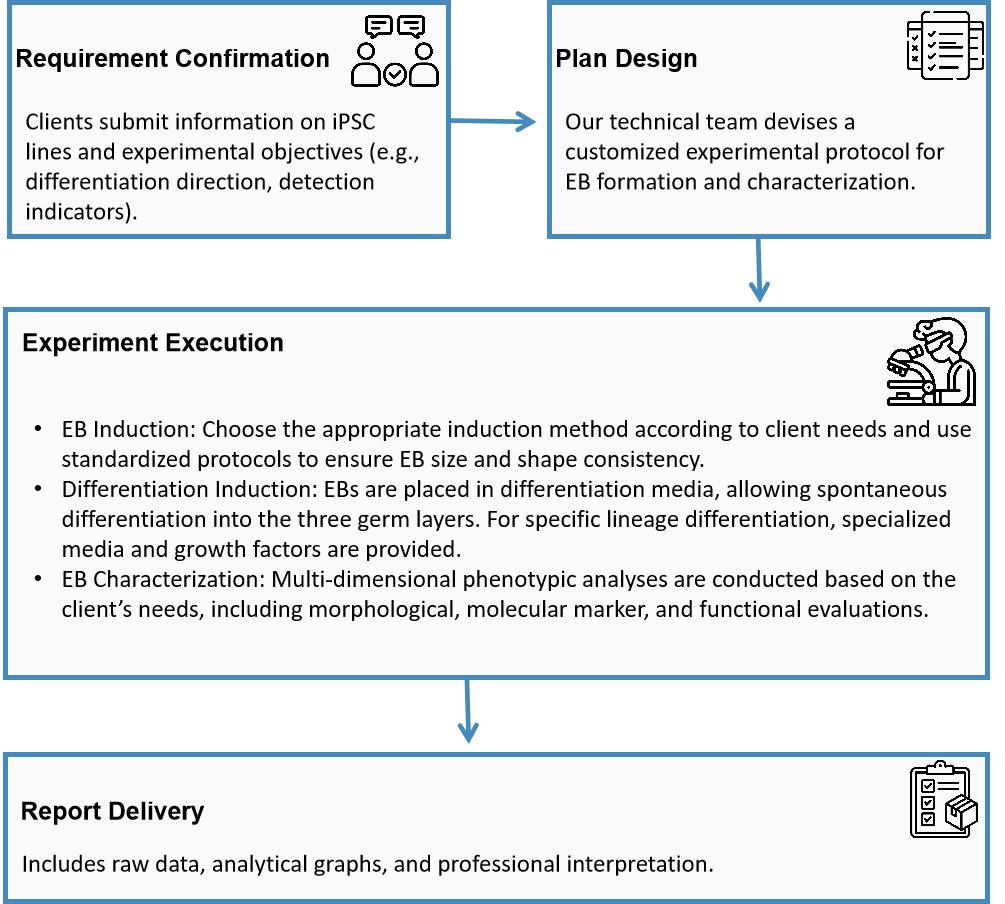
Embryoid Body (EB) Formation
- Service Details
- Workflow
- Features
- FAQ
- Explore Other Options
 Fig. 1. Cellular patterning during embryoid body formation
Fig. 1. Cellular patterning during embryoid body formation
(Zeevaert K, Elsafi Mabrouk MH, et al., 2020).
The Embryoid Body (EB) formation procedure is a crucial assay for assessing induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) as it mimics the early stages of embryonic development in vitro. By spontaneously aggregating and differentiating iPSCs into the three germ layers, EB formation offers valuable insights into pluripotency maintenance, lineage specification, and cellular heterogeneity. This vital test acts as a quality control measure in stem cell research and therapeutic applications, ensuring that iPSC lines meet stringent functional standards before further use.
The EB formation process depends significantly on precise culture conditions, cell density, and differentiation protocols, necessitating a standardized technical system. Our service offers specialized EB formation and multi-dimensional analysis, providing clients with an all-in-one solution from pluripotency validation to differentiative potential evaluation, thereby enhancing research precision and reproducibility.
Creative Bioarray's Embryoid Body (EB) Formation Services
Various methods for EB formation:
- Including Liquid Overlay, Microwell Culture, and Matrigel/Methylcellulose,etc.
Multi-dimensional phenotypic analysis:
- Morphological Assessment: Dynamic monitoring of EB size and structural consistency via microscopy imaging and quantitative image analysis.
- Molecular Marker Detection:
Immunofluorescence staining for germ layer markers (e.g., NESTIN, BMP4, and SOX17).
qPCR analysis of lineage-specific gene expression (e.g., SOX1, Brachyury, GATA4).
Functional Validation: Evaluate functional maturation through spontaneous contraction of embryoid bodies (cardiac differentiation model) or specific metabolic activity tests.
Customized services:
- Directed Differentiation Protocols: Tailored strategies for specific lineages (e.g., neural ectoderm, cardiac mesoderm).
- High-throughput Screening: Evaluate EB formation efficiency across multiple iPSC lines for large-scale studies.
Workflow
Service Features

Customized Experimental Plans
Our stem cell biology team optimizes EB formation conditions for various iPSC backgrounds (e.g., disease-specific, gene-edited cell lines) to ensure over 95% reproducibility.
Flexible Scalability
Adaptable procedures to accommodate research needs from small-scale validations (1-3 lines) to large-scale screenings (100+ lines).
Comprehensive Analytical Methods
Utilize various techniques to characterize EBs, ensuring accuracy and reliability of results.
FAQ
1. What information is required when submitting iPSCs for EB formation and characterization?
We need details about the origin and background of the cells, including the method of reprogramming, passage number and any genetic modifications known. Researchers must supply existing characterization data along with culture conditions and required protocols for differentiation or analysis.
2. Do you offer subsequent differentiation services after EB formation?
Yes, we offer services for directed differentiation into cell types such as cardiomyocytes or neural spheres. For more details, please contact us.
3. What does the data report include?
The report comprises raw images, qPCR amplification curves, quantitative analysis of markers, and statistical comparisons.
4. How much iPSC material is required?
We recommend providing at least 1×106 cells (with a viability greater than 90%), which suffices for three independent EB formation experiments.
Reference
- Zeevaert K, Elsafi Mabrouk MH, et al. Cell Mechanics in Embryoid Bodies. Cells. 2020; 9(10):2270.
Explore Other Options