Peritoneal Fibrosis Model
Peritoneal fibrosis is the end-stage consequence of progressive changes in the peritoneal membrane, often driven by clinical interventions such as peritoneal dialysis (PD). PD provides an alternative to hemodialysis for patients with end-stage renal disease, but 50-80% of patients develop peritoneal fibrosis within one to two years, highlighting the need for effective anti-fibrotic therapies.
Creative Bioarray offers a validated peritoneal fibrosis animal model to support preclinical evaluation of anti-fibrotic drug candidates. This model recapitulates key pathological and functional features of PD-associated peritoneal fibrosis, providing a reliable platform for assessing tissue remodeling, collagen deposition, and peritoneal membrane function, thereby accelerating drug discovery and mechanistic studies.
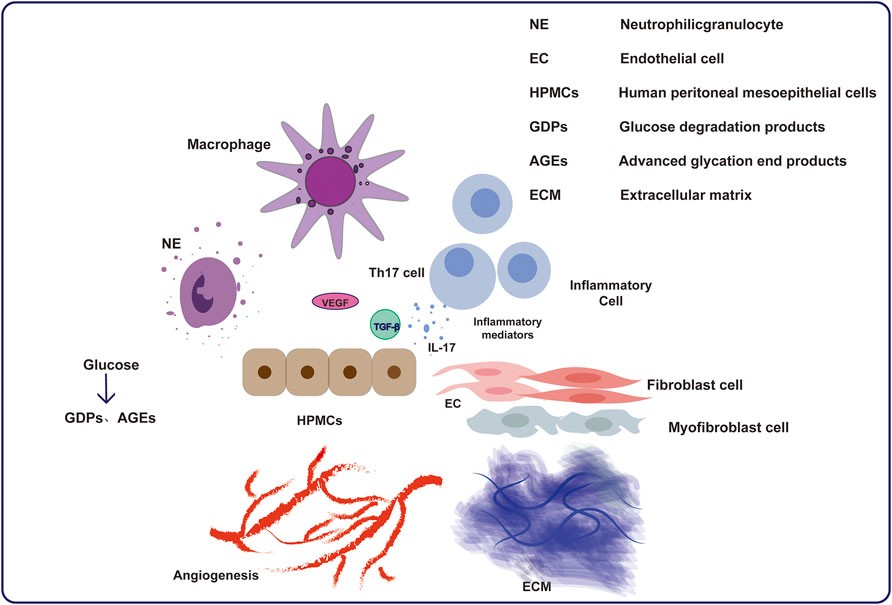
Our Peritoneal Fibrosis Model
Animal Species
Rat
Modeling Method
Daily intraperitoneal injection of peritoneal dialysis solution (e.g., lactate-buffered, 4.25% glucose).
Endpoints
- General health: Body weight, survival rate, clinical observation
- Serum biochemistry: Creatinine, blood urea nitrogen (BUN)
- Fibrosis markers: Soluble, insoluble, and total collagen content, and hydroxyproline levels in the peritoneum
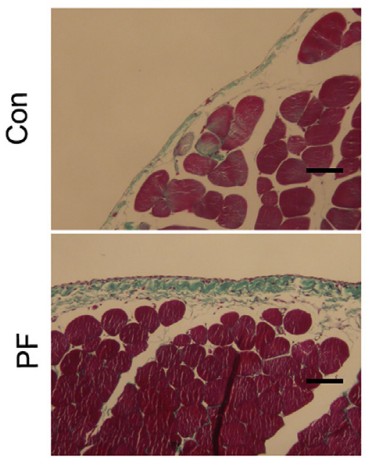
- Histological analysis: H&E and Masson's trichrome staining of peritoneum
- Functional assessment: Peritoneal equilibration test (PET)
- Molecular analysis: qPCR or Western blot
- Customized endpoints
Key Features
- Clinically Relevant
Mimics long-term dialysis-associated injury.
- Comprehensive Endpoints
Structural, biochemical, functional, and molecular evaluation.
- Fully Customizable
Study designs tailored to project goals.
Example Data
Quotation and Ordering
Interested in leveraging our Peritoneal Fibrosis Model for anti-fibrotic drug discovery or mechanistic research? Please contact us directly or submit an inquiry to discuss your specific project requirements.
References
- Kang, Y., et al. Peritoneal fibrosis: from pathophysiological mechanism to medicine. Frontiers in Physiology, 2024, 15: 1438952.
- Sun, C.Y., et al. Prevention and Treatment of Peritoneal Dialysis-Associated Fibrosis with Intraperitoneal Anti-Fibrotic Therapy in Experimental Peritoneal Fibrosis. Pharmaceuticals, 2025, 18(2): 188.
- Li, L., et al. Inhibiting core fucosylation attenuates glucose-induced peritoneal fibrosis in rats. Kidney International, 2018, 93(6): 1384-1396.
For research use only. Not for any other purpose.
Disease Models
- Oncology Models
-
Inflammation & Autoimmune Disease Models
- Rheumatoid Arthritis Models
- Glomerulonephritis Models
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS) Models
- Ocular Inflammation Models
- Sjögren's Syndrome Model
- LPS-induced Acute Lung Injury Model
- Peritonitis Models
- Passive Cutaneous Anaphylaxis Model
- Delayed-Type Hypersensitivity (DTH) Models
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease Models
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Animal Models
- Oral Mucositis Model
- Asthma Model
- Sepsis Model
- Psoriasis Model
- Atopic Dermatitis (AD) Model
- Scleroderma Model
- Gouty Arthritis Model
- Carrageenan-Induced Air Pouch Synovitis Model
- Carrageenan-Induced Paw Edema Model
- Experimental Autoimmune Myasthenia Gravis (EAMG) Model
- Graft-versus-host Disease (GvHD) Models
-
Cardiovascular Disease Models
- Surgical Models
- Animal Models of Hypertension
- Venous Thrombosis Model
- Atherosclerosis model
- Cardiac Arrhythmia Model
- Hyperlipoidemia Model
- Doxorubicin-induced Heart Failure Model
- Isoproterenol-induced Heart Failure Model
- Arterial Thrombosis Model
- Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH) Models
- Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction (HFpEF) Model
- Cardio-Renal-Metabolic (CKM) Syndrome Model
-
Neurological Disease Models
- Alzheimer's Disease Modeling and Assays
- Seizure Models
- Parkinson's Disease Models
- Ischemic Stroke Models
- Acute Spinal Cord Injury (ASCI) Model
- Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) Model
- Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy (HIE) Model
- Tourette Syndrome (TS) Model
- Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) Model
- Huntington's Disease (HD) Model
- Intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) Models
- Schizophrenia Model
- Depression Models
- Pain Models
-
Metabolic Disease Models
- Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Model
- Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Model
- Animal Model of Hyperuricemia
-
Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Model
- High-Fat Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
- Methionine and Choline Deficient (MCD) Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
- Gubra-Amylin NASH (GAN) Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
- Streptozotocin (STZ) Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
- High Fat Diet-Induced Obesity Model
- Diabetic Foot Ulcer (DFU) Model
- Cardio-Renal-Metabolic (CKM) Syndrome Model
- Liver Disease Models
- Rare Disease Models
- Respiratory Disease Models
- Digestive Disease Models
-
Urology Disease Models
- Cisplatin-induced Nephrotoxicity Model
- Unilateral Ureteral Obstruction Model
- 5/6 Nephrectomy Model
- Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury (RIRI) Model
- Diabetic Nephropathy (DN) Models
- Passive Heymann Nephritis (PHN) Model
- Adenine-Induced Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Model
- Kidney Stone Model
- Doxorubicin-Induced Nephropathy Model
- Orthotopic Kidney Transplantation Model
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) Model
- Peritoneal Fibrosis Model
- Cardio-Renal-Metabolic (CKM) Syndrome Model
- Orthopedic Disease Models
- Ocular Disease Models
- Skin Disease Models
- Infectious Disease Models
- Otology Disease Models