Lu-135
Cat.No.: CSC-C6509J
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
Source: Lung
Morphology: other
Culture Properties: Adherent/Suspension cells
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
Store in liquid nitrogen.
The Lu-135 cell line originates from the lung tissue of a 69-year-old male with small cell lung carcinoma (SCLC). SCLC emerges as a highly aggressive lung cancer which develops from Kulchitsky cells found in the bronchial mucosa or glandular epithelium. This cancer represents 15% of all lung cancer cases and exhibits high malignancy along with rapid doubling time and early metastasis but responds to chemo and radiotherapy before eventually relapsing. In vitro, the Lu-135 cell line grows as suspended cell clusters and exhibits strong migratory and invasive capabilities. Additionally, research indicates that PC-9/ECM substrates cause these cells to develop neuron-like protrusions which is a signature trait of SCLC cells when cultured.
As a model of small cell lung cancer, the Lu-135 cell line is primarily used in research to simulate the growth, proliferation, invasion, and metastasis behavior of SCLC. For example, Lu-135 cells show a strong dependence on the cell cycle protein KIF11 which leads to cell cycle arrest at G2/M phase and reduced cell proliferation upon KIF11 knockdown according to research findings. The BCL2L1 inhibitor WEHI-539 causes high sensitivity in Lu-135 cells while combining it with SB743921 treatment leads to even lower cell viability. The Lu-135 cell line is also utilized in evaluating the efficacy of CAR-T cell therapy, with studies demonstrating that CAR-T cells modified with IL-7 and CCL19 exhibit significant cytotoxic effects against Lu-135 tumors.
Lu-135 Cells Are Highly Sensitive to HSL175-DT3C Conjugates
Few effective treatments are available for small cell lung cancer (SCLC), particularly due to the ineffectiveness of current therapies such as TKIs and immune checkpoint inhibitors. Therefore, the main objective of the study is to explore the potential of antibody–drug conjugates (ADCs) targeting the L1 cell adhesion molecule (L1CAM), which is found to be overexpressed in SCLC cells (Lu-135 and STC-1). Yamaguchi et al. evaluated the efficacy of a newly developed ADC, specifically the HSL175-DT3C conjugate, against SCLC-N cell lines. The results showed that when treated with HSL175-DT3C conjugates, NC siRNA-transfected (control) Lu-135 cells declined in viability in a concentration-dependent manner, whereas L1CAM-silenced cells became significantly less sensitive to the conjugates (Fig. 1A and B). Figure 1B also illustrates that L1CAM knockdown, especially when using siRNA #2, induced Lu-135 cells to form spheroids, as evidenced by the GO enrichment analysis. As presented in Figure 1C, the viability of Lu-135 cells decreased in a time-dependent manner when treated with HSL175-DT3C conjugates. Unlike the control IgG-DT3C conjugates, HSL175-DT3C conjugates effectively prompted Lu-135 cells to undergo apoptosis (Fig. 1D).
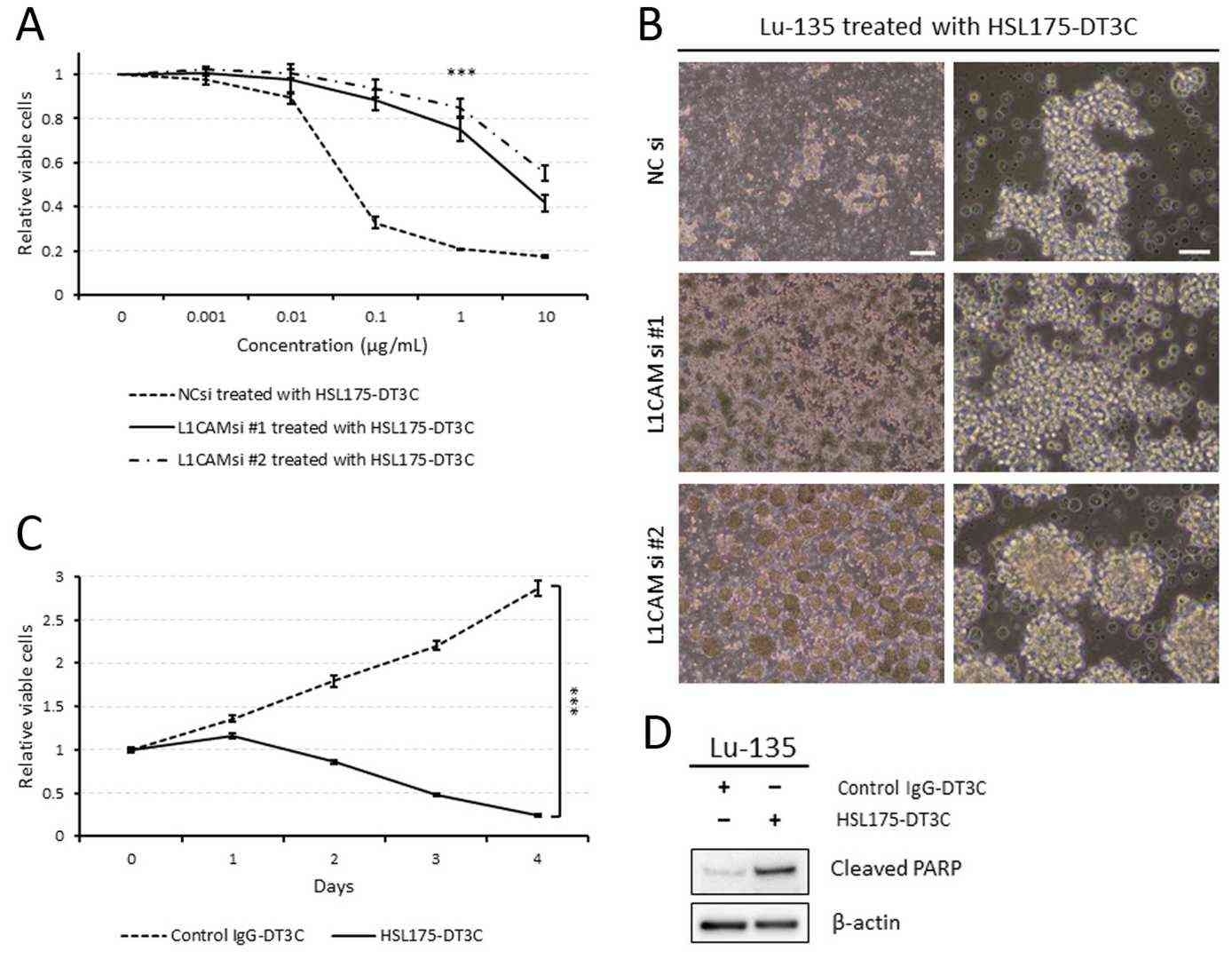 Fig. 1. Lu-135 cells are highly sensitive to HSL175-DT3C conjugates (Yamaguchi M, Hirai S, et al., 2024).
Fig. 1. Lu-135 cells are highly sensitive to HSL175-DT3C conjugates (Yamaguchi M, Hirai S, et al., 2024).
Small Cell Lung Carcinoma Cells Depend on KIF11 for Survival
The limited effective treatments available for small cell lung carcinoma patients make it essential to develop innovative therapeutic strategies. In this study, Sakuma et al. Researchers investigated kinesin family member 11 (KIF11) as a potential SCLC treatment target.
The expression of KIF11 mRNA shows a significant increase in SCLC tissues when compared to normal lung tissues. According to Figure 2A, Lu-135 and H69 cell lines are categorized as SCLC-N and SCLC-A, respectively. Inhibition of KIF11 by RNAi or SB743921 led to cell cycle arrest in the G2/M phase (Fig. 2B). Despite this, KIF11 knockdown fully suppressed cell growth without dephosphorylating AKT, indicating no direct impact on the PI3K/AKT pathway (Fig. 2A and C). SB743921 reduced viability by inducing some apoptosis in Lu-135 cells (Fig. 3A–C). Subsequent treatment with WEHI-539 after SB743921 further enhanced apoptosis and reduced viability in Lu-135 cells (Fig. 3A–C). As anticipated, WEHI-539 following KIF11 knockdown had a more pronounced effect than KIF11 knockdown alone.
