Cisplatin-Induced Hearing Loss (CIHL) Model
Creative Bioarray has established a robust Cisplatin-Induced Hearing Loss (CIHL) Model to support the investigation of ototoxicity mechanisms and accelerate the development of effective hearing protection therapies.
What is Cisplatin-Induced Hearing Loss (CIHL)?
Cisplatin-induced hearing loss (CIHL) is a major dose-limiting side effect of cisplatin, a widely used chemotherapeutic agent. It typically presents as irreversible, bilateral, high-frequency sensorineural hearing loss, affecting up to 60% of patients. Cisplatin causes hair cell death by forming DNA adducts, mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress, and inflammation, culminating in programmed cell death by apoptosis, necroptosis, pyroptosis, or ferroptosis. Current clinical management is limited to prosthetic devices such as hearing aids, which cannot repair cochlear damage, highlighting the urgent need for effective protective strategies and reliable preclinical models.
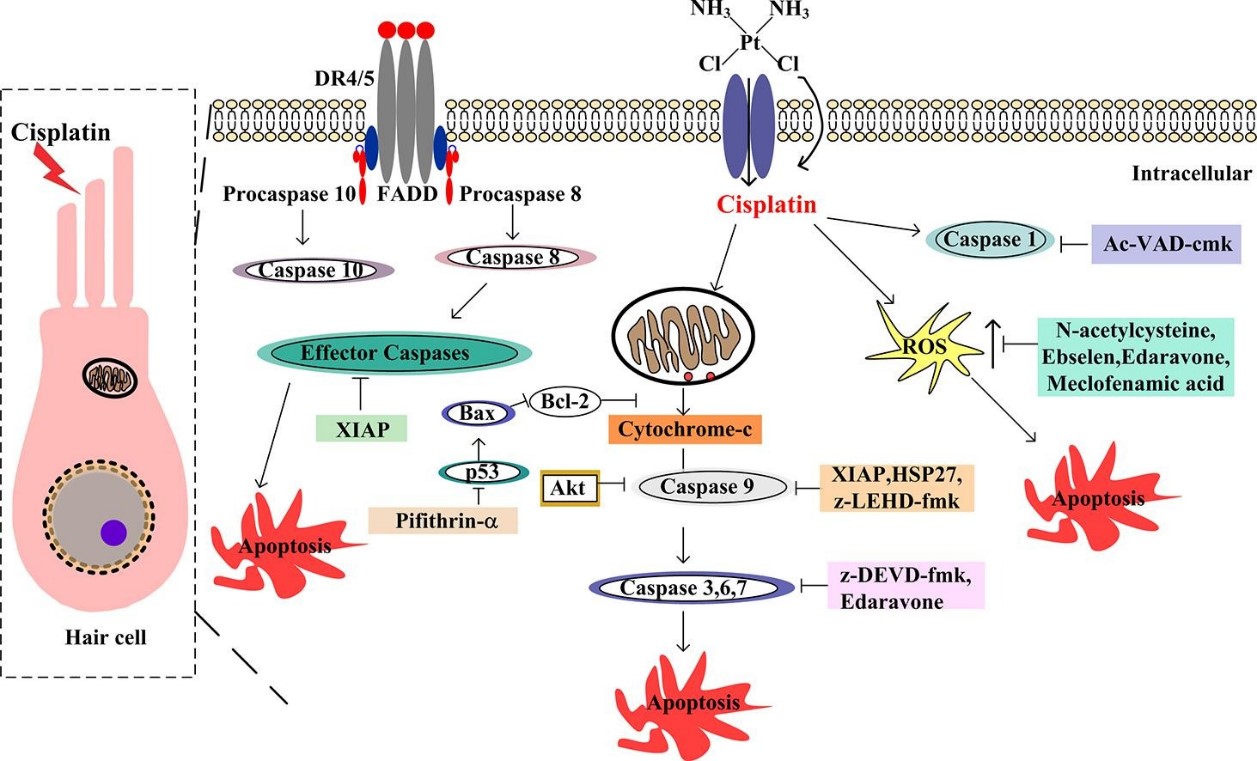
Creative Bioarray's Cisplatin-Induced Hearing Loss (CIHL) Model
- Available Animal
- Rat
- Mouse
- Modeling Method
All animals receive cisplatin treatment to induce a hearing loss model.
- Route of Administration
- Middle Ear: Tympanic membrane puncture (TT), bulla osteotomy
- Inner Ear: Round window membrane administration (RWM), posterior semicircular canal administration (PSC), cochleostomy
- Endpoints
- Auditory brainstem response (ABR) measurement
- Distortion product otoacoustic emission (DPOAE)
- Histology analysis of cochlea
- qPCR or Western blot
- Customized endpoints tailored to your specific research requirements
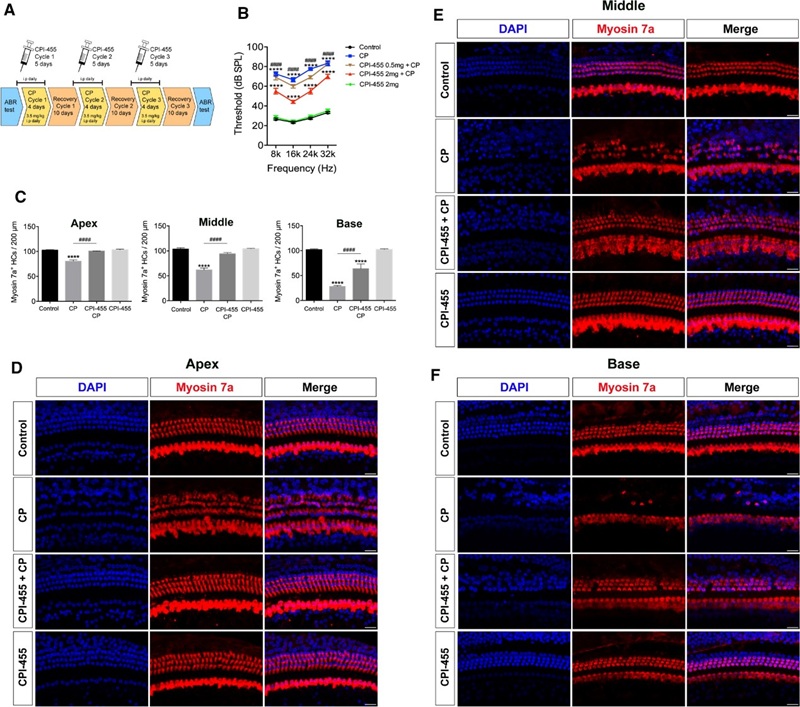
Example Data
Quotation and Ordering
Creative Bioarray is committed to supporting auditory research with reliable, well-characterized in vivo models. For pricing, technical consultation, or to place an order, please contact us directly. Our team is ready to assist you in customizing a study that fits your specific needs.
References
- Tang, Q., et al. Cisplatin-induced ototoxicity: Updates on molecular mechanisms and otoprotective strategies. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2021;163:60-71.
- Liu, C., et al. Inhibition of KDM5A attenuates cisplatin-induced hearing loss via regulation of the MAPK/AKT pathway. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022;79(12):596.
For research use only. Not for any other purpose.
Disease Models
- Oncology Models
-
Inflammation & Autoimmune Disease Models
- Rheumatoid Arthritis Models
- Glomerulonephritis Models
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS) Models
- Ocular Inflammation Models
- Sjögren's Syndrome Model
- LPS-induced Acute Lung Injury Model
- Peritonitis Models
- Passive Cutaneous Anaphylaxis Model
- Delayed-Type Hypersensitivity (DTH) Models
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease Models
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Animal Models
- Oral Mucositis Model
- Asthma Model
- Sepsis Model
- Psoriasis Model
- Atopic Dermatitis (AD) Model
- Scleroderma Model
- Gouty Arthritis Model
- Carrageenan-Induced Air Pouch Synovitis Model
- Carrageenan-Induced Paw Edema Model
- Experimental Autoimmune Myasthenia Gravis (EAMG) Model
- Graft-versus-host Disease (GvHD) Models
-
Cardiovascular Disease Models
- Surgical Models
- Animal Models of Hypertension
- Venous Thrombosis Model
- Atherosclerosis model
- Cardiac Arrhythmia Model
- Hyperlipoidemia Model
- Doxorubicin-induced Heart Failure Model
- Isoproterenol-induced Heart Failure Model
- Arterial Thrombosis Model
- Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH) Models
- Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction (HFpEF) Model
- Cardio-Renal-Metabolic (CKM) Syndrome Model
-
Neurological Disease Models
- Alzheimer's Disease Modeling and Assays
- Seizure Models
- Parkinson's Disease Models
- Ischemic Stroke Models
- Acute Spinal Cord Injury (ASCI) Model
- Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) Model
- Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy (HIE) Model
- Tourette Syndrome (TS) Model
- Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) Model
- Huntington's Disease (HD) Model
- Intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) Models
- Schizophrenia Model
- Depression Models
- Pain Models
-
Metabolic Disease Models
- Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Model
- Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Model
- Animal Model of Hyperuricemia
-
Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Model
- High-Fat Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
- Methionine and Choline Deficient (MCD) Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
- Gubra-Amylin NASH (GAN) Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
- Streptozotocin (STZ) Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
- High Fat Diet-Induced Obesity Model
- Diabetic Foot Ulcer (DFU) Model
- Cardio-Renal-Metabolic (CKM) Syndrome Model
- Liver Disease Models
- Rare Disease Models
- Respiratory Disease Models
- Digestive Disease Models
-
Urology Disease Models
- Cisplatin-induced Nephrotoxicity Model
- Unilateral Ureteral Obstruction Model
- 5/6 Nephrectomy Model
- Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury (RIRI) Model
- Diabetic Nephropathy (DN) Models
- Passive Heymann Nephritis (PHN) Model
- Adenine-Induced Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Model
- Kidney Stone Model
- Doxorubicin-Induced Nephropathy Model
- Orthotopic Kidney Transplantation Model
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) Model
- Peritoneal Fibrosis Model
- Cardio-Renal-Metabolic (CKM) Syndrome Model
- Orthopedic Disease Models
- Ocular Disease Models
- Skin Disease Models
- Infectious Disease Models
- Otology Disease Models