ECC4
Cat.No.: CSC-C6440J
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
Source: Rectum
Morphology: epithelial-like
Culture Properties: Adherent cells
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
Store in liquid nitrogen.
In 1994 Ishihara Noriko created the ECC4 cell line from the rectal small cell gastrointestinal cancer of a 45-year-old Japanese male patient. The rectum functions as a digestive system section at the large intestine's outermost part where it stores feces before removal. Small cell gastrointestinal cancer remains rare yet shares pathological characteristics with small cell lung cancer. This cancer displays high aggressiveness and frequently metastasizes early to the liver and bones. Its aggressive behavior results in poor patient outcomes because the median survival period remains short. Histopathological examination and immunohistochemical staining form the basis for diagnosing small cell gastrointestinal cancer. Pro-Gastrin-Releasing Peptide (Pro-GRP) functions as a crucial diagnostic marker for small cell lung cancer and demonstrates high specificity and sensitivity when expressed in small cell gastrointestinal cancer.
The ECC4 cell line represents a crucial model for research into how small cell gastrointestinal cancer of the rectum develops and progresses. The study of ECC4 cells reveals the molecular mechanisms behind rectal cell transformation through gene mutations, chromosomal abnormalities, signal pathway activations, and epigenetic changes involved in tumor development. Understanding small cell gastrointestinal cancer of the rectum pathogenesis could establish a theoretical foundation for creating new diagnostic and therapeutic approaches.
Delta-Like 3 Plays a Pivotal Role in Gastrointestinal Neuroendocrine Malignancy
Delta-like 3 (DLL3) functions as a Notch signaling ligand that possesses unusual structural characteristics while simultaneously inhibiting Notch signaling. DLL3 maintains a recognized function in lung neuroendocrine carcinoma but its role and expression status in the gastrointestinal tract and GI neuroendocrine carcinoma (GI-NEC) have not yet been fully determined. Matsuo et al.investigates these aspects, aiming to elucidate DLL3's role and expression in the GI tract and GI-NEC. To assess DLL3 mRNA levels, RT-qPCR on GI-NEC cell lines ECC4, ECC10, and ECC12 revealed significant upregulation (ECC4: 2000-fold, ECC10: 1800-fold, ECC12: 3000-fold) of DLL3 mRNA compared to other cancer cell lines (Fig. 1A). The Western blot analysis validated the observed trend at the protein level (Fig. 1B). ECC cells displayed DLL3 mRNA levels that matched those found in SCLC cells. Using double fluorescent immunocytochemistry both DLL3 and CHGA showed cytoplasmic localization (Fig. 2A), while electron microscopy displayed DLL3 inside neurosecretory granules (Fig. 2B and C). To investigate DLL3 functions in GI-NEC cells, they silenced DLL3, resulting in significant growth inhibition (Fig. 3A). The elevation of cleaved PARP levels along with caspase 3 and caspase 9 demonstrated an augmentation of apoptosis as shown in Figure 7B. The Hoechst 33342 stain demonstrated an increase in apoptotic cells within ECC cells treated with siR-DLL3 (Fig. 3B). Treatment with the pan-caspase inhibitor Z-VAD-FMK led to restored cell growth and lower levels of cleaved PARP expression as shown in Figure 3D, E. Additionally, DLL3 silencing hindered spheroid formation in ECC4 cells (Fig. 3F and G).
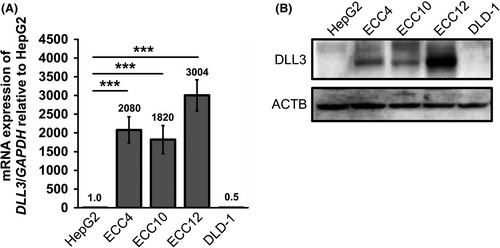 Fig. 1. The expression levels of delta-like 3 (DLL3) in gastrointestinal-neuroendocrine carcinoma ECC cell lines (Matsuo K, Taniguchi K, et al., 2019).
Fig. 1. The expression levels of delta-like 3 (DLL3) in gastrointestinal-neuroendocrine carcinoma ECC cell lines (Matsuo K, Taniguchi K, et al., 2019).
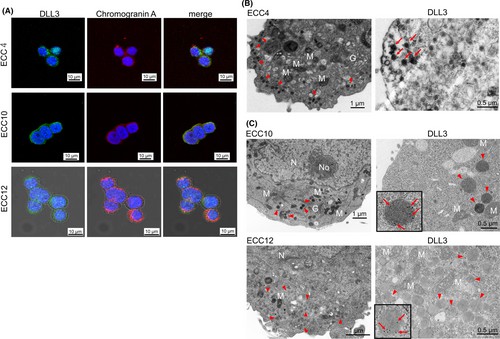 Fig. 2. The morphological features of delta-like 3 (DLL3) expression in GI-NEC ECC cell lines (Matsuo K, Taniguchi K, et al., 2019).
Fig. 2. The morphological features of delta-like 3 (DLL3) expression in GI-NEC ECC cell lines (Matsuo K, Taniguchi K, et al., 2019).
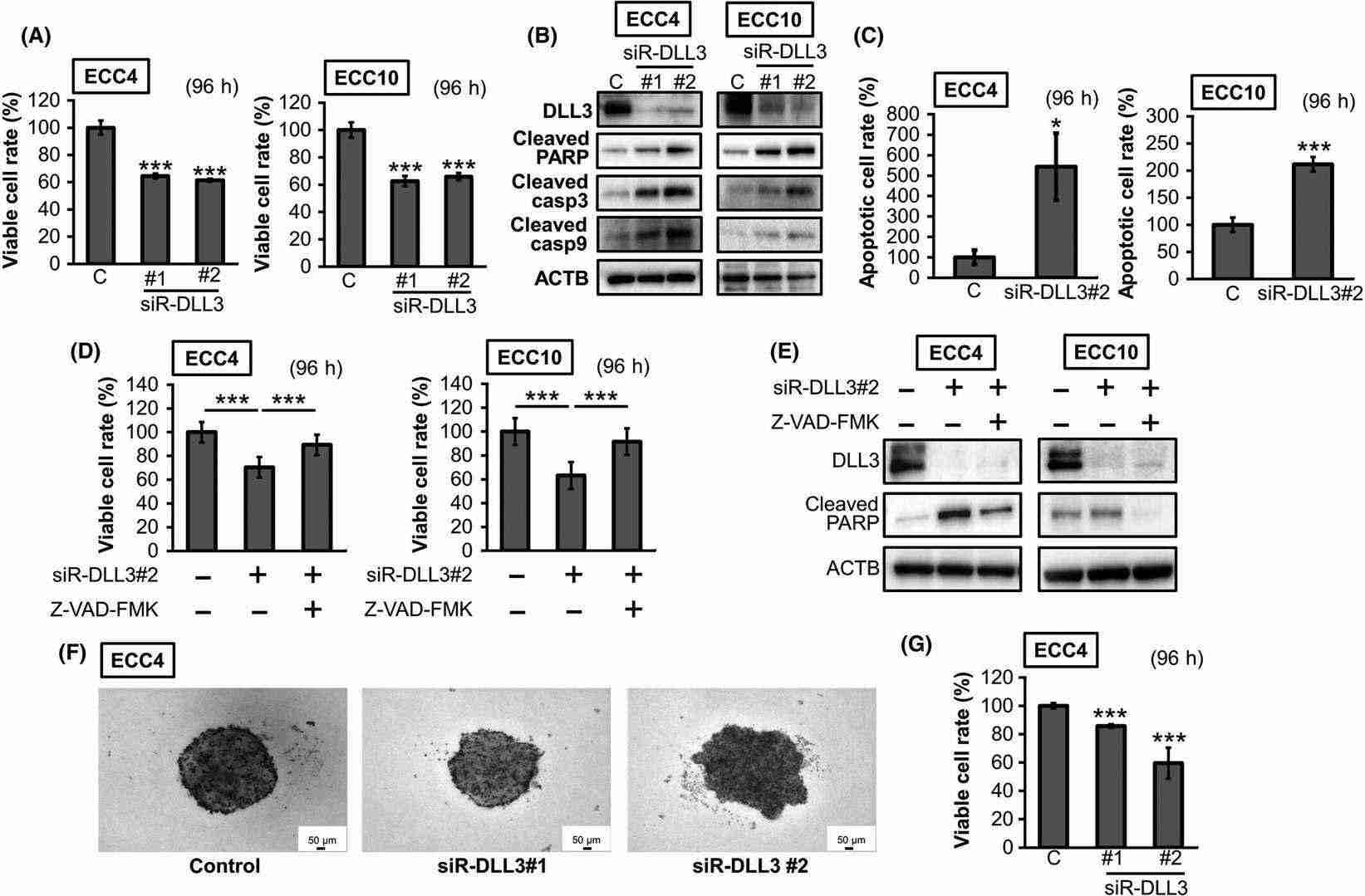 Fig. 3. The effects of gene silencing of delta-like 3 (DLL3) in ECC cell lines (Matsuo K, Taniguchi K, et al., 2019).
Fig. 3. The effects of gene silencing of delta-like 3 (DLL3) in ECC cell lines (Matsuo K, Taniguchi K, et al., 2019).
Shared Expression of Mucin12 in Ascaris lumbricoides and the Human Small Intestine
Accounting for the widespread infection caused by A. lumbricoides, the study highlights its ability to thrive in the human small intestine by potentially sharing antigenic features with host proteins. Using molecular techniques and screening, Hayashi et al. identified DNA clones showing antigenic similarities between A. lumbricoides and human mucin12, suggesting an immune evasion strategy. To confirm proteins cross-reacting with human mucin12, western blotting was conducted. As illustrated in Fig. 4, mucin12 protein appeared in the lysates of human gastrointestinal cells CACO-2 and ECC4, showing bands around 45 kDa and 85 kDa when immunostained with polyclonal anti-mucin12 antibody (Fig. 4b). In contrast, A. lumbricoides crude antigen displayed bands of 37 kDa and 100 kDa using the same antibody (Fig. 4b). Moreover, the main bands, reacting with commercial anti-mucin12 antibody, were approximately 90 kDa in both cell lines (Fig. 4c). In A. lumbricoides crude antigen, a 100 kDa band matched the one detected with polyclonal anti-mucin12 antibody (Fig. 4c). These findings reveal different proteins detected in A. lumbricoides and human gastrointestinal cells with a common anti-mucin12 antibody.
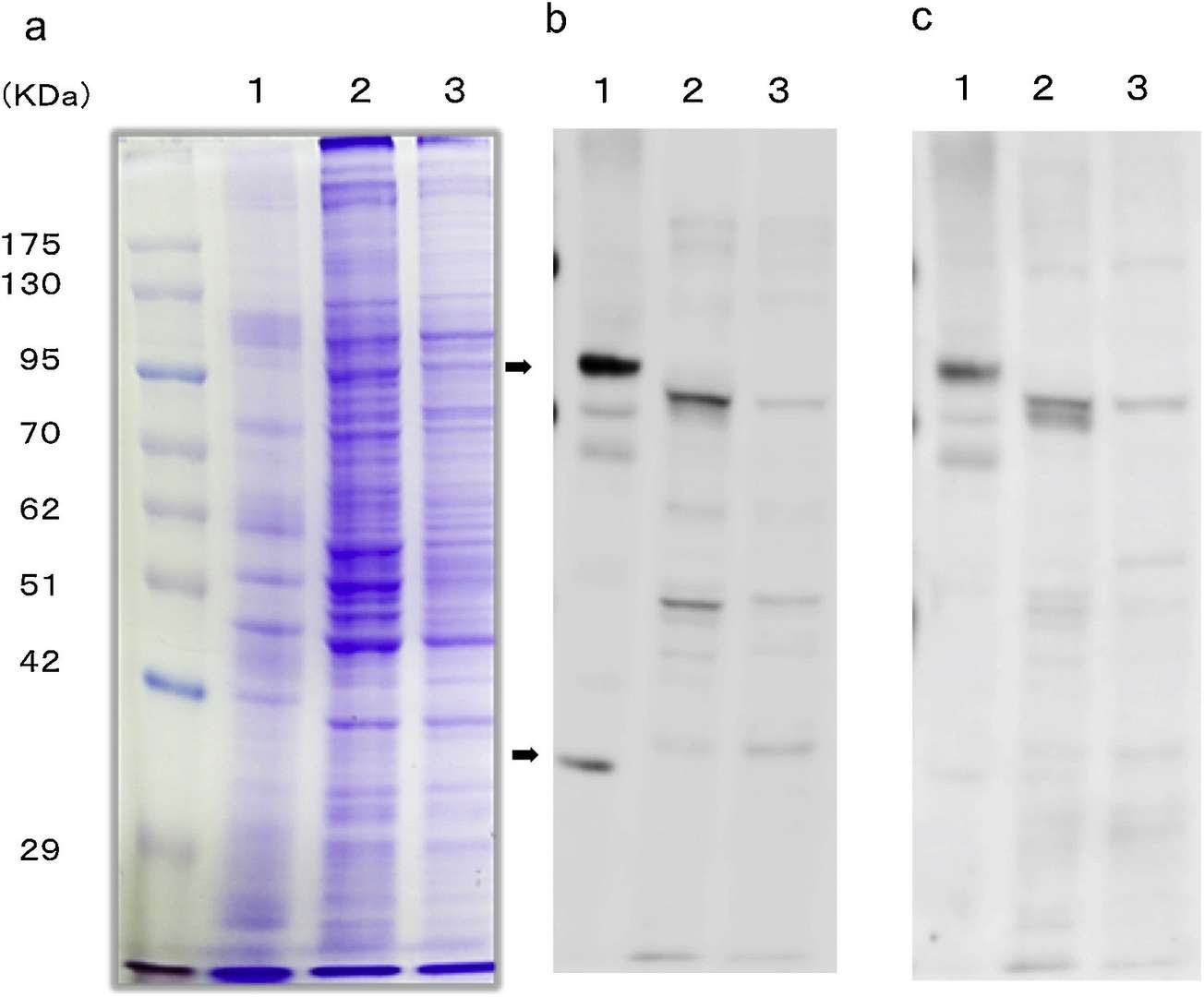 Fig. 4. Western blotting for mucin12 protein in A. lumbricoides crude antigen and human gastrointestinal cells (Hayashi I, Kanda S, et al., 2019).
Fig. 4. Western blotting for mucin12 protein in A. lumbricoides crude antigen and human gastrointestinal cells (Hayashi I, Kanda S, et al., 2019).
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- You May Also Need
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells