KM12L4
Cat.No.: CSC-C9463L
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
Source: Intestine; Colon
Culture Properties: monolayer
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
Shipping Condition: Room Temperature
KM12L4 is a human highly metastatic colon cancer cell line that was isolated from liver metastasis-selected subpopulation of parental KM12 line, which was serially passaged in vivo in nude mice to develop its specific liver tropism. Molecular features such as KRAS G12V driver mutation and TP53 R273H mutation recapitulate the clinical refractory mCRC genetic landscape. KM12L4 cells grow as epithelial-like adherent culture with upregulation of metastasis-associated markers (CXCR4, MMP9), are resistant to 5-FU and partially sensitive to EGFR inhibition. This cell line considered as "gold standard" model to study mechanisms of liver metastasis. It is also useful to study tumor microenvironment crosstalk, circulating tumor cell survival and has translational research potential in targeted therapy evaluation in KRAS-mutant mCRC.
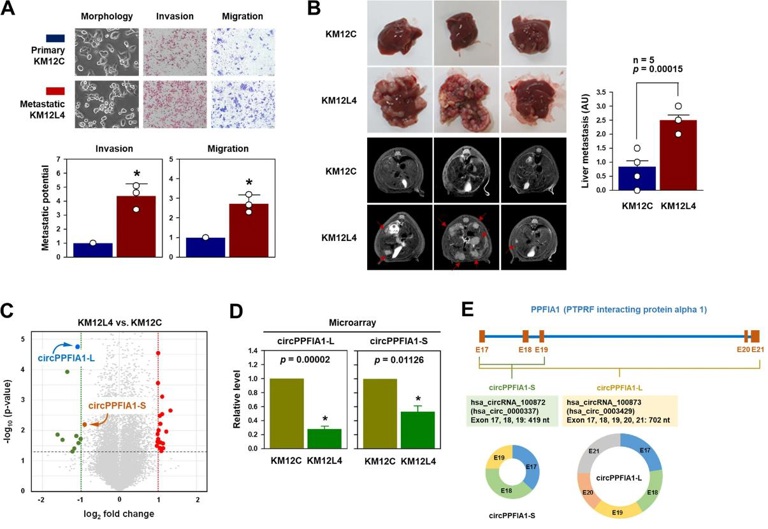
circPPFIA1s were Downregulated in Liver Metastatic Colon Cancer Cells
Circular RNAs (circRNAs) are widely involved in the progression of colorectal cancer (CRC), especially the metastasis process. The specific molecular mechanisms remain unclear. In this study, Ji et al. focused on the role of circRNAs in CRC liver metastasis and sought to reveal their molecular mechanisms.
To screen for metastasis-related circRNAs, they performed circRNA expression profile analysis on KM12C (primary colon cancer) and KM12L4 (liver metastatic) cells. As shown in Fig. 1A, KM12L4 had a higher invasion and migration ability than KM12C by Transwell assay. The liver metastasis in vivo was also evaluated by spleen injection followed by MRI analysis, and more metastases were found in KM12L4-injected mice (Fig. 1B). A circRNA microarray indicated 29 differentially expressed circRNAs between KM12C and KM12L4 cells, with 9 downregulated and 20 upregulated circRNAs in KM12L4 (Fig. 1C, D). One of the significantly downregulated circRNAs, hsa_circRNA_100873 (hsa_circ_0003429), is an exonic circRNA spanning PPFIA1 exons 17–21 (Fig. 1E). They also found another PPFIA1-derived circRNA, hsa_circRNA_100872 (hsa_circ_0000337) (Fig. 1C, D). The circRNAs were named as circPPFIA1-L (702 bp) and circPPFIA1-S (419 bp) according to the exon length, from which they were spliced (Fig. 1E). There are 37 candidate PPFIA1-derived circRNAs in the circBase database, and the functions and mechanisms of most of them have not been defined or characterized.
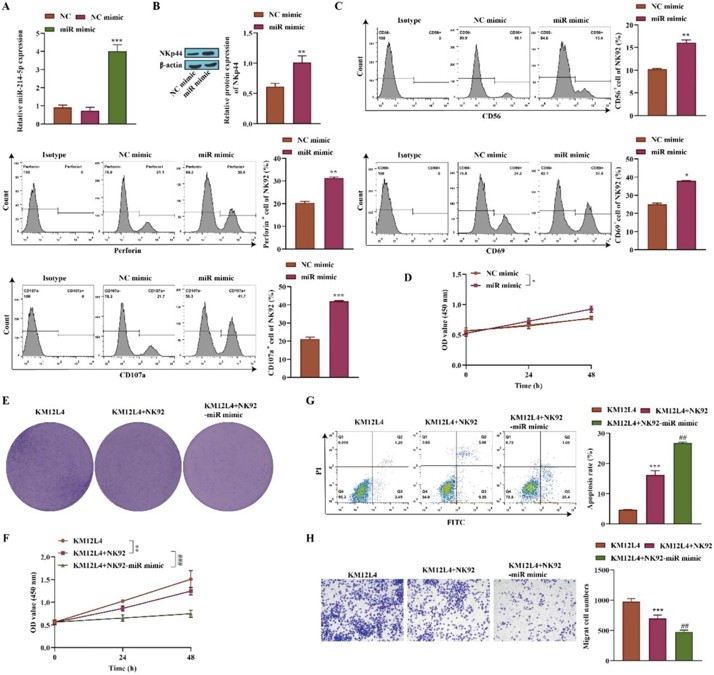
miR-214-5p Restrains CRC Cell Migration by Affecting NK Cell Activity
Colorectal cancer (CRC) often metastasizes to the liver, reducing patient survival. NK cells are key in anti-tumor immunity. He’s team investigated the mechanism of miR-214-5p on NK cells in CRC liver metastasis. Clinical samples and cell lines NK92 and KM12L4 were used.
To determine whether miR-214-5p affects NK cell viability and CRC cells, they measured the level of miR-214-5p in NK92 cells by RT-qPCR. The results showed that miR-214-5p was significantly upregulated after transfection with the miR-214-5p mimic (Fig. 2A). Western blot analysis showed that NKp44, an activation marker, was upregulated after overexpression of miR-214-5p (Fig. 2B). Flow cytometry indicated elevated levels of CD56, Perforin, CD69, and CD107a in NK92 cells transfected with the miR-214-5p mimic (Fig. 2C). CCK-8 assay demonstrated that NK92 cell viability was upregulated after transfection (Fig. 2D). KM12L4 cell proliferation was measured by CCK-8 assay and was found to be inhibited after coculture with NK92 cells and more suppressed after coculture with NK92 cells transfected with the miR-214-5p mimic (Fig. 2E). Cell viability assay of KM12L4 cells was also reduced after coculture with NK92 cells and especially when NK92 cells overexpressed miR-214-5p (Fig. 2F). Flow cytometry revealed increased apoptosis in KM12L4 cells after coculture with NK92 cells, with more pronounced effects when miR-214-5p was overexpressed (Fig. 2G). Transwell assays showed that KM12L4 cell migration was decreased after coculture with NK92 cells and more when NK92 cells were transfected with the miR-214-5p mimic (Fig. 2H). In conclusion, miR-214-5p improves NK cell function and inhibits CRC cell proliferation and migration.
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- You May Also Need
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells