Immortalized Murine Tenocyte Cells for Tendon Research
Scientific Reports. 2023 Jan 28; 13 (1): 1566.
Authors: Oreff GL, Maurer B, ELKhamary AN, Gerner I, Sexl V, Jenner F.
INTRODUCTION
- Tendinopathy is the most common musculoskeletal complaint for which patients seek medical attention. It is prevalent in occupational and athletic settings, afflicting 25% of the adult population and accounting for 30-50% of sports injuries.
- The cell cycle regulators p16Ink4a/Arf and p14ARF (p19ARF in mice) are encoded by the Ink4a/Arf locus. p16Ink4a/Arf is a cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor that prevents G1-S phase progression. p14ARF influences responses to a wide range of cellular stress signals by interfering with p53-mediated transcription. Both proteins play an essential role in cell growth, survival, and senescence and act as tumor suppressors.
METHODS
- C57BL/6N (wild-type = wt, n = 3) and Ink4a/Arf-deficient (Ink4a/Arf−/−, n = 3) female mice were housed under Specific-pathogen-free (SPF) conditions. Tenocytes were isolated by enzymatic digestion using 3 mg/mL Collagenase Type II in culture media (minimal essential medium) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS), 1% L-Glutamine, 100 U/mL penicillin and 0.1 mg/mL Streptomycin for 6 h. After washing with PBS (centrifugation for 5 min at 400 g), cells were cultivated in culture media at 37°C and 5% CO2.
- Western blot analysis. Western blotting (WB) was performed using standard protocols, including extraction of total protein, electrophoresis, membrane transfer, incubation with primary antibody, incubation with secondary antibody, and detection by the imaging system.
- Proliferation assay. Cells were plated in 96-well plates (3000 cells/well). The proliferation rate was measured via DNA fluorescence 24, 48, 72, and 96 h after seeding.
- Cellular senescence/β-galactosidase activity. Cells were plated in 96-well plates (3000 cells/well). Cellular senescence was quantified by measuring senescence-associated β-galactosidase (SA-β-gal) activity 48 h after seeding.
- RNA extraction and quantitative real-time-polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR). RNA extraction by chloroform method. The mRNA levels were calculated by first normalizing using the BestKeeper Index (Housekeeping genes used- GAPDH, 36B4, Rps18) and then using the 2^ct∆ method.
- Histology. Following formalin fixation, the 3D tendon-like constructs were removed, dried, and embedded in paraffin. Paraffin-embedded 2-µm sections were stained with hematoxylin and eosin G.
- Browse our recommendations
With extensive experience and state-of-the-art technologies, Creative Bioarray offers a range of services related to immortalized cells, including Cell Proliferation Assay Services, DNA/RNA Extraction Services, Immunohistochemistry (IHC), Immunofluorescence (IF) Services, Special Staining Services, and others. We have developed the most comprehensive immortalized cell lines comprising human-immortalized cells, mouse-immortalized cells, and other immortalized cells.
RESULTS
- The proliferation rates of Ink4a/Arf−/− cells at the intermediate and higher passage remained consistently high. Ink4a/Arf−/− tenocytes proliferated even faster than wt controls and Ink4a/Arf−/− cells at a low passage. The viability of Ink4a/Arf−/− tenocytes was not affected by the freeze-thaw cycle and remained significantly higher than the viability of wt cells. Cell morphology remained unchanged, and tenocytes maintained their fusiform appearance.
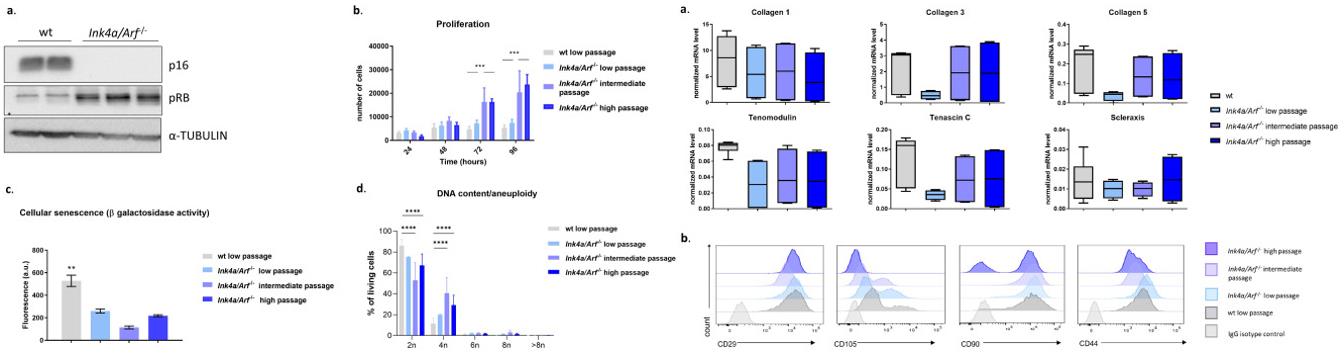 Fig. 1 Left: Characterization of Ink4a/Arf−/− compared to wild-type (wt) tenocytes; Right: Tenocytes from Ink4a/Arf−/− mice in passage exhibit tenogenic characteristics.
Fig. 1 Left: Characterization of Ink4a/Arf−/− compared to wild-type (wt) tenocytes; Right: Tenocytes from Ink4a/Arf−/− mice in passage exhibit tenogenic characteristics.
- The expression of tenocyte markers (collagen type 1 (Col1), Col3, Col5, Scleraxis (Scx), Tenomodulin (Tnmd) and Tenascin-C (Tnc)) expression of Ink4a/Arf−/− cells at low, intermediate, and high passage remained stable at all time points investigated and equivalent to wt cells. Histological analysis confirmed the tendon structure of the 3D constructs characterized by a longitudinal arrangement of extracellular matrix (ECM) with cells scattered therein arranged parallel to the fibers irrespective of the phenotype and passage number.
SUMMARY
This study establishes an immortalized tenocyte cell line from Achilles tenocytes isolated from Ink4a/Arf deficient mice (Ink4a/Arf−/−). The immortalized tenocytes behave like their wild-type primary counterparts in monolayer and 3D culture but in contrast to wild-type primary cells preserve their proliferation potential and tenogenic properties even during long-term culture and after freeze-thaw cycles, thus providing a valuable in vitro alternative to animal models for tendon research.
RELATED PRODUCTS & SERVICES
Reference
- Oreff GL, et al. (2023). "Immortalized murine tenocyte cells: a novel and innovative tool for tendon research." Sci Rep. 13 (1), 1566.