IgA Nephropathy (IgAN) Model
Creative Bioarray offers a well-established IgA Nephropathy (IgAN) model induced by BSA/LPS/CCl4 in both rats and mice. This model is designed for the screening, testing, and evaluation of new drugs and formulations. It has been meticulously developed to closely mimic the pathophysiology of human IgAN, providing a reliable platform for researchers and pharmaceutical companies to evaluate the efficacy and safety of potential therapeutic agents.
IgAN is a progressive, rare kidney disease and a leading cause of chronic kidney disease and kidney failure. Annually, approximately 25 individuals per million worldwide receive a new diagnosis of IgAN. Despite being the most common form of primary glomerulonephritis (GN) and having been initially described over 50 years ago, our understanding of the disease's pathophysiology remains incomplete, and treatment approaches have largely been empirical. Consequently, the development of preclinical animal models of IgAN is crucial for advancing our knowledge of the disease. These models provide a vital platform for researchers to study the mechanisms of IgAN, test potential therapies, and ultimately improve treatment outcomes for patients affected by this condition.
Our IgA Nephropathy (IgAN) Model
- Available Animal
- Rat
- Mouse
- Modeling Method
To induce the IgAN model, animals undergo a series of procedures, including intragastric administration of bovine serum albumin (BSA), tail vein injection of lipopolysaccharide (LPS), and subcutaneous injection of carbon tetrachloride (CCl4). This combination of treatments is designed to replicate the pathophysiological features of IgAN, providing a reliable model for studying the disease and evaluating potential therapies.
- Endpoints
- Serum analysis: BUN, creatinine, albumin
- Histology analysis: H&E staining, PAS staining, Immunofluorescence
- Urine protein analysis
- qPCR or Western Blot
- Other customized endpoints
Example Data
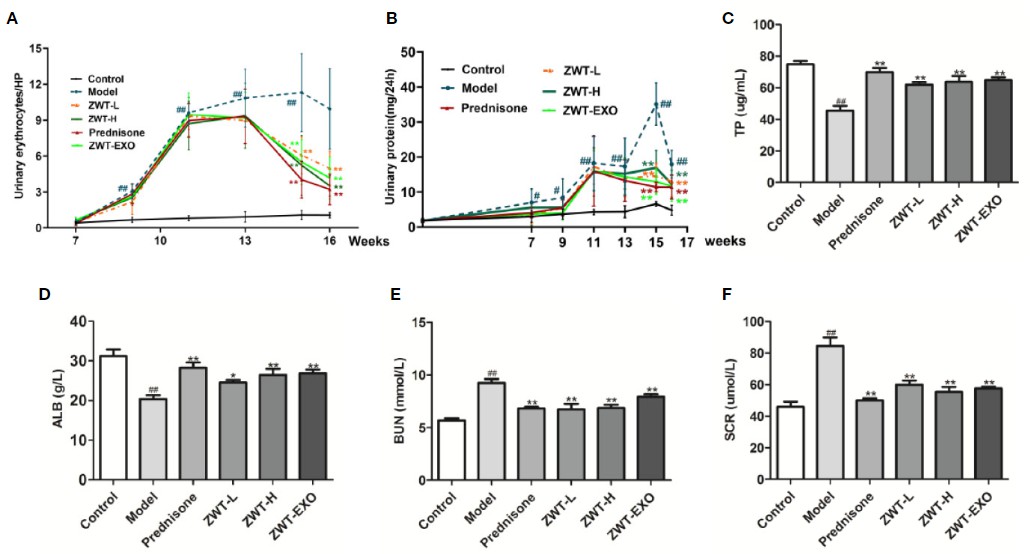 Fig. 1 ZWT-EXO improved renal function of immunoglobulin A nephropathy (IgAN) rats. (A) 24-h urine protein of the IgAN rats in the different periods. (B) Urinary erythrocyte numbers at high power field of the IgAN rats in the different periods. (C–F) The content of total protein (TP), albumin (ALB), blood urea nitrogen (BUN), and serum creatinine (SCR) in the serum of IgAN rats. All values were presented as mean ± SD. #P < 0.05, ## P < 0.01, compared with control group; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, compared with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) group. (Li et al. 2020)
Fig. 1 ZWT-EXO improved renal function of immunoglobulin A nephropathy (IgAN) rats. (A) 24-h urine protein of the IgAN rats in the different periods. (B) Urinary erythrocyte numbers at high power field of the IgAN rats in the different periods. (C–F) The content of total protein (TP), albumin (ALB), blood urea nitrogen (BUN), and serum creatinine (SCR) in the serum of IgAN rats. All values were presented as mean ± SD. #P < 0.05, ## P < 0.01, compared with control group; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, compared with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) group. (Li et al. 2020)
Quotation and Ordering
Creative Bioarray offers an extensive collection of well-characterized urological system disease models to our clients, designed to expedite their drug development processes. These models are meticulously developed and validated to closely mimic human urological conditions, enabling researchers to effectively study disease mechanisms, evaluate potential therapies, and optimize drug candidates. If you are interested in our services, please feel free to contact us at any time or submit an inquiry to us directly.
Reference
- Li, H., et al. Zhen-Wu-Tang protects IgA nephropathy in rats by regulating exosomes to inhibit NF-κB/NLRP3 pathway. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 2020, 11: 1080.
For research use only. Not for any other purpose.
Disease Models
- Oncology Models
-
Inflammation & Autoimmune Disease Models
- Rheumatoid Arthritis Models
- Glomerulonephritis Models
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS) Models
- Ocular Inflammation Models
- Sjögren's Syndrome Model
- LPS-induced Acute Lung Injury Model
- Peritonitis Models
- Passive Cutaneous Anaphylaxis Model
- Delayed-Type Hypersensitivity (DTH) Models
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease Models
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Animal Models
- Oral Mucositis Model
- Asthma Model
- Sepsis Model
- Psoriasis Model
- Atopic Dermatitis (AD) Model
- Scleroderma Model
- Gouty Arthritis Model
- Carrageenan-Induced Air Pouch Synovitis Model
- Carrageenan-Induced Paw Edema Model
- Experimental Autoimmune Myasthenia Gravis (EAMG) Model
- Graft-versus-host Disease (GvHD) Models
-
Cardiovascular Disease Models
- Surgical Models
- Animal Models of Hypertension
- Venous Thrombosis Model
- Atherosclerosis model
- Cardiac Arrhythmia Model
- Hyperlipoidemia Model
- Doxorubicin-induced Heart Failure Model
- Isoproterenol-induced Heart Failure Model
- Arterial Thrombosis Model
- Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH) Models
- Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction (HFpEF) Model
- Cardio-Renal-Metabolic (CKM) Syndrome Model
-
Neurological Disease Models
- Alzheimer's Disease Modeling and Assays
- Seizure Models
- Parkinson's Disease Models
- Ischemic Stroke Models
- Acute Spinal Cord Injury (ASCI) Model
- Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) Model
- Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy (HIE) Model
- Tourette Syndrome (TS) Model
- Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) Model
- Huntington's Disease (HD) Model
- Intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) Models
- Schizophrenia Model
- Depression Models
- Pain Models
-
Metabolic Disease Models
- Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Model
- Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Model
- Animal Model of Hyperuricemia
-
Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Model
- High-Fat Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
- Methionine and Choline Deficient (MCD) Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
- Gubra-Amylin NASH (GAN) Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
- Streptozotocin (STZ) Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
- High Fat Diet-Induced Obesity Model
- Diabetic Foot Ulcer (DFU) Model
- Cardio-Renal-Metabolic (CKM) Syndrome Model
- Liver Disease Models
- Rare Disease Models
- Respiratory Disease Models
- Digestive Disease Models
-
Urology Disease Models
- Cisplatin-induced Nephrotoxicity Model
- Unilateral Ureteral Obstruction Model
- 5/6 Nephrectomy Model
- Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury (RIRI) Model
- Diabetic Nephropathy (DN) Models
- Passive Heymann Nephritis (PHN) Model
- Adenine-Induced Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Model
- Kidney Stone Model
- Doxorubicin-Induced Nephropathy Model
- Orthotopic Kidney Transplantation Model
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) Model
- Peritoneal Fibrosis Model
- Cardio-Renal-Metabolic (CKM) Syndrome Model
- Orthopedic Disease Models
- Ocular Disease Models
- Skin Disease Models
- Infectious Disease Models
- Otology Disease Models