Combined Immunohistochemical Labeling and ISH Protocol to Colocalize mRNA and Protein
GUIDELINE
- Sensitive techniques developed to detect biologically relevant proteins at the mRNA and protein levels have been major research tools in basic and applied biomedical research. The combination of these two techniques has been particularly valuable when the biological protein being studied is a secreted cell product that can bind to components of the extracellular matrix or receptors on target cells within the same tissue.
- If it is important to determine which of the cellular components of the tissue under study is producing the biological protein, the combination of in situ hybridization to detect mRNA and immunohistochemical labeling to detect the protein offers the ability to distinguish between the cells responsible for the production of the protein and its target cells.
METHODS
Generation of Riboprobe
- Restrict cDNAs to a size equal to or less than 2000 bp within the coding sequence, using appropriate restriction endonucleases.
- Insert cDNA into an appropriate vector, e.g., SP72, pGEM 3, pGEM 7z.
- Transform an appropriate strain of E.coli using the calcium chloride procedure.
- Select colonies, grow bacteria, and make plasmid DNA mini-preparations.
- Check the suitability of selected clones by restriction endonuclease digests of plasmid DNA to confirm the presence of the correct sized insert.
- Make large-scale preparation of plasmid DNA using a kit.
- Recheck cDNA by restriction endonuclease digests to confirm the presence of the correct insert.
- cDNA fragments cloned into the plasmid vector were linearized using appropriate restriction endonucleases in such a manner that the cDNA insert could be transcribed into an RNA copy from either the SP6 or T7 RNA polymerase promoters without including any vector sequence.
- Generate riboprobes using a commercial riboprobe generation kit containing either biotin-labeled UTP (Gibco-BRL) or digoxigenin-labeled UTP as part of the nucleotide mix. This results in biotin- or digoxigenin-labeled riboprobes that are a copy of either the sense or antisense strand of the cDNA.
- Remove template DNA with an RNase-free DNase and unincorporated nucleotides by passage through affinity columns.
- Precipitate riboprobes in 2 M LiCl2 in 100% ethanol and resuspend in diethylpyrocarbonate (DEPC)-treated water.
- Confirm labeling with biotin or digoxigenin by dot-blot hybridization and appropriate size by Northern blot analysis.
Hybridization
- Place slides in 0.2 N HCl for 20 min at room temperature. Rinse sections in DEPC-treated water for 5 min in two changes.
- Digest slides with 50 μg/mL of proteinase K for 30 min at 37°C. Rinse sections in DEPC-treated water for 5 min in two changes.
- Incubate sections with 0.1 M Tris-HCl, 0.2 M glycine solution, pH 7.2, for 10 min at room temperature followed by rinsing in DEPC-treated water.
- Rinse sections in 2×SSC solution for 5 min (two changes).
- Cover sections in prehybridization buffer and incubate for 90-120 min at 50°C.
- Remove the prehybridization solution and replace it with the desired concentration of riboprobe in the prehybridization buffer.
- Cover each section with an acid-cleaned coverslip, seal with nail polish, and incubate overnight at 50°C.
- Remove coverslips with a scalpel blade. Wash slides twice in 2×SSC solution for 10 min, 1×SSC solution for 10 min, 0.1×SSC solution for 15 min at 45°C, in 0.1×SSC for 5 min at room temperature, and finally in water for 5 min at room temperature. The sections are then ready for biotin or digoxigenin detection.
Detection of in situ hybridization
- Wash slides in hybridization buffer I solution for 5 min.
- Block nonspecific binding by incubating the slides in 10% normal sheep serum diluted in hybridization buffer I for 45 min.
- Incubate sections with anti-digoxigenin alkaline phosphatase-labeled antibody in 1:500 dilution in hybridization buffer containing 10% normal sheep serum.
- Wash sections with hybridization buffer I and equilibrate in hybridization buffer solution III for 2 min.
- Incubate sections with the color substrate, NBT in the dark for 1-4 h. Stop color development by washing slides in water.
Immunohistochemical labeling for protein
- Cover with normal sheep serum for 2 h to block nonspecific binding, then wash in TBS buffer.
- Incubate sections overnight at room temperature with the primary antibody (mouse IgG).
- Wash sections in TBS buffer the incubate with secondary sheep anti-mouse antibody for 60 min.
- Wash sections in TBS buffer, then incubated with alkaline phosphatase anti-alkaline phosphatase complex for 60 min at room temperature.
- Wash sections in TBS buffer, then apply a chromogenic substrate to the sections for 15 min.
- Stop the color development by washing slides in water.
- Counterstain the sections with dilute hematoxylin and mount in aqueous mount ant.
- Quantitation can be performed on hybridized sections.
Creative Bioarray Relevant Recommendations
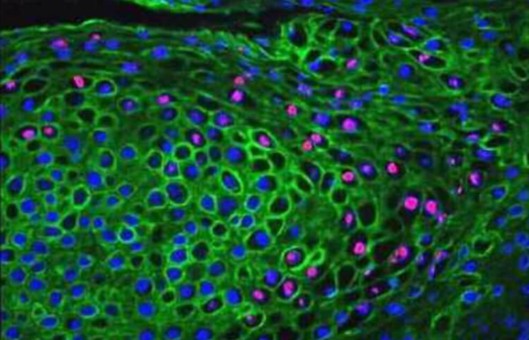
- From practical applications, we provide ImmunoFISH Analysis (FISH+IHC). ImmunoFISH is a combination of a standard immunohistochemical stain with a standard FISH technique, which provides additional information about the association between transcription level, cellular localization, and protein expression in individual cells.
NOTES
- Proteinase K is necessary to expose epitopes in formalin-fixed tissues and to permeabilize tissue to allow access to the riboprobes with the in situ hybridization step. Alternatives include pepsin digestion and microwave retrieval steps which, in our hands, are less reliable than the use of proteinase K digestion.
- Although silver enhancement of the DAB reagent can be used to produce a darker stain, it adds little to the procedure.
RELATED PRODUCTS & SERVICES
Reference
- Asp J, et al. (2006). "Nonradioactive in situ hybridization on frozen sections and whole mounts." Methods Mol Biol. 326, 89-102.