AMO-1
Cat.No.: CSC-C0546
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
Source: Ascites
Morphology: round cells growing singly in suspension
Culture Properties: suspension
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
- Documents
Immunology: CD3 -, CD10 -, CD19 -, CD20 -, CD34 -, CD37 -, CD38 +, cyCD79a+, CD80 -, CD138 +, HLA-DR +, sm/cyIgG -, sm/c
AMO-1 cells are a cell line that was established in 1984 from the ascitic fluid of a 64-year-old woman with plasmacytoma of the duodenum. Plasmacytoma is a type of cancer that arises from plasma cells, which are a specialized type of white blood cell involved in antibody production. Plasmacytoma is closely related to multiple myeloma, a malignancy characterized by the abnormal proliferation of plasma cells in the bone marrow.
AMO-1 cells are characterized by the presence of IgAkappa, which refers to the immunoglobulin subtype (IgA) and light chain type (kappa) produced by the cancer cells. Immunoglobulins, also known as antibodies, play a crucial role in the immune system by recognizing and neutralizing foreign substances. The production of IgAkappa by AMO-1 cells suggests that they are derived from plasma cells that produce this particular immunoglobulin.
AMO-1 cells are an important tool in cancer research, especially in the study of plasma cell disorders like plasmacytoma and multiple myeloma. This cell line has been utilized to investigate the biology, molecular mechanisms, and drug responses associated with these malignancies. Additionally, AMO-1 cells have been instrumental in the development of potential therapeutic approaches targeted toward treating plasma cell-related cancers.
Activation of NEAT1 Leading to Survival Advantage of Multiple Myeloma Cells
Long non-coding RNA NEAT1 is the core structural component of the nuclear paraspeckle (PS) organelles and it is deregulated in multiple myeloma (MM) patients. NEAT1 silencing negatively impacts the proliferation and viability of MM cells both in vitro and in vivo.
To elucidate the biological and molecular relevance of NEAT1 upregulation in MM disease, the CRISPR/Cas9 synergistic activation mediator genome editing system was exploited to engineer the AMO-1 MM cell line. The AMO-1 cell line was engineered to stably express the components of the CRISPR activation system (dCas9/ MS2-p65-HSF1. Then, AMO-1 cells were individually transduced with three sgRNA targeting the NEAT1 promoter or a scramble sgRNA. qRT-PCR of selected cells demonstrated that two of three NEAT1 targeting sgRNA induced significant NEAT1 transactivation (AMO-1N#5 and AMO-1N#8 cells) compared to the scramble condition (AMO-1SCR cells) (Fig. 1).
From a biological point of view, upon FBS starvation NEAT1-activated cells showed significantly higher viability as compared to AMO-1SCR cells (Fig. 2A). This finding is supported also by a cell cycle analysis that showed a higher percentage of cells distributed in sub-G0/G1 phase (Fig. 2B). Additionally, the presence of a significantly higher percentage of apoptotic cells (Fig. 2C) in AMO-1SCR cells suggests also an anti-apoptotic role of NEAT1. Moreover, NEAT1 transactivation significantly increased the clonogenic potential of MM cells cultured in the same conditions (Fig. 2D).
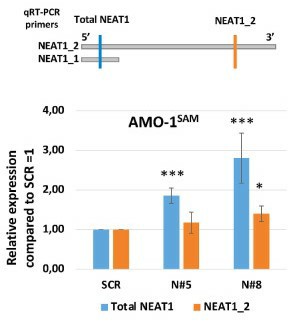 Fig. 1 Analyses of total NEAT1 and NEAT1_2 expression levels in NEAT1-transactivated AMO cell lines. (Taiana E, et al., 2023)
Fig. 1 Analyses of total NEAT1 and NEAT1_2 expression levels in NEAT1-transactivated AMO cell lines. (Taiana E, et al., 2023)
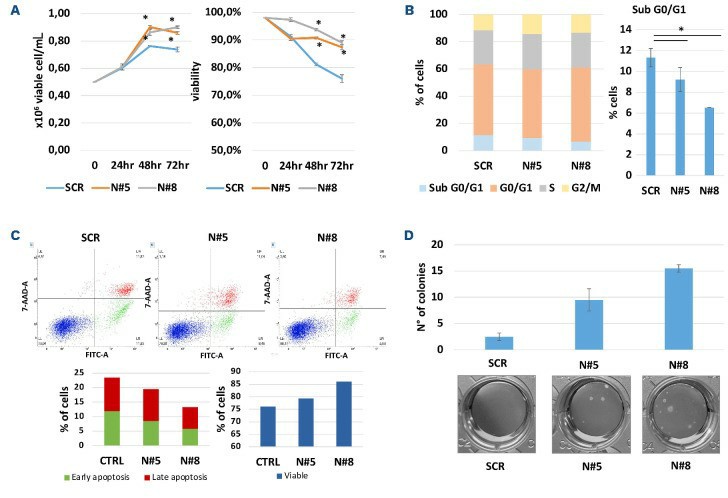 Fig. 2 NEAT1 transactivation improves multiple AMO cell survival and oncogenic potential in non-physiological culturing conditions. (Taiana E, et al., 2023)
Fig. 2 NEAT1 transactivation improves multiple AMO cell survival and oncogenic potential in non-physiological culturing conditions. (Taiana E, et al., 2023)
Knockdown of LAMP5 Promoting Apoptosis in MM Cells
Multiple myeloma (MM) is the second most common tumor of the hematologic system. Lysosome-associated membrane protein (LAMP) affects various cellular processes, including phagocytosis, autophagy, lipid transport, and senescence, and is involved in cancer. LAMP5 is a member of the LAMP family. The study silenced LAMP5 expression in RPMI-8226 and AMO-1 cell lines and explored the effects of LAMP5 silencing on MM cell apoptosis.
LAMP5 expression was highest in RPMI-8226 and AMO-1, followed by H929, and lowest in U266 (Fig. 3A). PMI-8226 and AMO-1 for the follow-up experiments. Four different siRNA sequences were used for cell transfection and found that si3 and si4 were the most efficient in reducing LAMP5 expression, so these two sequences were selected for the next experiments (Fig. 3B, C).
In AMO-1, the apoptosis rates were 33.05% ± 3.74%, 43.34% ± 4.27% and 44.52% ± 1.47% for siNC, si3 and si4, respectively (Fig. 4A). knockdown of LAMP5 increased the expression of the pro-apoptotic protein bax, downregulated the expression of the anti-apoptotic protein bcl-2, and upregulated the expression of cleaved caspase3 (Fig. 4B). Therefore, the study concluded that knockdown of LAMP5 gene could lead to apoptosis in MM cells.
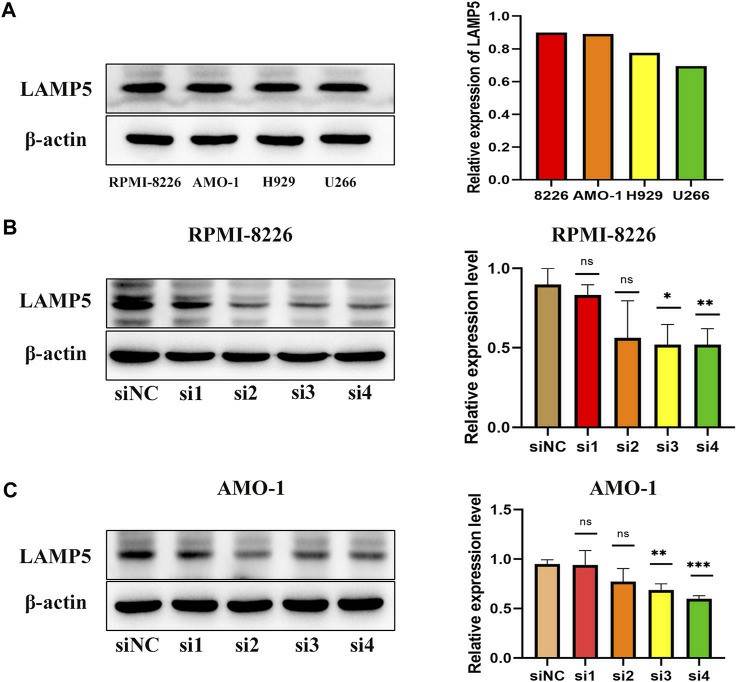 Fig. 3 Expression of LAMP5 in MM cell lines (RPMI-8226, AMO-1, H929, and U266) and screening of siRNA for knockdown of LAMP5. (Chen Y and Ma T, 2023)
Fig. 3 Expression of LAMP5 in MM cell lines (RPMI-8226, AMO-1, H929, and U266) and screening of siRNA for knockdown of LAMP5. (Chen Y and Ma T, 2023)
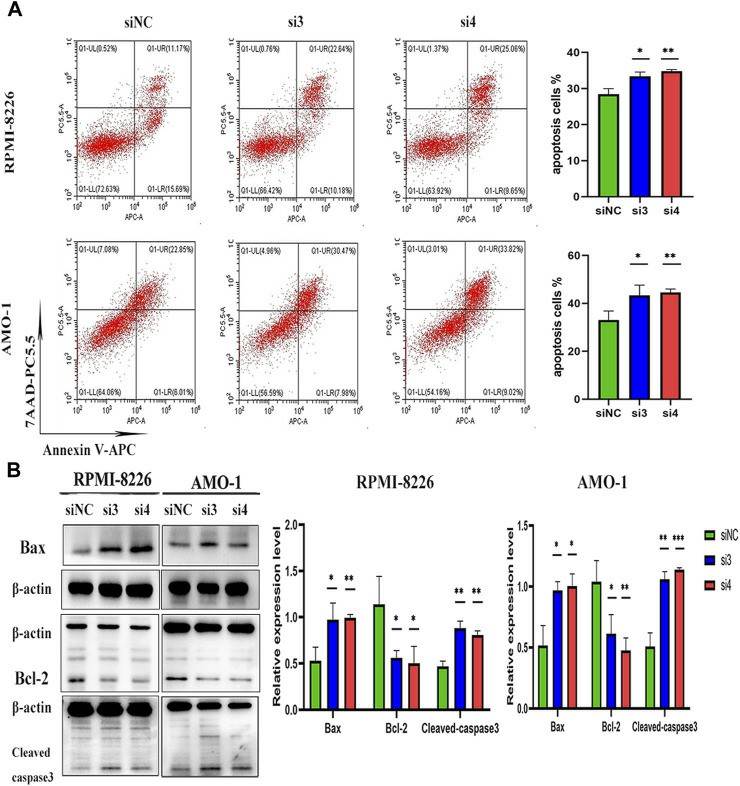 Fig. 4 Knockdown of LAMP5 in MM cell lines (RPMI-8226, AMO-1) promotes apoptosis. (Chen Y and Ma T, 2023)
Fig. 4 Knockdown of LAMP5 in MM cell lines (RPMI-8226, AMO-1) promotes apoptosis. (Chen Y and Ma T, 2023)
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- You May Also Need
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells