Chronic Unpredictable Mild Stress (CUMS) Model
The Chronic Unpredictable Mild Stress (CUMS) Model is a well-established and widely validated animal model for studying depression-like behaviors and the pathophysiology of mood disorders. By exposing animals to a variety of mild and unpredictable stressors over a period of time, the CUMS model mimics chronic stress conditions in humans and induces behavioral and neurobiological changes relevant to major depressive disorder (MDD).
At Creative Bioarray, we provide highly reproducible and customizable CUMS modeling services in mice, enabling preclinical evaluation of antidepressant candidates and central nervous system (CNS)-targeted therapies.
Creative Bioarray's Depression Models
Animal Species
Mouse
Modeling Method
Animals are subjected to 1-2 mild stressors per day, for a continuous period of 3 to 6 weeks. These stressors include:
- Food or water deprivation
- Cage tilt at 45°
- Wet bedding
- Cold swim
- Hot swim
- Restraint stress
- Tail pinch
- Unpredictable shock
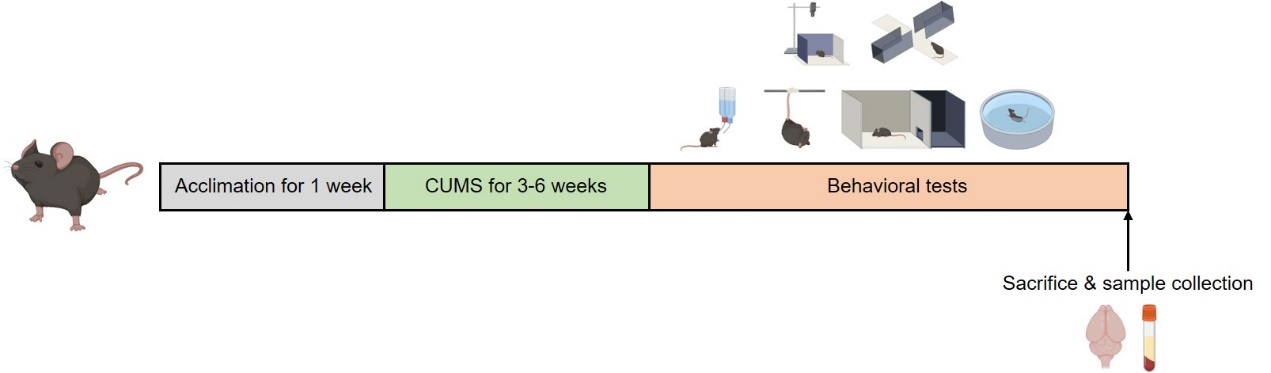
Endpoints
- Sucrose preference test (SPT)
- Tail suspension test (TST)
- Forced swim test (FST)
- Open field test
- Elevated plus maze (EPM)
- Light/Dark box test
- Other customized endpoints
Applications
- Evaluation of antidepressant efficacy
- Mechanism of action studies for CNS drugs
- Research on stress-induced neuroplasticity
- Assessment of anti-anxiety and neuroprotective agents
- Behavioral pharmacology screening
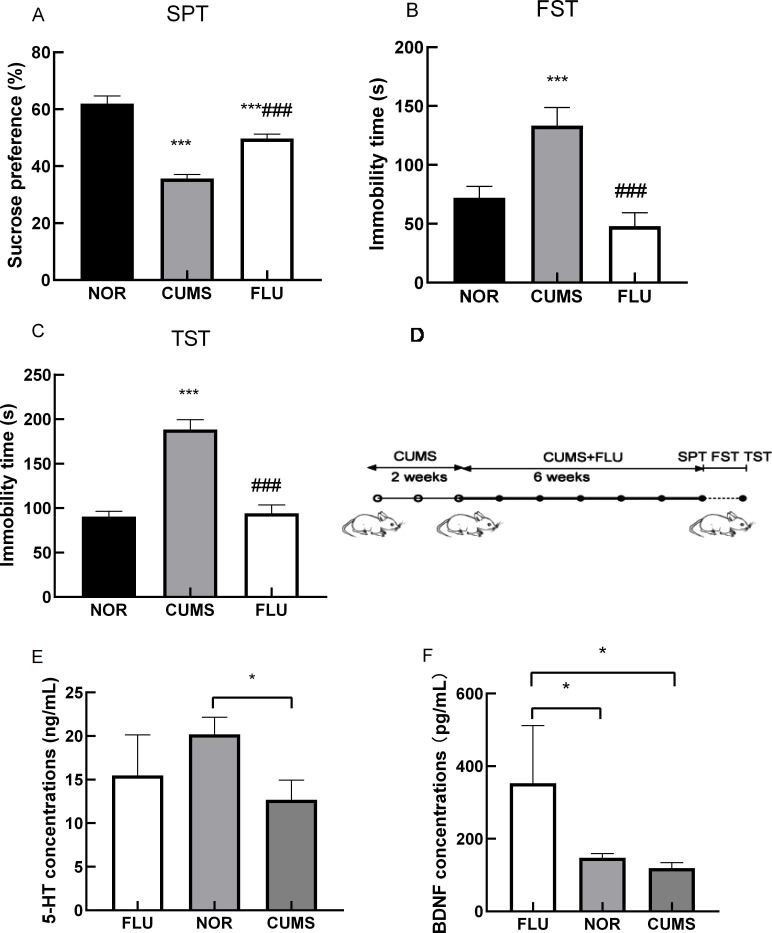
Example Data
Quotation and Ordering
If you have any special needs or questions regarding our depression models, please do not hesitate to contact us or submit an inquiry to us directly. We look forward to cooperating with you in the future.
Reference
- Zhang, C.L., et al. Fluoxetine ameliorates depressive symptoms by regulating lncRNA expression in the mouse hippocampus. Zool Res. 2021;42(1):28-42.
For research use only. Not for any other purpose.
Disease Models
- Oncology Models
-
Inflammation & Autoimmune Disease Models
- Rheumatoid Arthritis Models
- Glomerulonephritis Models
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS) Models
- Ocular Inflammation Models
- Sjögren's Syndrome Model
- LPS-induced Acute Lung Injury Model
- Peritonitis Models
- Passive Cutaneous Anaphylaxis Model
- Delayed-Type Hypersensitivity (DTH) Models
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease Models
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Animal Models
- Oral Mucositis Model
- Asthma Model
- Sepsis Model
- Psoriasis Model
- Atopic Dermatitis (AD) Model
- Scleroderma Model
- Gouty Arthritis Model
- Carrageenan-Induced Air Pouch Synovitis Model
- Carrageenan-Induced Paw Edema Model
- Experimental Autoimmune Myasthenia Gravis (EAMG) Model
- Graft-versus-host Disease (GvHD) Models
-
Cardiovascular Disease Models
- Surgical Models
- Animal Models of Hypertension
- Venous Thrombosis Model
- Atherosclerosis model
- Cardiac Arrhythmia Model
- Hyperlipoidemia Model
- Doxorubicin-induced Heart Failure Model
- Isoproterenol-induced Heart Failure Model
- Arterial Thrombosis Model
- Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH) Models
- Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction (HFpEF) Model
- Cardio-Renal-Metabolic (CKM) Syndrome Model
-
Neurological Disease Models
- Alzheimer's Disease Modeling and Assays
- Seizure Models
- Parkinson's Disease Models
- Ischemic Stroke Models
- Acute Spinal Cord Injury (ASCI) Model
- Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) Model
- Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy (HIE) Model
- Tourette Syndrome (TS) Model
- Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) Model
- Huntington's Disease (HD) Model
- Intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) Models
- Schizophrenia Model
- Depression Models
- Pain Models
-
Metabolic Disease Models
- Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Model
- Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Model
- Animal Model of Hyperuricemia
-
Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Model
- High-Fat Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
- Methionine and Choline Deficient (MCD) Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
- Gubra-Amylin NASH (GAN) Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
- Streptozotocin (STZ) Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
- High Fat Diet-Induced Obesity Model
- Diabetic Foot Ulcer (DFU) Model
- Cardio-Renal-Metabolic (CKM) Syndrome Model
- Liver Disease Models
- Rare Disease Models
- Respiratory Disease Models
- Digestive Disease Models
-
Urology Disease Models
- Cisplatin-induced Nephrotoxicity Model
- Unilateral Ureteral Obstruction Model
- 5/6 Nephrectomy Model
- Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury (RIRI) Model
- Diabetic Nephropathy (DN) Models
- Passive Heymann Nephritis (PHN) Model
- Adenine-Induced Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Model
- Kidney Stone Model
- Doxorubicin-Induced Nephropathy Model
- Orthotopic Kidney Transplantation Model
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) Model
- Peritoneal Fibrosis Model
- Cardio-Renal-Metabolic (CKM) Syndrome Model
- Orthopedic Disease Models
- Ocular Disease Models
- Skin Disease Models
- Infectious Disease Models
- Otology Disease Models