Immortalized Mouse Dendritic Cells (MutuDC1940)
Cat.No.: CSC-I9098L
Species: Mus musculus
Source: Spleen
Morphology: Small Aggregates
Culture Properties: Adherent
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
Note: Never can cells be kept at -20 °C.
CIK-HT003 HT® Lenti-SV40T Immortalization Kit
2) proteome profile and surface markers assessed by RT-PCR; RT-PCR;
3) IL-12 cytokine secretion analyzed using ELISA;
4) Response to PAMP stimulation evaluated by functional assays.
MutuDC1940 is an immortalized mouse dendritic cell line derived from CD8α+ conventional dendritic cell tumors in the spleen of C57BL/6J mice. Cells isolated from CD11c-SV40LgT transgenic mice display spontaneous in vitro immortalization which allows them to proliferate without needing extra growth factors or maturation inducers. The MutuDC1940 cells display similar phenotypic characteristics and functional properties to CD8α+ conventional dendritic cells present in healthy mouse spleens. These cells display surface markers including Clec9A, DEC205, and CD24 and show positive responses to TLR3 and TLR9 activation. The secretion of cytokines and chemokines such as IL-12, IFN-γ, and CCL19 by MutuDC1940 cells shows their mature dendritic cell functionality. They efficiently uptake and process exogenous antigens for presentation to T cells. Studies indicate that in the presence of F-actin and myosin II, MutuDC1940 cells are more effective at cross-presentation. Under IFN-β stimulation, they upregulate the expression of MARCH1 and MARCH8, crucial molecules in antiviral immunity. MutuDC1940 cells can also effectively activate CD8+ and CD4+ T cells, exhibiting strong stimulatory capacity in mixed lymphocyte reactions (MLR).
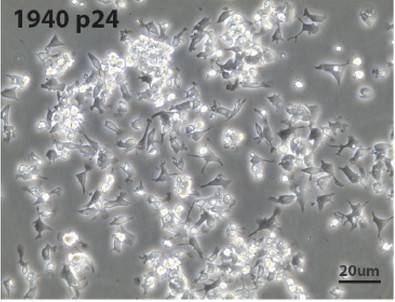 Fig. 1. Morphology of MutuDC1940 line cultures (Marraco SAF, Grosjean F, et al., 2012).
Fig. 1. Morphology of MutuDC1940 line cultures (Marraco SAF, Grosjean F, et al., 2012).
In Vitro Uptake of Nanobody-Functionalized Carriers in Dendritic Cells
Targeting dendritic cells is critical for developing effective tumor nanovaccines. The use of antibodies for targeting requires intricate modifications which consume significant time and money to ensure site-specific attachment. Jung et al. focuses on enhancing the targeting system through nanobody applications rather than using antibodies. The technique employs thiol-maleimide conjugation to attach nanobodies to nanocarriers which results in functionalization time decreasing from days to hours.
To find the optimal nanobody amount per nanocarrier, nanocarriers with increasing nanobody amounts were tested in vitro for uptake by dendritic cells (DCs) (Fig. 2). In MutuDC1940 cells, a type of DC, uptake saturated with higher nanobody amounts (Fig. 2A). At 1000 nanobodies per carrier and above, all cells took up the nanocarriers. Additional experiments used a non-binding reference nanobody and a sample with nanobodies absorbed (not covalently linked) to the carrier (Fig. 2B). Neither control showed significant uptake compared to unmodified nanocarriers. This suggests that targeting is specific to the CD11c receptor and confirms covalent attachment of nanobodies.
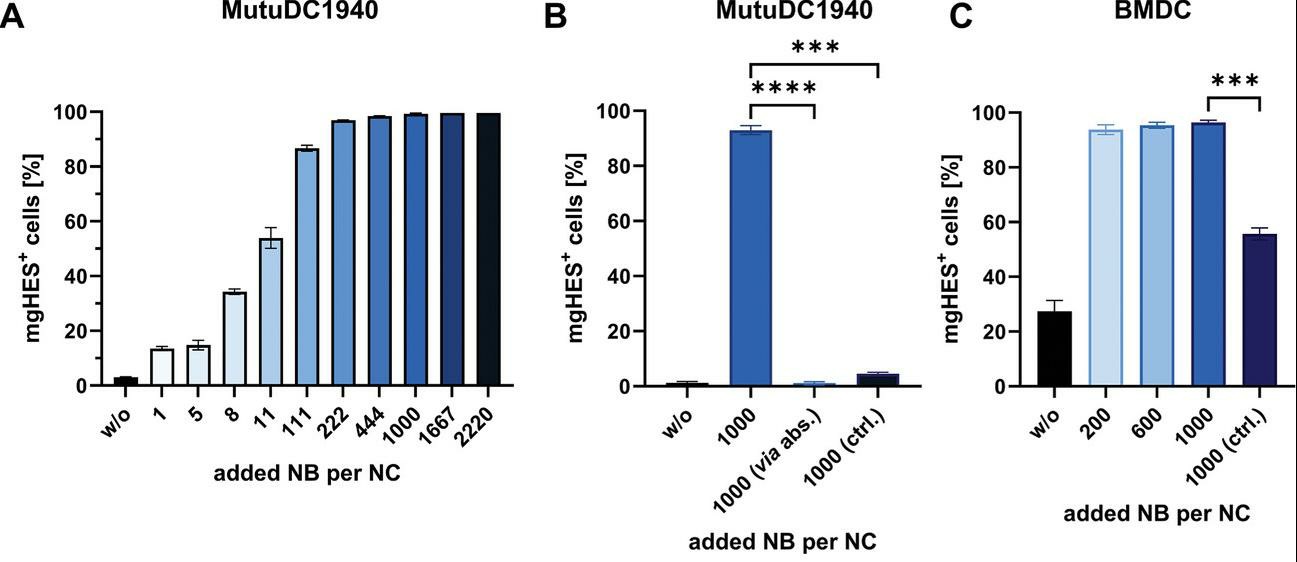 Fig. 2. Determination of the optimal NB amount via in vitro studies with DCs (Jung C, Fichter M, et al., 2024).
Fig. 2. Determination of the optimal NB amount via in vitro studies with DCs (Jung C, Fichter M, et al., 2024).
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells