8305C
Cat.No.: CSC-C0290
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
Source: Thyroid Gland
Morphology: adherent, large spindle-shaped cells growing as monolayer
Culture Properties: monolayer
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
Immunology: cytokeratin +, cytokeratin-7 +, cytokeratin-8 +, cytokeratin-17 -, cytokeratin-18 +, cytokeratin-19 -, desmin -, endothel -, EpCAM -, GFAP +, neurofilament -, thyr
8305C is a human cell line that was developed from an anaplastic thyroid carcinoma (ATC) tumor. ATC is a rare, undifferentiated, and highly aggressive form of thyroid cancer with poor differentiation and resistance to most forms of treatment. This cell line was originally derived from a thyroid tumor sample that was taken from a 67-year-old woman with ATC. 8305C cells show epithelial-like morphology with significant pleomorphism, a common feature of malignancy, and are adherent cells that grow in standard cell culture media.
8305C cells lose common thyroid features, such as iodine uptake, with dedifferentiation but retain a high proliferative and invasive potential, similar to ATC in the clinic. This cell line is used to study the molecular basis of tumor progression, metastasis, and drug and radiation resistance, including to targeted agents such as tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs). It has also been used to define the signaling pathways (e.g., PI3K/AKT, MAPK) involved in the pathogenesis of ATC and its aggressive clinical course.
8305C's rapid growth rate and genetic stability have made it a widely used cell line for drug screening assays, apoptosis studies, and molecular profiling, which have led to the development of novel anticancer therapies. The 8305C cell line has also been used in radiation biology studies due to its relative radioresistance, which can provide insights into strategies to increase the efficacy of this treatment modality. Overall, 8305C continues to be an important tool in the study of thyroid cancer and has contributed to many translational and clinical advances in this deadly disease.
TF Containment of the Malignant Tumor Phenotype of 8305C Cells
Anaplastic thyroid cancer (ATC) is a rare but extremely aggressive type of thyroid cancer derived from follicular cells of the thyroid gland. Theaflavin (TF) has anti-cancer effects; however, no study has examined whether TF inhibits the malignant progression of ATC. Therefore, Cai's team explored the effects of TF on ATC and to provide a preliminary exploration of its mechanism.
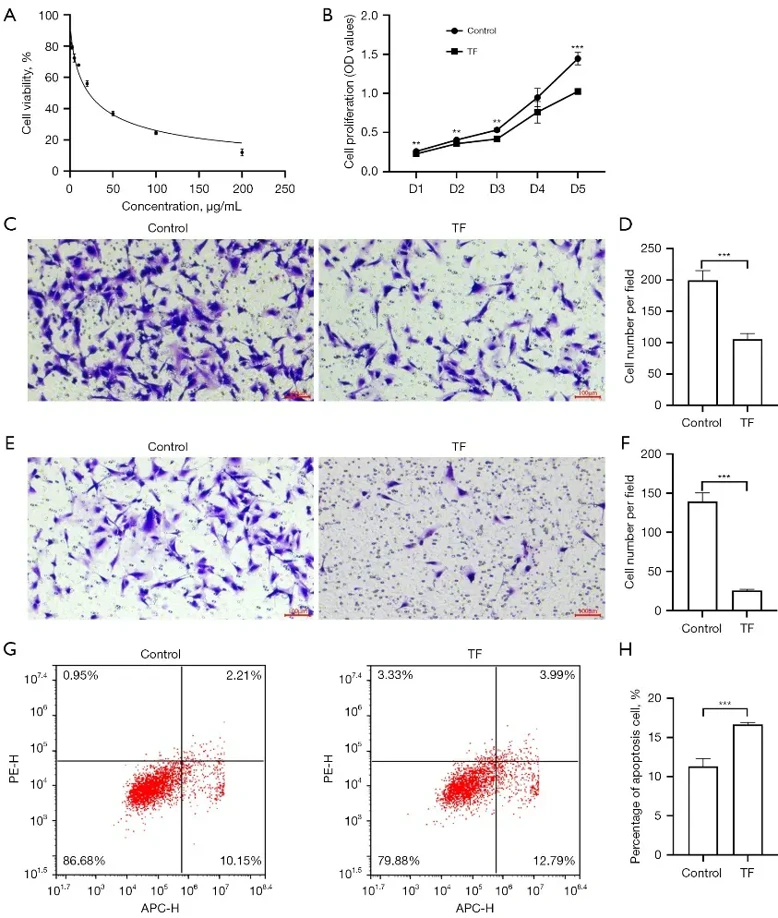
As Figure 1 shows, TF dose-dependently inhibited 8305C growth: viability fell from 100% to 12.01% after 48 h, IC50 = 21.79 µg/mL; 11 µg/mL (½ IC50) was used hereafter (Fig. 1A). CCK-8 assay was used to detect the cell viability and cell proliferation ability of the control and TF cells at 24, 48, 72, 96, and 120 h (Fig. 1B). The effects of TF on 8305C cell migration and invasion were examined by transwell assay. In the transwell chamber, the number of cells migrating to the bottom side of the membrane in the TF-treated group was significantly inhibited compared to that of the control group (Fig. 1C and D). The invasion experiment results also showed that TF inhibited the invasive behavior of the 8305C cells (Fig. 1E and F). Flow cytometry was used to detect the level of cell apoptosis (Fig.1G and H). Compared with the control group, the level of cell apoptosis in the TF group was significantly increased after 48 h.
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- You May Also Need
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells