Tg2576 Mouse Model
Aβ is classified as a neurotoxic peptides containing 36–43 amino acids and it is a natural product by metabolism generated from β and γ -secretase activity dependent APP cleavage in the amyloidogenic pathway. Aβ can lead to the formation of senile plaques in the brain and apoptosis of neurons, which has been believed to be an important factor causing Alzheimer's disease. Among these peptides, Aβ42 has the highest toxicity as it aggregates the most. And the over-expression of APP normally leads to higher production of Aβ peptides. Tg2576, a transgenic mice line, overexpresses Human APP695 which contains two mutations exhibits significant cognitive impairment at 9 months of age. Besides, the expression of APP, Aβ plaque formation and behavioral deficits in Tg2576 mice were similar to clinical symptoms of Alzheimer's disease. Hence, these advantages in Tg2576 offer opportunities for researchers to explore AD-related pharmacological mechanisms.
Our capabilities
- We can provide comprehensive behavioral and cognitive testing on AD model and the drug screening.
- We can utilize LTP (long-term potentiation) assay to evaluate your preclinical drug candidates against the synaptic impairments in animals.
- We can evaluate anti-oxidative stress in the hippocampus of animals treated with drug candidates.
- We can evaluate various biomarkers through WB, IHC, ELISA, sequencing, etc.
Assays available
- Learning and memory deficits tests
- Synaptic impairment
- Oxidative stress
- Neuroinflammation
- Glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta (GSK3β)
- Neuronal loss
- β-AP level
- Plaque load
- β-sheet load
- pE(3)-Aβ load
- NMDA receptor function and excitotoxicity
- Mitochondrial dysfunction
- Brain slice staining and synaptic electrophysiology
With 10 years of hard working and continuous development, as a senior leader specialize in AD research with enormous industrial experience, Creative Bioarray is exceptional to be worked with for you. We will make our best efforts to meet your unique requires by providing individually customized service.
Study examples
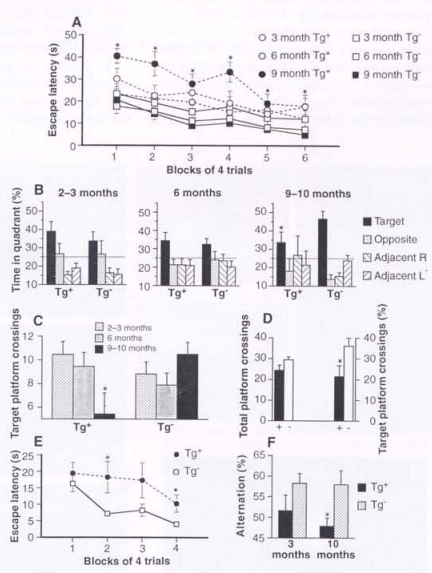 Figure. 1. Learning and memory tests of transgenic and control mice. Asterisks indicate measures in which transgenic mice differed significantly from controls. (P<0.05). (A) The latency to escape to hidden platform in the water maze is impired in Tg+ mice relative to age-mached nontransgenic controls. (B) After 24 trails (over 6 days) with the platform in its fixed location, mouse were given a probe trail in which they swam for 60s with the platform removed. 2 and 6-month-old Tg+ and Tg- mice spent significantly more than 25% of their time in the target quadrant, indicating that they had learned its location. Although 9 and 10-month-old control mice still search selectively for the platform, older transgenic mice spent no more time in the target quadrant than in the other three quadrant, suggesting that they had not learned the platforms location. (C) The implication of (B) are supported by the observation that on probe trails, 9 and 10-month-old Tg+ mice crossed what had been the exact location of the platform signficantly less frequently than did aged-mached Tg- mice. (D) The bars on the left indicate that transgenic (+) mice differ from the control(-) mice in the total number of the platform locations crossed (that is, the center of all four quadrants); the bars on the right show the sigficant difference between 9 and 10-month-old transgenic mice and controls on the percentage of total platform crossings that were over the target. (E) 9 and 10-month-old Tg+ mice were also impired in swimming to a visible platform, although escape latency did not differ significant on the first visible platform training trail. (F) Aged-Tg+ mice were impired in thier tendency to spontaneously alternate arm-entry in a Y-maze, another behavioral task sensitive to hippocapal damage.
