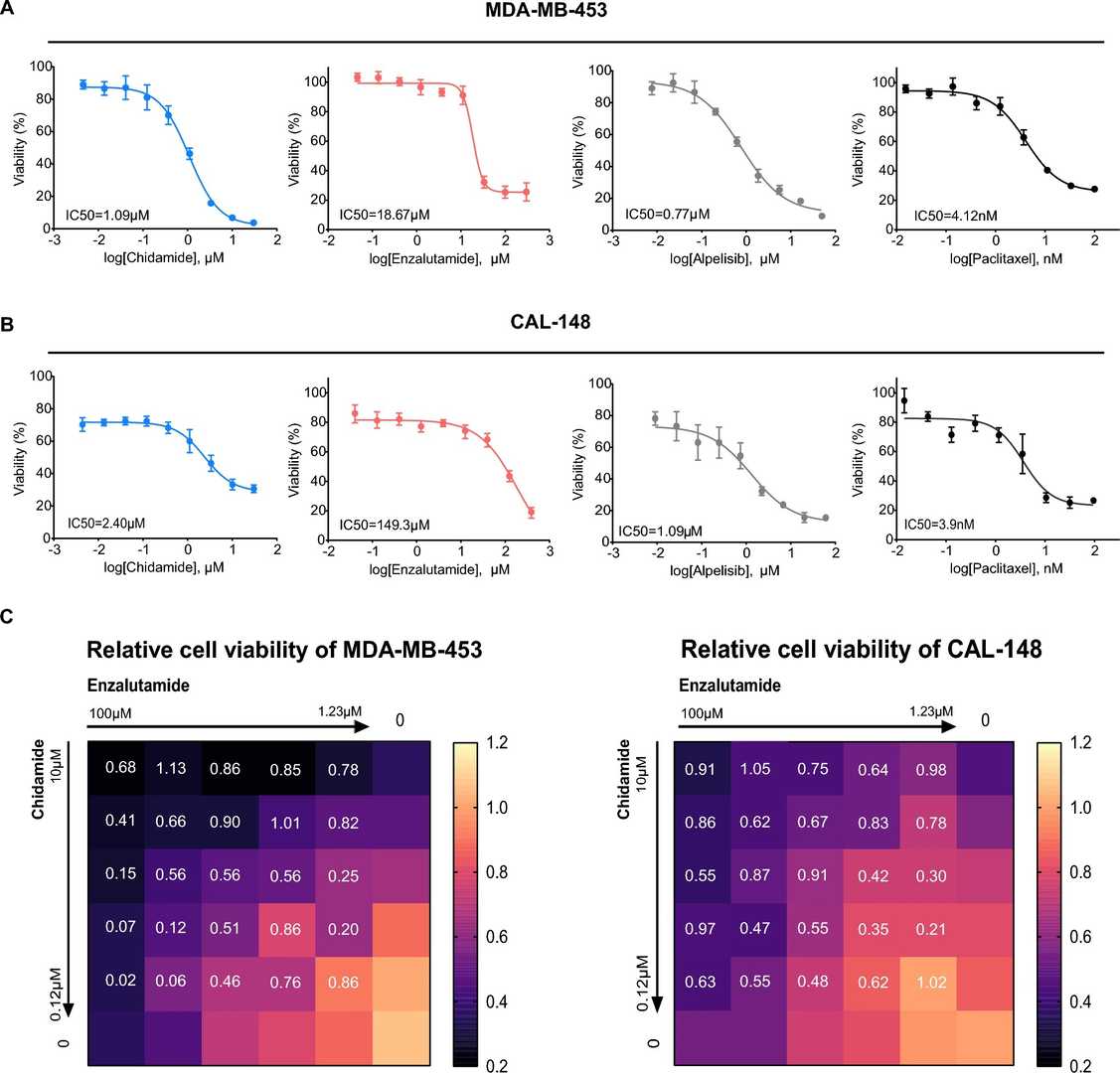 Fig. 2. Cell viability of MDA-MB-453 and CAL-148 cell lines treated with chidamide or enzalutamide (Zhao, Ya-Xin, et al. 2024).
Fig. 2. Cell viability of MDA-MB-453 and CAL-148 cell lines treated with chidamide or enzalutamide (Zhao, Ya-Xin, et al. 2024).
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- You May Also Need
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells