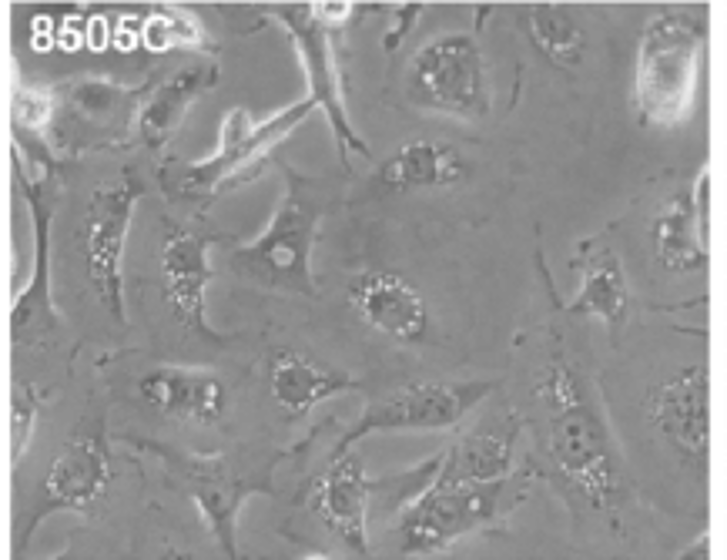
8505C
Cat.No.: CSC-C2224
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
Source: Thyroid Gland
Morphology: epithelial-like adherent cells growing as monolayer
Culture Properties: monolayer
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
Immunology: cytokeratin +, cytokeratin-7 +, cytokeratin-8 +, cytokeratin-17 -, cytokeratin-18 +, cytokeratin-19 +, desmin -, endothel -, EpCAM +, GFAP -, HMB-45 -, neurofilame
8505C is a human anaplastic thyroid carcinoma (ATC) cell line derived from an undifferentiated thyroid tumor from an adult patient. Anaplastic thyroid carcinoma is a highly aggressive and lethal endocrine cancer, marked by rapid progression, poor differentiation, and resistance to traditional treatments. As such, the 8505C cell line is commonly used as a model system for in vitro studies of advanced and treatment-resistant thyroid cancer biology.
8505C cells are poorly differentiated epithelial cells with polygonal to spindle-shaped morphology. The cells have rapid proliferation and stable growth across passages, in line with ATC's aggressive nature. Genetically, 8505C often displays alterations common to anaplastic thyroid carcinoma, including mutations in oncogenic and tumor suppressor pathways such as TP53 and components of the MAPK signaling cascade. Loss of thyroid differentiation markers and reduced thyroid-specific gene expression is consistent with the undifferentiated nature of the cell line. Functionally, 8505C cells have high proliferative and invasive capacity and can exhibit measurable responses to chemotherapeutics, targeted inhibitors, and novel anticancer compounds.
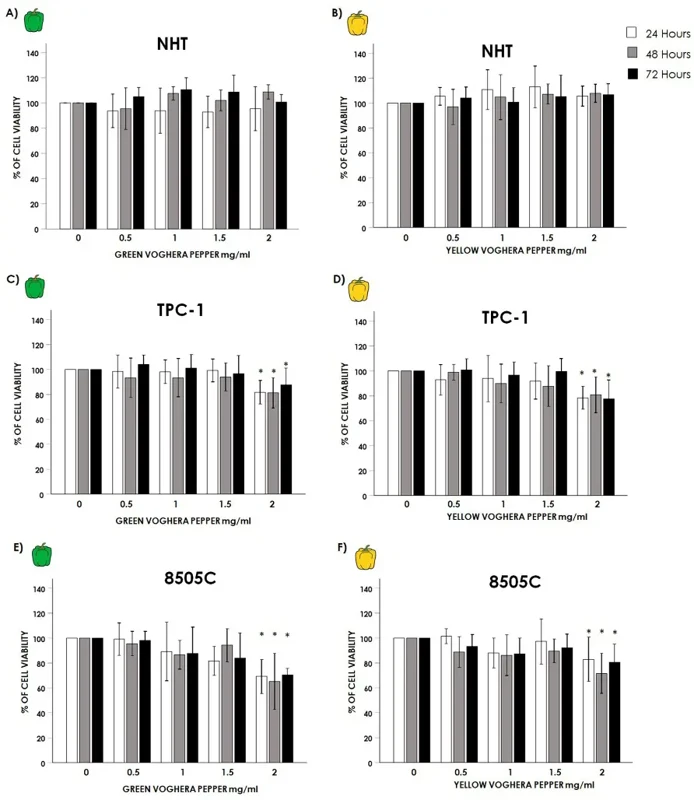
Effect of Voghera Pepper Extracts on Thyroid Cells Viability
Anti-oxidant properties for Voghera pepper (VP) extracts have been shown in different cell types. Coperchini et al. wanted to test whether VP-extracts reduced oxidative stress and modulated behavior in thyroid cancer (TC) cells in vitro.
Normal human thyroid cells (NHT) and thyroid cancer (TC) cell lines TPC-1 and 8505C were treated with increasing concentrations (0, 0.5, 1, 1.5, 2 mg/mL) of GVP or YVP for 24, 48, and 72 hours. The viability of NHT cells did not change with GVP (Fig. 1A) or YVP (Fig. 1B) at any of the concentrations or time points (GVP and YVP ANOVAs all non-significant). However, TC cell lines TPC-1 and 8505C had a reduced viability with the highest concentration (2 mg/mL) of both GVP and YVP. In TPC-1 cells, the treatment with 2 mg/mL GVP (Fig. 1C) and YVP (Fig. 1D) significantly reduced the viability at all time points (24, 48, and 72 hours). The same was found in 8505C cells treated with 2 mg/mL GVP (Fig. 1E) and YVP (Fig. 1F). These reductions were significant at all time points (24, 48, and 72 hours) compared to the 0 mg/mL control.
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- You May Also Need
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells