Tau Transgenic Models
Neurofbrillary tangles (NFTs) are neuronal inclusions of the microtubule-associated protein (MAP) tau. Its aggregated and hyperphosphorylated form are considered to be one of the most important histopathological hallmarks of Alzheimer’s disease. Transgenic mouse model that express the mutated human tau has been generated to mimic the characteristics of neurofibrillary tangles in Alzheimer's disease. Creative Bioarray specializes in providing customized pharmacodynamic research services to help customers assess the efficacy of drug candidates and study the associated pathological mechanisms through Tau transgenic models.
Tau transgenic models include but not limited to:
- Tau (P301L) [JNPL3] mouse
Our Capabilities
- We offer Tau transgenic models to screen drug candidates for treatment of Alzheimer's disease.
- We provide comprehensive behavioral and cognitive testing on AD model and the drug screening.
- We evaluate various biomarkers through WB, IHC, ELISA, sequencing, etc.
Assays available
- Learning and memory deficits tests
- Synaptic impairment
- Phosphorylated tau
- Neurofilament Light Chain levels
- Neuronal loss
- Brain slice staining and synaptic electrophysiology
With extensive experience in the field of AD, we are confident to help you to overcome any upcoming challenges. Our experts are fully capable of customizing our protocols and assays to meet your specific needs. With our help, we wish to facilitate your research with high efficiency.
Study examples
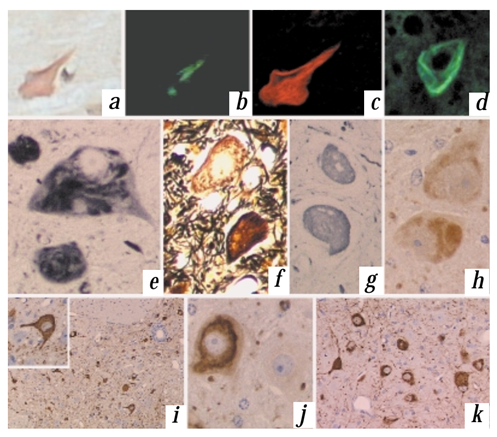 Figure. 1. Characterization of NFT from P301L (JNPL3) mice. NFT stained with Congo red under light microscopy (a), with polarization (b), and under confocal microscopy (c). Thioflavin-S (d) also stained NFT. NFT were positive with Gallyas (e), Bielschowsky (f) and Bodian (g) silver stains. Ubiquitin immunostaining was identified in most NFT (h). Tau hyperphosphorylation was evident from staining with numerous tau antibodies that recognize specific phosphoepitopes including AT8 (i and inset), AT180 (j) and CP13 (k). All sections are from spinal cord except (k), which is from cerebellar dentate nucleus.
Figure. 1. Characterization of NFT from P301L (JNPL3) mice. NFT stained with Congo red under light microscopy (a), with polarization (b), and under confocal microscopy (c). Thioflavin-S (d) also stained NFT. NFT were positive with Gallyas (e), Bielschowsky (f) and Bodian (g) silver stains. Ubiquitin immunostaining was identified in most NFT (h). Tau hyperphosphorylation was evident from staining with numerous tau antibodies that recognize specific phosphoepitopes including AT8 (i and inset), AT180 (j) and CP13 (k). All sections are from spinal cord except (k), which is from cerebellar dentate nucleus.
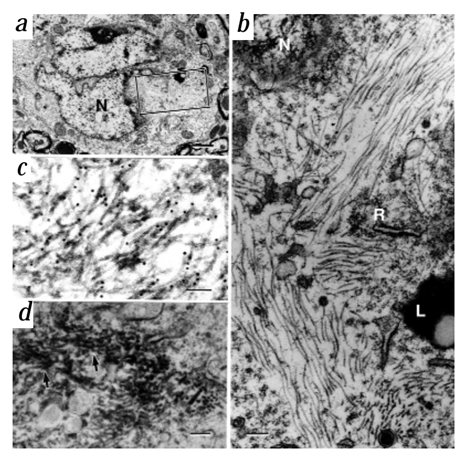 Figure. 2. Electron microscopy of NFT in P301L (JNPL3) mice. a, A neuron with a NFT shows deep nuclear infolding (N) and filamentous cytoplasmic aggregates (boxed area; bar, 1 µm). b, Magnification of boxed area in (a) shows filaments in longitudinal and cross sections. L, lipofuscin granule; N, nucleus; R, polyribosomes. Bar, 0.2 µm. c, Immunogold labelling (CP13) of neuronal filaments (bar, 0.1 µM). d, Immunolabelling of filaments (CP13) with arrows indicating heavy peroxidase reaction product association (bar, 0.2 µm).
Figure. 2. Electron microscopy of NFT in P301L (JNPL3) mice. a, A neuron with a NFT shows deep nuclear infolding (N) and filamentous cytoplasmic aggregates (boxed area; bar, 1 µm). b, Magnification of boxed area in (a) shows filaments in longitudinal and cross sections. L, lipofuscin granule; N, nucleus; R, polyribosomes. Bar, 0.2 µm. c, Immunogold labelling (CP13) of neuronal filaments (bar, 0.1 µM). d, Immunolabelling of filaments (CP13) with arrows indicating heavy peroxidase reaction product association (bar, 0.2 µm).
Quotation and ordering
If you have any special needs or questions regarding our services, please feel free to contact us. We look forward to cooperating with you in the future.
Reference
Lewis J et al. Neurofibrillary tangles, amyotrophy and progressive motor disturbance in mice expressing mutant (P301L) tau protein. Nat Genet. 2000 Aug;25(4):402-5.
For research use only. Not for any other purpose.
Disease Models
- Oncology Models
-
Inflammation & Autoimmune Disease Models
- Rheumatoid Arthritis Models
- Glomerulonephritis Models
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS) Models
- Ocular Inflammation Models
- Sjögren's Syndrome Model
- LPS-induced Acute Lung Injury Model
- Peritonitis Models
- Passive Cutaneous Anaphylaxis Model
- Delayed-Type Hypersensitivity (DTH) Models
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease Models
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Animal Models
- Oral Mucositis Model
- Asthma Model
- Sepsis Model
- Psoriasis Model
- Atopic Dermatitis (AD) Model
- Scleroderma Model
- Gouty Arthritis Model
- Carrageenan-Induced Air Pouch Synovitis Model
- Carrageenan-Induced Paw Edema Model
- Experimental Autoimmune Myasthenia Gravis (EAMG) Model
- Graft-versus-host Disease (GvHD) Models
-
Cardiovascular Disease Models
- Surgical Models
- Animal Models of Hypertension
- Venous Thrombosis Model
- Atherosclerosis model
- Cardiac Arrhythmia Model
- Hyperlipoidemia Model
- Doxorubicin-induced Heart Failure Model
- Isoproterenol-induced Heart Failure Model
- Arterial Thrombosis Model
- Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH) Models
- Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction (HFpEF) Model
- Cardio-Renal-Metabolic (CKM) Syndrome Model
-
Neurological Disease Models
- Alzheimer's Disease Modeling and Assays
- Seizure Models
- Parkinson's Disease Models
- Ischemic Stroke Models
- Acute Spinal Cord Injury (ASCI) Model
- Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) Model
- Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy (HIE) Model
- Tourette Syndrome (TS) Model
- Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) Model
- Huntington's Disease (HD) Model
- Intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) Models
- Schizophrenia Model
- Depression Models
- Pain Models
-
Metabolic Disease Models
- Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Model
- Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Model
- Animal Model of Hyperuricemia
-
Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Model
- High-Fat Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
- Methionine and Choline Deficient (MCD) Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
- Gubra-Amylin NASH (GAN) Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
- Streptozotocin (STZ) Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
- High Fat Diet-Induced Obesity Model
- Diabetic Foot Ulcer (DFU) Model
- Cardio-Renal-Metabolic (CKM) Syndrome Model
- Liver Disease Models
- Rare Disease Models
- Respiratory Disease Models
- Digestive Disease Models
-
Urology Disease Models
- Cisplatin-induced Nephrotoxicity Model
- Unilateral Ureteral Obstruction Model
- 5/6 Nephrectomy Model
- Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury (RIRI) Model
- Diabetic Nephropathy (DN) Models
- Passive Heymann Nephritis (PHN) Model
- Adenine-Induced Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Model
- Kidney Stone Model
- Doxorubicin-Induced Nephropathy Model
- Orthotopic Kidney Transplantation Model
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) Model
- Peritoneal Fibrosis Model
- Cardio-Renal-Metabolic (CKM) Syndrome Model
- Orthopedic Disease Models
- Ocular Disease Models
- Skin Disease Models
- Infectious Disease Models
- Otology Disease Models