DLD-1
Cat.No.: CSC-C9371L
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
Source: Intestine; Colon
Morphology: Epithelial
Culture Properties: monolayer
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
CSF1PO: 11,12
D13S317: 8,11
D16S539: 12,13
D5S818: 13
D7S820: 10,12
THO1: 7,9.3
TPOX: 8,11
vWA: 18,19
DLD-1 is a human colorectal adenocarcinoma cell line established from a male patient with Dukes' C stage colon cancer. It was originally developed from epithelial tumor tissue from the colon. It demonstrates an adherent growth pattern and exhibits the polygonal, epithelial-like morphology typical of colon adenocarcinoma. DLD-1 is a genetically stable, well-characterized, and easy-to-culture cell line, frequently used as a general representative model for the in vitro study of colorectal cancer.
DLD-1 is notable for its well-characterized molecular profile, which includes KRAS G13D mutation, APC and PIK3CA mutations, and alterations in several major tumor-associated signaling pathways. This unique genomic signature makes DLD-1 an important model system to study oncogenic RAS and Wnt/β-catenin signaling, as well as drug resistance mechanisms and responses to targeted therapies.
DLD-1 functions as an in vitro model for various cancer cell processes including cell proliferation and metabolic reprogramming as well as apoptosis, autophagy, epithelial-mesenchymal transition and invasion mechanisms. The defined KRAS mutation status of this cell line also makes it a useful model to study resistance to anti-EGFR therapies, such as cetuximab and panitumumab.
The Effect of the Cardaria draba Subspecies Shalepensis Exerts on the Cell Viability of the Human Colon Cancer Cell Line (DLD-1)
Metabolic dysregulation and aberrant melanogenesis lead to hyperglycaemia and hyperpigmentation, respectively. Conventional treatments are often suboptimal. Ortaakarsu et al. investigated the inhibitory effects of Cardaria draba extract on α-glucosidase and tyrosinase-related protein 1, and its antiproliferative effects on DLD-1 colon cancer cells, to explore its potential as a therapeutic agent.
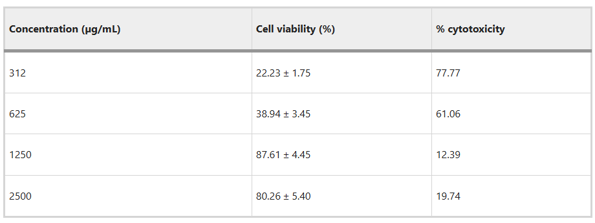
The cytotoxicity effect of the plant extract on Human Colon Cancer Cell Line (DLD-1) was evaluated by MTT method (Fig. 1). The viability values of DLD-1 cells were found to be 22.23% at 312 µg/mL and 38.94% at 625 µg/mL. The viability of cells at 1250 µg/mL was 87.61% and it decreased to 80.26% at 2500 µg/mL. The viability at 1250 and 2500 µg/mL increased, while at 312 and 625 µg/mL it decreased. Thus, the most suitable concentrations for DLD-1 were determined as 312 and 625 µg/mL. The IC50 value of DLD-1 cell line was found to be 767 µg/mL. ANOVA with Bonferroni corrections showed that the extract had significant effect. The change in trend at 2500 µg/mL was explained by the exceeding of threshold concentrations by the compounds of the extract, which causes a disturbance in the mechanisms that form the defense of the cell line.
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- You May Also Need
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells