Drug Loading Approaches of Exosomes
ACS Biomaterials Science Engineering. 2023 Feb 13; 9 (2): 577-594.
Authors: Kar R, Dhar R, Mukherjee S, Nag S, Gorai S, Mukerjee N, Mukherjee D, Vatsa R, Chandrakanth Jadhav M, Ghosh A, Devi A, Krishnan A, Thorat ND.
INTRODUCTION
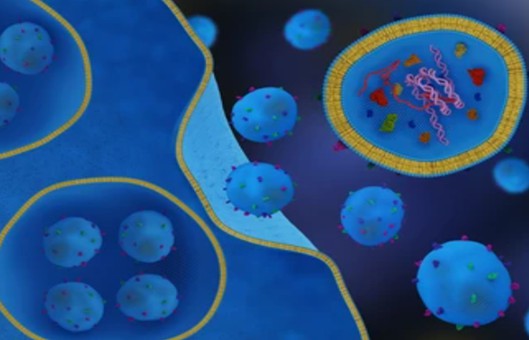
Exosomes are natural carriers into which drugs can be loaded. Exosomes are encapsulated with drugs to make them suitable for the various target therapies. Since the incorporation of the drug into this lipid bilayer membrane is challenging, two different methods are followed; active loading and passive methods. In active remote or post-drug loading, the cells are cleaned to obtain a naïve exosome that is then sealed with drugs, while in passive loading or preloading methods, the cells and the drugs are incubated together and the component later undergo purification to yield a drug-sealed exosome.
Active Loading Approaches
- Electroporation
Electroporation involves a high-intensity electric field, instantaneous changes in cell membrane permeability, and drug loading. The voltage settings for different types of donor cells, such as B. Hela cells, monocytes, and immature dendritic cells, generally range from 150 to 700 V. Drug molecules enter through holes created in the exosome membrane during electroporation, while the membrane is restored after loading. - Sonication
The premise of ultrasonic drug loading is that ultrasonic waves lower the micro-viscosity of the membrane (usually by at least twofold), allowing the hydrophobic drug to pass. Exosomes derived from parental cells or recipient cells are mixed with a specific drug and protein legend before being sonicated with a homogenizer probe. The integrity of the exosome membrane is disrupted by the mechanical shear stress generated during sonication, allowing bioactive chemicals to enter the exosome while the membrane is deformed. - Fusion method
Membrane fusion, itself a scientific achievement, can fuse exosomes and nanocomposites within a membrane structure. It allows for the prolonged release of nanodrugs, enhances absorption and efficacy, and performs an exocrine function in immune system response, antigen presentation, cell migration, cell differentiation, and tumor invasion. - Freeze-thaw cycles
Exosomes are incubated with selected drugs at room temperature for a set period before being quickly frozen at -80°C or in liquid nitrogen. Thereafter, the combination is allowed to thaw at room temperature. Freeze-thaw cycles are performed at least three times to improve drug encapsulation.
Passive Loading Approach
- Incubation
The passive loading approach involves two different types of incubation: incubation of the drug along with an exosome or with donor cells. In the case of incubating a drug with exosomes, this technique allows the drug to enter the exosome-based on the concentration gradient during the incubation. - Drug delivery via exosomes
The latest discoveries point to a unique property of exosomes, as it was found that exosomes can transport proteins and genetic and epigenetic information from one cell to another cell through receptor-ligand interactions. - Delivering small molecules via exosomes
Drugs can be encapsulated in exosomes, thereby prolonging the drug's half-life and improving the stability of drug release. Furthermore, due to their endogenous origin, exosomes are highly biocompatible and can be used as nanocarriers for tissue-specific targeted delivery.
Creative Bioarray Relevant Recommendations
Creative Bioarray provides professional products and services, including but not limited to the following.
| Product/Service Types | Description |
| Exosome Standards | Creative Bioarray provides the best quality lyophilized exosome standards obtained from several biological samples, including hundreds of different cell lines, plasma, serum, saliva, and urine as well as other bio-fluids. |
| Exosome Analysis | Creative Bioarray provides diverse exosomal species analysis to help you understand your exosome compositions. We provide RNA-seq, proteomics, lipidomics, and metabolomics analyses. |