Figure. 1. Learning and memory tests of transgenic and control mice. Asterisks indicate measures in which transgenic mice differed significantly from controls. (P<0.05). (A) The latency to escape to hidden platform in the water maze is impired in Tg+ mice relative to age-mached nontransgenic controls. (B) After 24 trails (over 6 days) with the platform in its fixed location, mouse were given a probe trail in which they swam for 60s with the platform removed. 2 and 6-month-old Tg+ and Tg- mice spent significantly more than 25% of their time in the target quadrant, indicating that they had learned its location. Although 9 and 10-month-old control mice still search selectively for the platform, older transgenic mice spent no more time in the target quadrant than in the other three quadrant, suggesting that they had not learned the platforms location. (C) The implication of (B) are supported by the observation that on probe trails, 9 and 10-month-old Tg+ mice crossed what had been the exact location of the platform signficantly less frequently than did aged-mached Tg- mice. (D) The bars on the left indicate that transgenic (+) mice differ from the control(-) mice in the total number of the platform locations crossed (that is, the center of all four quadrants); the bars on the right show the sigficant difference between 9 and 10-month-old transgenic mice and controls on the percentage of total platform crossings that were over the target. (E) 9 and 10-month-old Tg+ mice were also impired in swimming to a visible platform, although escape latency did not differ significant on the first visible platform training trail. (F) Aged-Tg+ mice were impired in thier tendency to spontaneously alternate arm-entry in a Y-maze, another behavioral task sensitive to hippocapal damage.
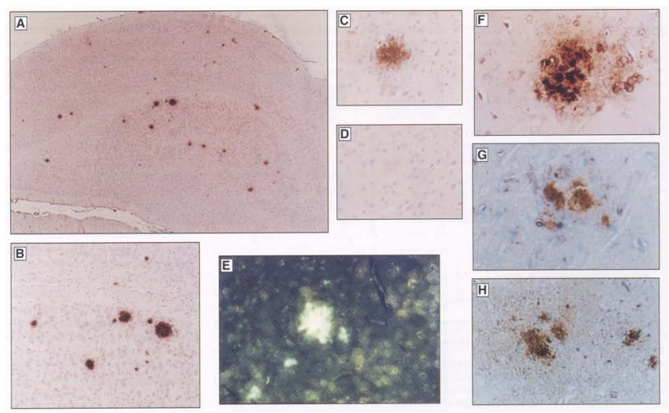 Figure. 2. Extracellur amyloid deposits in transgenic mice A01493(age, 368 days) and A01488(354 days) overexpressing Human APP695 with the K670N, M671L mutation. (A) A01493, multiple plaques in the cerebral cortex and subiculum staining with 4G8 mAb. (B) A01493, inset from (A). (C) A01488, plaque in section adjacent to (C) fails to stain with 4G8 mAb preabsorbed with Aβ(14-24). (E) A01488, plaques staining with thioflavin S. (F) A01488, plaque staining with Aβ(1) affinity-purified antiserum specifically recognizing the NH2-terminus of Aβ. (G) A01488, plaque staining with Aβ(42) affinity-purified antiserum specifically recognizing the COOH-terminus of Aβ(1-42). (H) A01488, plaque staining with α 40 affinity-purified antiserum specifically recognizing the COOH-terminus of Aβ(1-40).
Figure. 2. Extracellur amyloid deposits in transgenic mice A01493(age, 368 days) and A01488(354 days) overexpressing Human APP695 with the K670N, M671L mutation. (A) A01493, multiple plaques in the cerebral cortex and subiculum staining with 4G8 mAb. (B) A01493, inset from (A). (C) A01488, plaque in section adjacent to (C) fails to stain with 4G8 mAb preabsorbed with Aβ(14-24). (E) A01488, plaques staining with thioflavin S. (F) A01488, plaque staining with Aβ(1) affinity-purified antiserum specifically recognizing the NH2-terminus of Aβ. (G) A01488, plaque staining with Aβ(42) affinity-purified antiserum specifically recognizing the COOH-terminus of Aβ(1-42). (H) A01488, plaque staining with α 40 affinity-purified antiserum specifically recognizing the COOH-terminus of Aβ(1-40).
Quotation and ordering
If you have any special needs or questions regarding our services, please feel free to contact us. We look forward to cooperating with you in the future.
Reference
- Hsiao K et al. Correlative Memory Deficits, Abeta, Elevation, and Amyloid Plaques in Transgenic Mice[J]. Science, 1996, 274(5284):99-102.