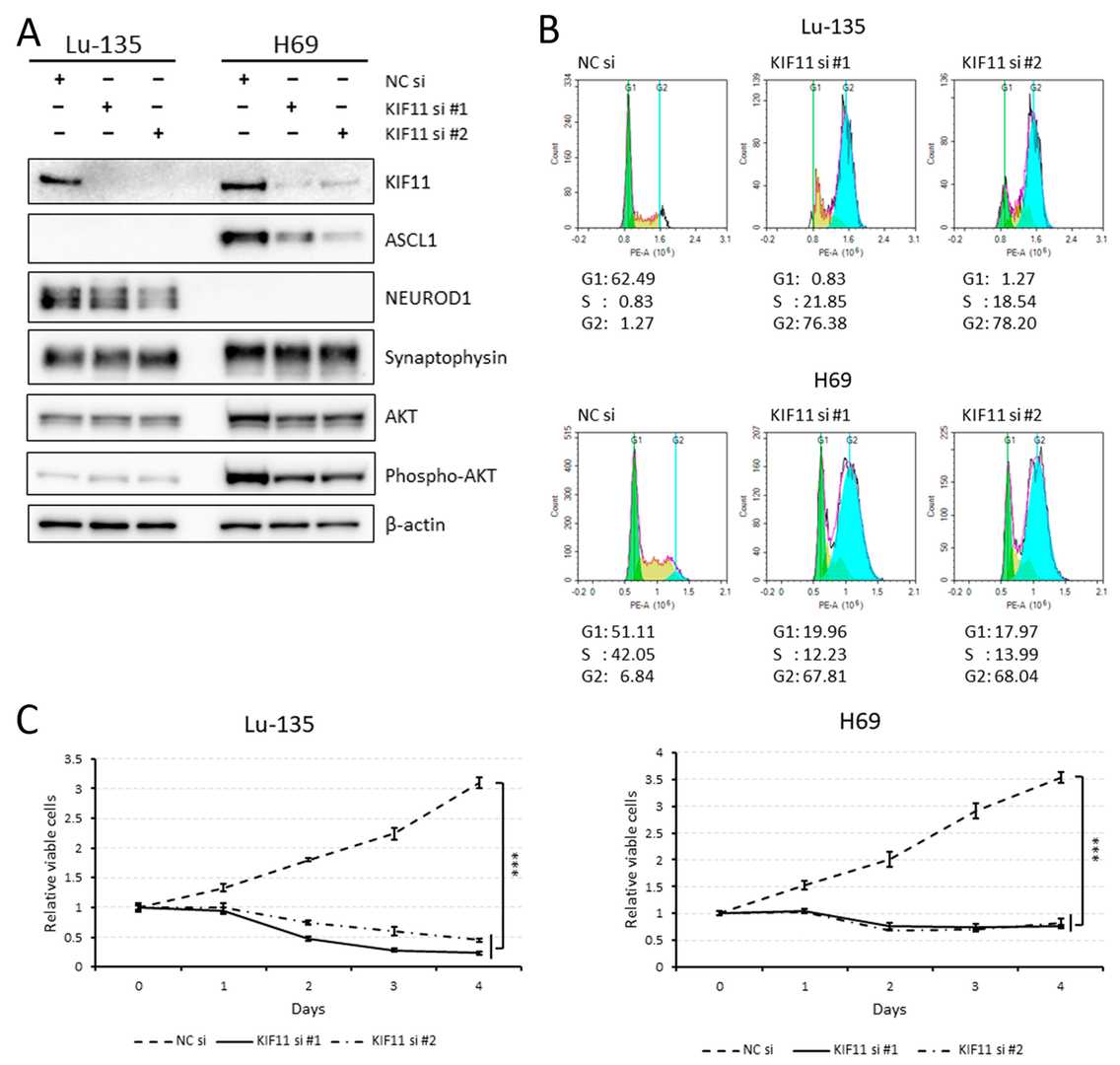 Fig. 2. KIF11 knockdown with small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) elicits cell cycle arrest at the G2/M phase in Lu-135 and H69 cells (Sakuma Y, Hirai S, et al., 2024).
Fig. 2. KIF11 knockdown with small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) elicits cell cycle arrest at the G2/M phase in Lu-135 and H69 cells (Sakuma Y, Hirai S, et al., 2024).
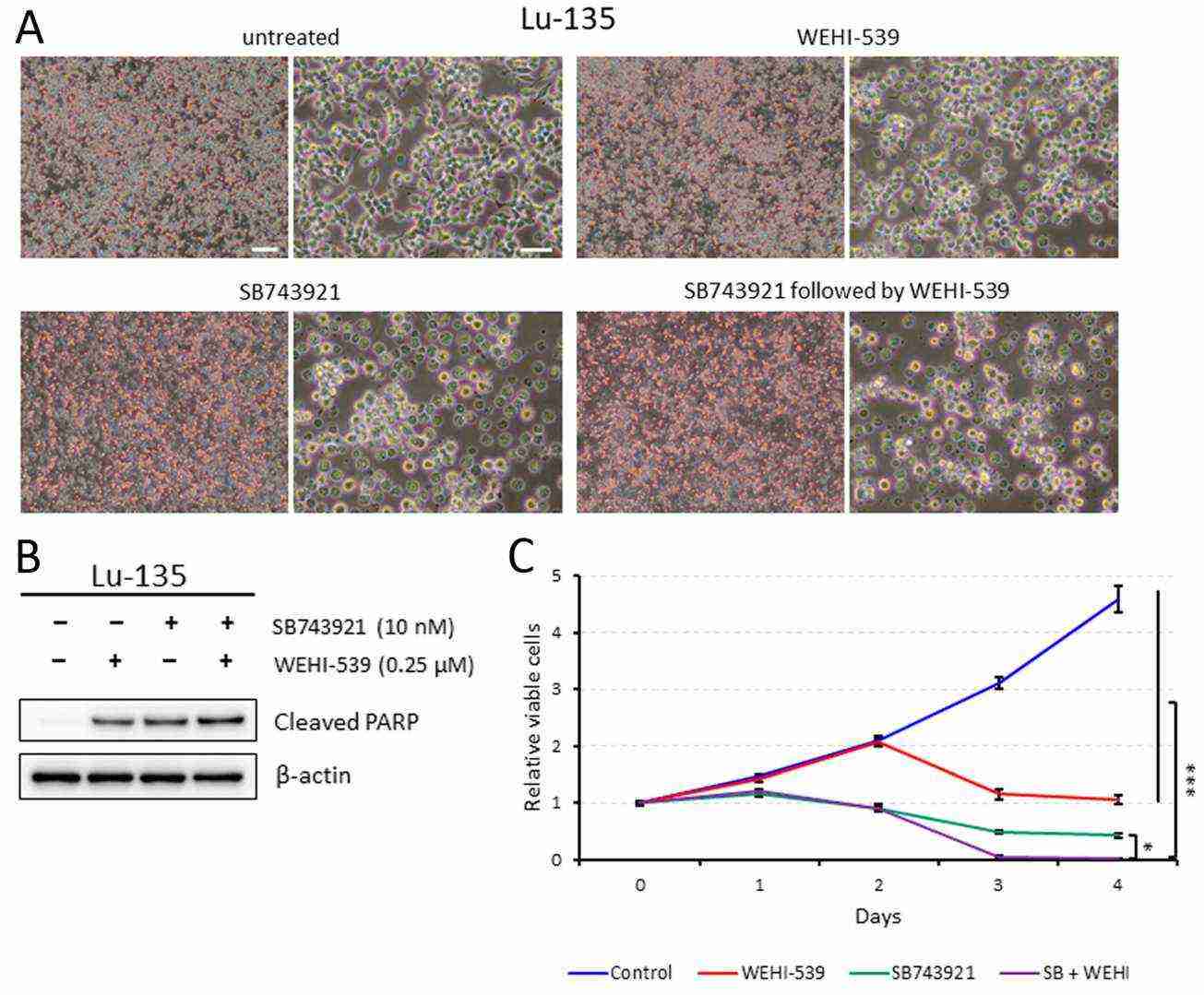 Fig. 3. Sequential treatment of Lu-135 cells with SB743921 followed by WEHI-539 markedly decreases cell viability (Sakuma Y, Hirai S, et al., 2024).
Fig. 3. Sequential treatment of Lu-135 cells with SB743921 followed by WEHI-539 markedly decreases cell viability (Sakuma Y, Hirai S, et al., 2024).
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- You May Also Need
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells