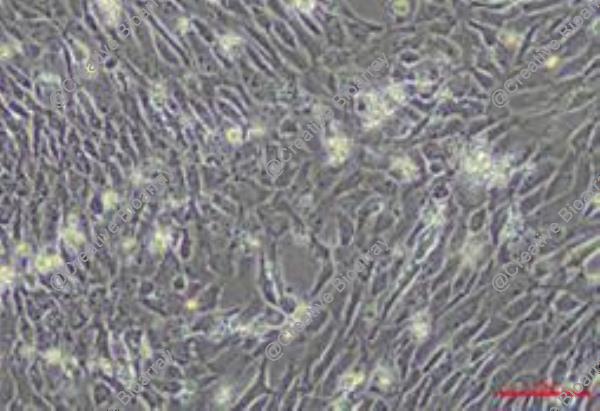
Immortalized Mouse Hepatic Stellate Cells-SV40T
Cat.No.: CSC-I9351L
Species: Mouse
Source: Liver
Morphology: Polygonal
Culture Properties: Adherent
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
2) NF-κB Activation Assay;
3) Cytokine ELISA Assays;
4) 3[H]-thymidine Cell Proliferation Assay.
Note: Never can cells be kept at -20°C.
Immortalized Mouse Hepatic Stellate Cells (HSCs) transformed with the Simian Virus 40 Large T anti gen (SV40T) constitute a fundamental in vitro model system for dissecting the pathogenesis of liver fibrosis and cirrhosis. In their physiological state, quiescent HSCs are vitamin A-storing pericytes residing in the space of Disse. Upon liver injury from diverse etiologies (e.g., viral hepatitis, metabolic dysfunction, toxins), they undergo a classic activation process, transdifferentiating into proliferative, contractile, and highly fibrogenic myofibroblasts. This activation is the central driver of pathological extracellular matrix (ECM) deposition. Primary HSCs are challenging to isolate, have a limited culture lifespan, and spontaneously activate in vitro, confounding studies. The SV40T immortalization strategy stabilizes a proliferative yet phenotypically malleable state, allowing researchers to control and study the activation program experimentally. The principal advantages of the Immortalized Mouse HSC-SV40T line are its robustness, reproducibility, and genetic tractability, making it an indispensable tool for mechanistic discovery.
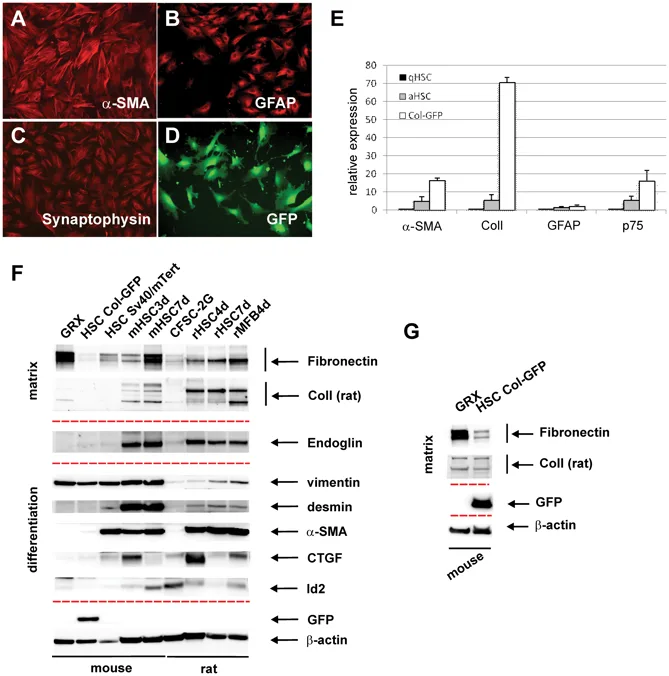
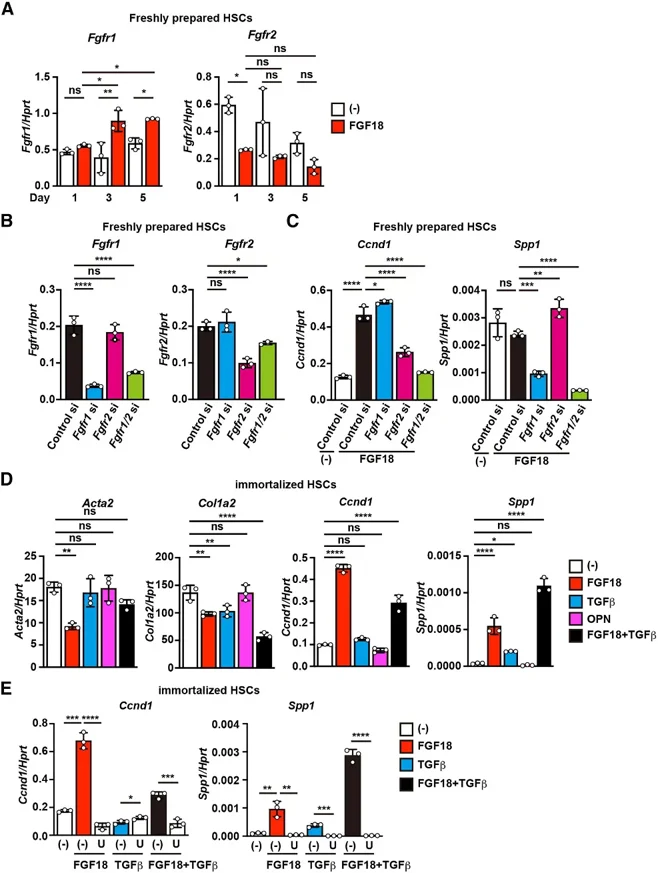
FGF18 Stimulates Osteopontin (OPN) Production in Culture-Activated αSMA+ HSCs to Promote Liver Fibrosis
Hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) play a central role in the development of liver fibrosis. We previously showed that fibroblast growth factor 18 (FGF18) promotes liver fibrosis by increasing HSC proliferation. However, the underlying mechanisms remain incompletely understood.
In this study, we identified osteopontin (OPN) as a novel downstream effector of FGF18 in promoting liver fibrosis. FGF18 specifically induced osteopontin (Spp1/OPN) expression in culture-activated αSMA+ HSCs, but not in freshly isolated quiescent HSCs. OPN secreted by culture-activated αSMA+ HSCs selectively stimulated quiescent HSCs, leading to the upregulation of profibrotic genes. Furthermore, we showed that FGF18 and TGFβ synergistically increased Spp1/OPN expression in culture-activated αSMA+ HSCs. Together, the results suggest that FGF18 drives a feed-forward loop between quiescent and activated HSCs/myofibroblasts via OPN signaling, thereby accelerating liver fibrosis progression.
We supply an optimal culture protocol, including recommended media composition, supplements, and environmental conditions required to sustain healthy growth and maintain stellate cell characteristics.
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells