HKBML
Cat.No.: CSC-C6448J
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
Source: Brain
Morphology: lymphocyte-like
Culture Properties: Suspension cells
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
Store in liquid nitrogen.
HKBML cell line derives from Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma (PCNSL). PCNSL is a rare brain tumor that emerges in the central nervous system and impacts both brain tissue and structures like the meninges and optic nerves. HKBML cells exhibit typical lymphoma cell morphology, grow rapidly, and maintain high proliferative activity under culture conditions. The HKBML cell line expresses several markers that are characteristic of B cells including CD19 and CD20. Scientific studies reveal that HKBML cells initiate multiple cellular signaling pathways. MCP-1 stimulation activates the MAPK signaling pathway that leads to cellular proliferation.
The HKBML cell line functions as a primary central lymphoma model which facilitates research into lymphoma development and evaluation of potential therapies. The HKBML cells exhibit high resistance levels to methotrexate (MTX). The IC50 value of MTX for HKBML cells measures at 71.1 nM which surpasses resistance thresholds seen in most lymphoma cell lines.
Differential Expression of the Gene Signature Candidates in MTX-resistant PCNSL Cells
Primary central nervous system lymphoma (PCNSL) is a highly aggressive brain lymphoma with poor prognosis. Dysregulation of cell morphology and microenvironment interactions promotes cancer progression. Takashima et al.used next-generation sequencing (NGS) on 31 PCNSL samples to identify gene signatures related to cytoskeleton, adhesion, ECM, and MMP.
The MTX-resistant PCNSL cell lines, TK-MTX and HKBML-MTX, derived from TK and HKBML, were analyzed for 204 study-focused genes. Differential expression genes (DEGs) were identified with |log2(fold change)| > 1 and categorized into four patterns. Thirteen genes had similar expressions in both cell lines (Fig. 1a), while nine showed opposite expressions (Fig. 1b). TK-MTX and HKBML-MTX had cell-type specific DEGs with 26 and 57 differences, respectively (Fig. 1c and d), suggesting implications for personalized medicine in PCNSL. Comparing DEGs with survival analyses, COL11A2's high expression indicated poor prognoses in both (Fig. 1a). ITGB7's high and ITGA2's low expression correlated with poor and good prognoses in TK-MTX (Fig. 1c), while ADAM28, MMP11, and KRT17's high expression showed poor outcomes in HKBML-MTX (Fig. 1d). COL8A2 and CDH18's expressions could serve as diagnostic markers but not as MTX resistance factors.
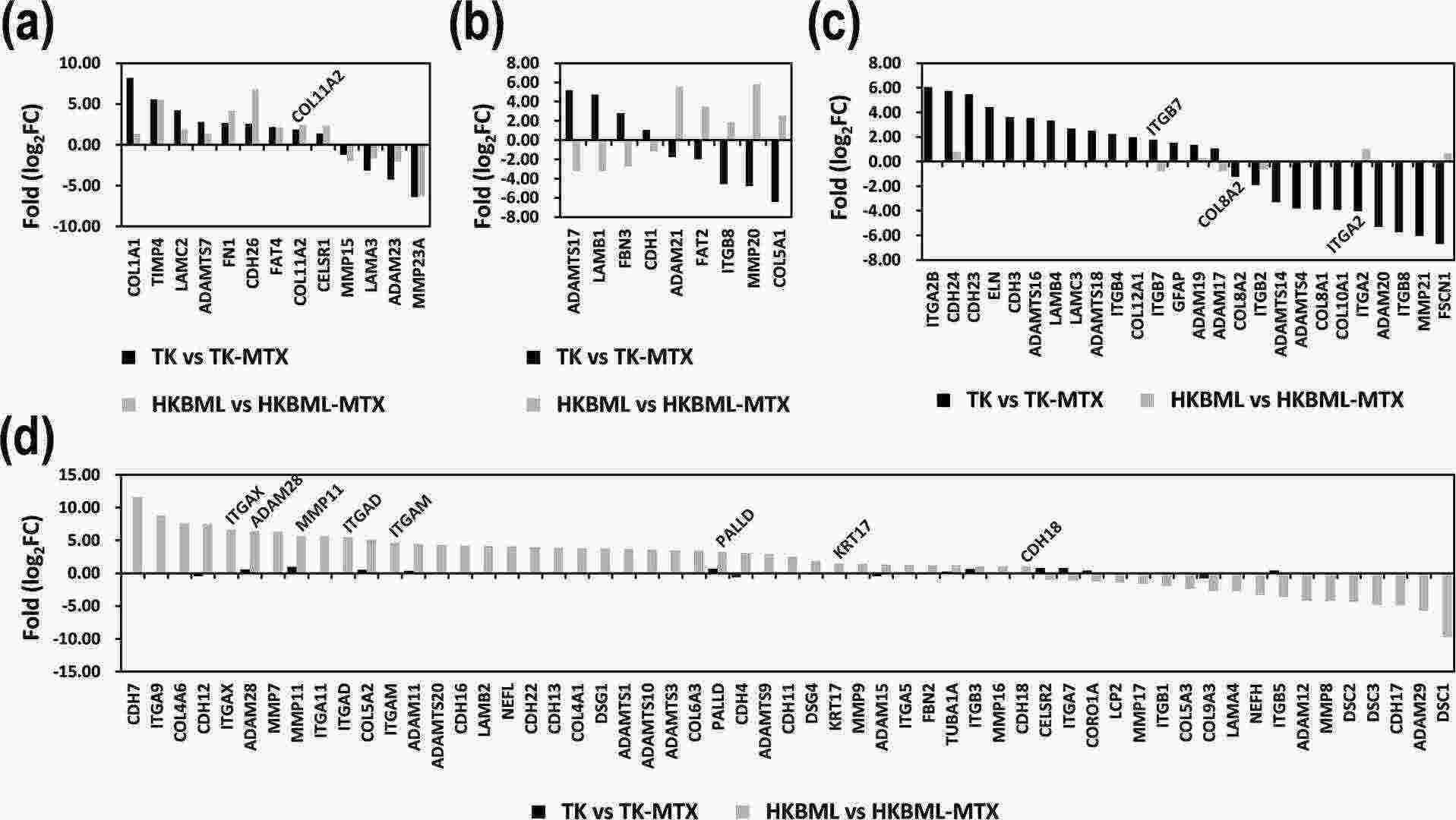 Fig. 1. Expressing patterns of the genes associated with cell morphology and microenvironment in MTT-resistant PCNSL cells (Takashima Y, Kawaguchi A, et al., 2021).
Fig. 1. Expressing patterns of the genes associated with cell morphology and microenvironment in MTT-resistant PCNSL cells (Takashima Y, Kawaguchi A, et al., 2021).
GSEA in MTX-resistant PCNSL Cells and Clinical Samples
Primary central nervous system lymphoma (PCNSL) is a rare and aggressive non-Hodgkin's B-cell lymphoma with a median overall survival of about four years. Standard treatments include high-dose methotrexate (MTX)-based chemotherapy and deferred whole brain radiotherapy, but MTX resistance is common.
Takashima et al. used next-generation sequencing (NGS) and gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) on PCNSL cell lines HKBML and TK and their MTX-resistant cells (HKBML-MTX and TK-MTX), and PCNSL tumor tissues to identify differentially expressed genes and signaling pathways associated with MTX resistance. In HKBML-MTX and TK-MTX cells, 200 upregulated genes were enriched in PCNSL with poor prognoses, with top ESs of 0.479 and 0.534, respectively (Fig. 2a and b). Similarly, 200 downregulated genes were enriched in PCNSL with poor prognoses, with top ESs of 0.324 and 0.260, respectively (Fig. 2c and d). These findings suggest that upregulated genes in HKBML-MTX and TK-MTX are strongly associated with poor prognosis in PCNSL, while some downregulated genes are inversely correlated with good prognosis, indicating malignancy.
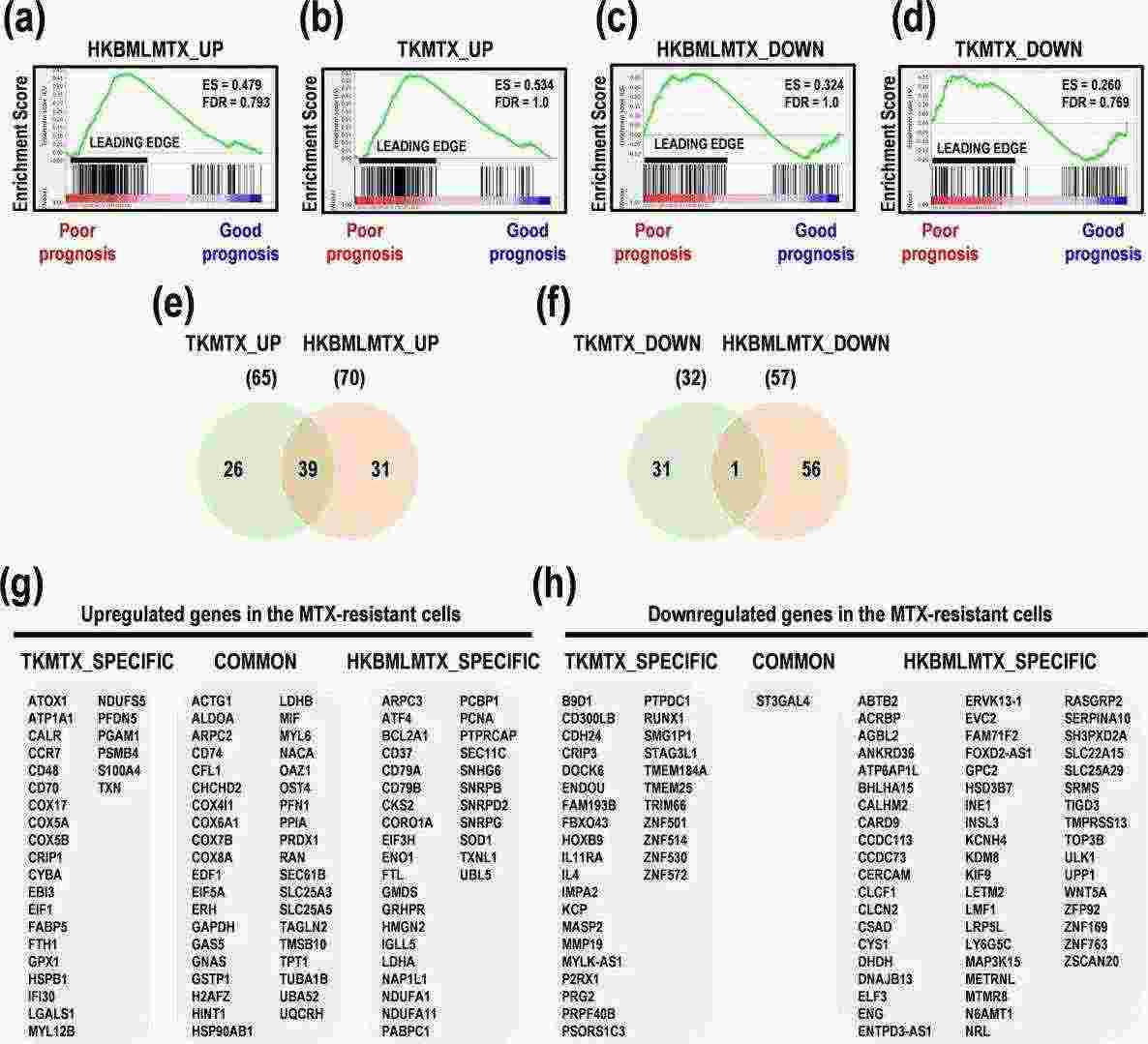 Fig. 2. Gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) in MTX-resistant PCNSL cells (Takashima Y, Hamano M, et al., 2020).
Fig. 2. Gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) in MTX-resistant PCNSL cells (Takashima Y, Hamano M, et al., 2020).
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- You May Also Need
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells