
CMK
Cat.No.: CSC-C0439
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
Source: Blood; Peripheral Blood
Morphology: single, multiformed, large cells growing in suspension, sometimes loosely adherent
Culture Properties: suspension
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
Immunology: CD3 -, CD13 +, CD14 -, CD15 -, CD19 -, CD33 +, CD34 +, CD41 +, CD71 +, CD235a +
Viruses: ELISA: reverse transcriptase negative; PCR: EBV -, HBV -, HCV -, HHV-
CMK cells are a suspension-cultured human acute megakaryoblastic leukemia (AML-M7) cell line, established in 1984 from the bone marrow sample of a 7-year-old male. The leukemia cells are known to have the t(1;22) chromosomal translocation that forms the RBM15-MKL1 fusion gene. The CMK cell line expresses the megakaryocytic markers CD41 and CD61. CMK cells, which grow in RPMI-1640 medium, have a round or oval morphology, and may exhibit some megakaryocyte-like characteristics. They can also be induced to undergo limited differentiation with TPO.
CMK cells have highly active PI3K/AKT and JAK-STAT signaling, and the cell line is used for leukemogenesis studies and drug screening, including the testing of targeted inhibitors (e.g., LY294002) and differentiation-inducing agents. While the clinical use of CMK has been limited due to lack of heterogeneity, the cell line is a classic tool for studying AML-M7, as well as a platform for developing novel therapies to combat megakaryocytic differentiation defects.
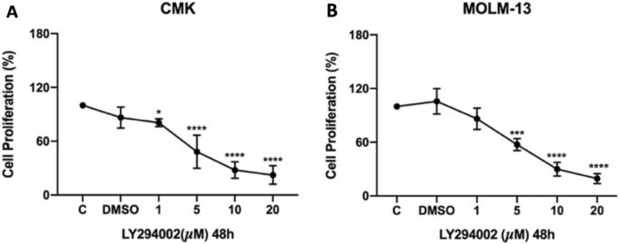
The PI3K Inhibitor, LY294002, Reduces the Cell Viability of CMK and MOLM-13 AML Cell Lines
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML), accounting for 80% of blood cancer cases, has a poor prognosis. Despite existing treatments, the disease's heterogeneity necessitates novel therapies. Şansaçar et al. explored the anticancer effects of PI3K and HDAC inhibition on CMK and MOLM-13 AML cell lines.
LY294002, a specific PI3K inhibitor, blocks AKT phosphorylation by binding to the kinase's ATP site, suppressing the PI3K/AKT pathway crucial for cancer cell proliferation. We treated CMK and MOLM-13 cells with 1–20 µM LY294002 (Fig. 1). Both cell lines showed significant viability reduction at low micromolar doses, with similar sensitivity (IC20: CMK = 1 µM, MOLM-13 = 2.8 µM). Additional HDAC inhibitors (SAHA, Tubastatin A, PCI-34051) were tested (Fig. 1a, b). Our findings suggest LY294002 effectively inhibits leukemia cell proliferation via PI3K/AKT pathway suppression.
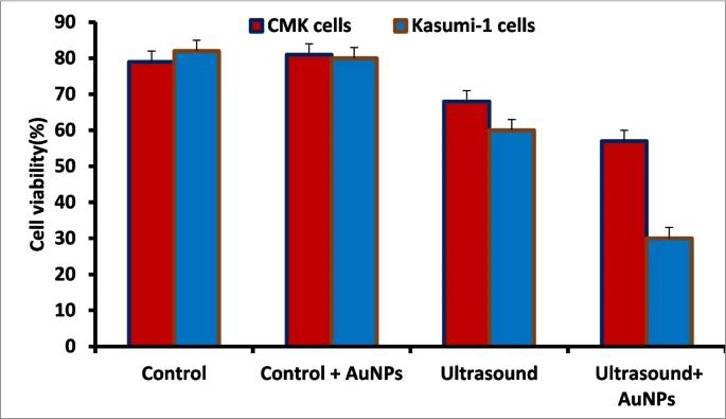
Anticancer Activity of AuNPs and Ultrasound Against Pediatric Acute Leukemia Cell Lines
Pediatric acute leukemia remains a challenging disease with limited therapeutic options. Green-synthesized gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) and ultrasound (US) therapy have emerged as potential anticancer strategies due to their biocompatibility and targeted effects. Guo's team explored the synergistic anticancer effect of Memecylon edule-mediated AuNPs combined with US therapy against pediatric acute leukemia cell lines (Kasumi-1), while minimizing damage to normal cells (CMK).
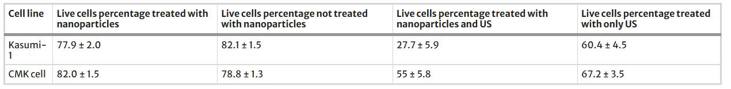
Flow cytometry is being used to investigate AuNPs and US treatment in both Kasumi-1 and CMK cell lines by determining the number of viable cells (Fig. 2). Figure 3 presented the Kasumi-1 and CMK cell median counts from five repeated tests. These outcomes revealed a modest reduction in the ratio from 67.1 ± 3.2 to 55 ± 6.2% of the viable cells after application of the synthesized AuNPs to normal CMK cell lines treated with US. In contrast, the total number of viable Kasumi-1 cancer cells decreased dramatically after combined AuNPs and US treatment, from 60.4 ± 4.5 to 27.7 ± 5.9%. Therefore, these findings suggest that Kasumi-1 cancer cells are more susceptible to US-induced cell damage than CMK cells. The findings, on the other hand, show that combining AuNPs with cell cultures resulted in a significant increase in cancer cell death, thus demonstrating the synergistic effect of AuNPs and US disruption. In addition, normal CMK cells appear to be highly resistant to the synergistic impact. As a result of the study, the current findings provide promise in the destruction of cancer cells, especially when compared to some of the standard approaches for cancer cell destruction.
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- You May Also Need
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells





