Isolation and Cell Line Construction Protocol of Monkey Embryonic Stem Cells
GUIDELINE
Embryonic stem cells (ESCs) are totipotent embryonic cells isolated from the inner cell mass (ICM) or primordial germ cells (PGCs) of animal or human blastocysts and screened by in vitro differentiation inhibition culture. ESCs can differentiate into one or more cell types with appropriate factor induction.
METHODS
Acquisition of macaque blastocysts
- The eggs are surgically retrieved from adult macaques. Stimulate follicle development using ESH until follicle volume is greater than 3 mm.
- Oocytes with normal morphology, dense nuclear membrane, and at least two layers of granulosa cells are selected and incubated in HECM-10 medium with 20% neonatal bovine serum (BCS), FSH (ovine FSH, USDADFSH-18), LH (ovineLH, NANDD), and culture at 37°C for 36-40h in vitro.
- After that, in vitro fertilization (IVF) is performed with pre-prepared fertile sperm.
- After 12-16 hours of IVF, a microscopic examination is performed and the fertilized eggs with double protoplasts are selected for further culture.
- At the 8-cell stage, the eggs are transferred to CMRL-1066 medium containing 20% BCS and incubated at 37°C for 10.7 days under 5% CO2, 5% O2 and equilibrium N2 until blastocysts are obtained.
Preparation and culture of murine embryonic fibroblasts
Pure-line BALBC mice at 13-14 days post-pregnancy are selected for the preparation of murine embryonic feeder cells (primary muse embryonic fibroblasts, PMEFs). The obtained PMEFs could be continuously cultured, passaged, and frozen by a 10% NCS DMEM culture system.
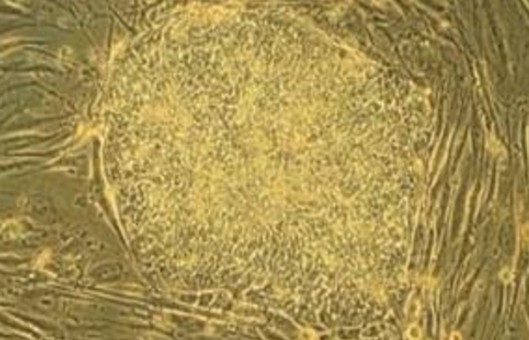
Isolation and culture of macaque embryonic stem cells
- Prepare a small culture dish lined with gelatin and PMEFs.
- Collect the blastocysts that have been cultured in vitro.
- Take a thin Pasteur pipette, inhale a small amount of ES medium, then carefully aspirate the blastocysts, transfer the blastocysts into a small culture dish lined with PMEFs, add ES medium, and incubate them in an incubator at 37°C for about 5 days, during which the blastocysts can be gradually observed to hatch out of the zona pellucida, and the trophoblast cells migrate out and adhere to the surface of PMEFs, and the inner cell masses (ICMs) gradually grow.
- When the ICMs grow to an appropriate size (4-5 days in culture), they are carefully picked out from the trophoblast cells with a needle-shaped Pasteur pipette and washed twice with PBS in another dish.
- Aspirate a small amount of trypsin digest with a finely drawn Pasteur pipette, then carefully aspirate the ICMs, transfer the ICMs into the digest droplets spotted in a small culture dish (note that there should be no air bubbles), cover with paraffin oil and incubate for 3-4 minutes at 37°C in an incubator.
- Take another Pasteur pipette with a finer pull, inhale a small amount of ES medium, then insert it into the digestion droplet to absorb ICMs, carefully blow and wash it several times to disperse it into small cell clusters of 3-4 cells.
- Transfer the cell clusters into small culture dishes that have been lined with PMEFS, incubate them at 37°C, and observe their growth every day. After 2 days, cell clones should appear. Continue to culture, observe, and select colonies with morphology similar to ES.
- After 7-8 days of culture, pick out the ES-like cell colonies, transfer them into the droplets of digesting solution spotted in the small culture dish (note that there should be no air bubbles), cover them with paraffin oil and incubate them for 3-4 minutes at 37°C incubator.
- Prepare small culture plates with gelatin and MEFs in four-well plates.
- Take another Pasteur pipette, inhale a small amount of ES medium, then insert it into the digestion droplet to aspirate the cells, carefully blow and wash several times to disperse the cells, then transfer to a new small culture dish or four-well plate lined with PMEFS for passaging.
- Prepare large culture six-well plates lined with gelatin and PMEFs.
- After 3-5 days of culture, pass the culture again. First, aspirate the medium, wash the cells twice with PBS, then add the digestion solution, incubate at 37°C for 3-4 minutes, and add ES pellet after microscopic examination to see the cell colonies rolled up. The culture medium is terminated by gently blowing to disperse the cells, which could be transferred to a large culture six-well plate that has been paved with PMEFS.
Creative Bioarray Relevant Recommendations
- Stem cells have become the frontier and hotspot of life science and medical research. In addition to embryonic stem cells, we offer our customers a wider selection of stem cells and culture media. We are committed to providing you with fully characterized cells to accelerate the research.
NOTES
- Strictly operate according to the norms for non-human primate experiments, conform to the ethical requirements for non-human primate experiments, minimize the number of animals used, and avoid damage to animals as much as possible.
- Since ESCs are derived from early embryonic cells that are very active in division and proliferation, the nutrition required to maintain their growth and metabolism should be adequate. The feeder layer cell culture medium used for ESCs culture contains high sugar and glutamine, along with fetal bovine serum, neonatal bovine serum, and β-mercaptoethanol. The role of high sugar is to increase the proliferation rate of ESCs and to provide the energy required for the growth of feeder cells; glutamine is essential for the feeder cell medium as a raw material for the synthesis of proteins and nucleic acids by cells; β-mercaptoethanol serves to promote the division and proliferation of embryonic cells and to reduce sulfur-containing compounds in serum to prevent damage to ESCs by peroxides.