Assessment of MDPV Permeability Across the Caco-2 Monolayer
International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023 Jan 31; 24 (3): 2680.
Authors: Almeida AS, Silva B, Remião F, Fernandes C.
INTRODUCTION
3,4-Methylenedioxypyrovalerone (MDPV) is a widely studied synthetic cathinone heterocycle mainly concerning its psychoactive effects. It is a chiral molecule and one of the most abused new psychoactive substances worldwide. Enantioselectivity studies for MDPV are still scarce and the extent to which it crosses the intestinal membrane is still unknown.
Herein, an in vitro permeability study was performed to evaluate the passage of the enantiomers of MDPV across the Caco-2 monolayer. To detect and quantify MDPV, a UHPLC-UV method was developed and validated. Acceptable values within the recommended limits were obtained for all evaluated parameters (specificity, linearity, accuracy, limit of detection (LOD), limit of quantification (LOQ), and precision). The enantiomers of MDPV were found to be highly permeable across the Caco-2 monolayer, which can indicate a high intestinal permeability. Enantioselectivity was observed for the Papp values in the basolateral (BL) to apical (AP) direction. Furthermore, efflux ratios are indicative of efflux through a facilitated diffusion mechanism.
METHODS
- Twenty blank samples (HBSS (+/+)) were injected into the UHPLC to detect the presence of potential co-eluting peaks that could affect the analysis by the tested method. To evaluate linearity, calibrators with concentrations ranging from 0.5 to 500 μM of MDPV (0.5, 1, 5, 10, 25, 50, 100, 250, and 500 μM) were independently prepared on five different days and injected into the UHPLC to obtain a calibration curve each day.
- To evaluate stability, three different calibrators within the linear concentration range (10 (low), 100 (medium), and 500 (high) μM) were prepared and injected into the UHPLC. The remaining volume of each calibrator was divided into several vials and further stored at different temperatures (room temperature, 4°C, -20°C, and -80°C) for 6 weeks (the same storage time of the samples obtained from the permeability assay with Caco-2 cells).
- The Caco-2 cell line was routinely maintained in DMEM supplemented with 10% FBS, 1% penicillin/streptomycin solution, and 1% non-essential amino acids at 37°C in a humidified atmosphere of 5% CO2 with the medium changed every two days. Subcultures were obtained by trypsinization with a 0.25% trypsin/EDTA solution. For all assays, cells were used between the 14th and 20th passages. MDPV cytotoxicity for the Caco-2 cell line was evaluated through the NR assay.
- For the in vitro permeability assay, Caco-2 cells were seeded on polycarbonate trans-well inserts (12-well, 0.4 μm pores) using a density of 120,000 cells/cm2 and cultivated for twenty-one days to allow the development of a differentiated monolayer. TEER was measured to control the integrity of the monolayers for twenty-one days. After twenty-one days, the cells were incubated with 300 µM of each enantiomer of MDPV (in HBSS (+/+)). The assay was performed for both AP to BL and BL to AP directions.
- Browse our recommendations
| Product/Service Types | Description |
| In Vitro DMPK Services | Creative Bioarray provides a variety of in vitro ADME/PK services, including high-throughput ADME screening, in vitro binding, in vitro metabolism, in vitro permeability, and transporter assays. |
| In Vitro Permeability and Transporters | Creative Bioarray provides several in vitro permeability and transporter assays to evaluate drug permeability and predict drug absorption and distribution. |
| Caco-2 Permeability Assay | Creative Bioarray is offering Caco-2 permeability assays to help determine the absorption and the bioavailability of drug candidates, facilitating the lead optimization process in drug discovery. |
| Cell Line Testing and Assays | Creative Bioarray offers a wide range of cell line testing and assays from cell viability and proliferation to cellular phosphorylation assays. |
| Cell Viability Assays | Creative Bioarray offers a wide selection of cell viability assays for drug screening and cytotoxicity tests of chemicals. |
RESULTS
- The optimum wavelength selected for the detection and quantification of MDPV was 236 nm. In the optimized chromatographic conditions, a good resolution was obtained for the peak of MDPV being eluted in less than 5 min.
- To evaluate specificity, twenty blank samples containing only an HBSS (+/+) solution were injected and analyzed. No interference was observed between 4 and 5 min, the retention time corresponding to MDPV. For the evaluation of linearity, five curves in a concentration range of 0.5-500 µM, independently prepared on five different days, were used to obtain the average linear regression equation and coefficient of determination (r2). An average r2 of 0.9999 was found.
- After injecting three selected calibrators contained in the linear concentration interval (6 (low), 40 (medium), and 300 (high) μM) along with a calibration curve, the experimental concentrations of each calibrator were calculated through the linear regression equation of the curve. Percentages between 102% and 109% were obtained. The results showed coefficients of variation (CV) between 2.88% and 13.87%. A LOD of 0.063 µM and a LOQ of 0.190 µM were calculated for this method.
- The concentration of 300 µM was selected for the permeability assay. The trans-epithelial electrical resistance (TEER) was monitored for 21 days after seeding. Significant TEER values were observed from day 6 (over 500 Ω·cm2). They gradually increased to approximately 1000 Ω·cm2 until day 18, after which they remained constant until day 21 with a final average value of 1052 Ω·cm2.
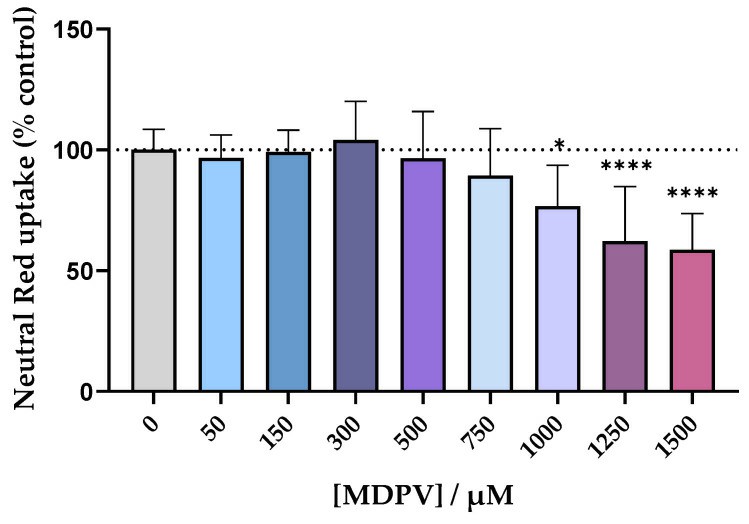
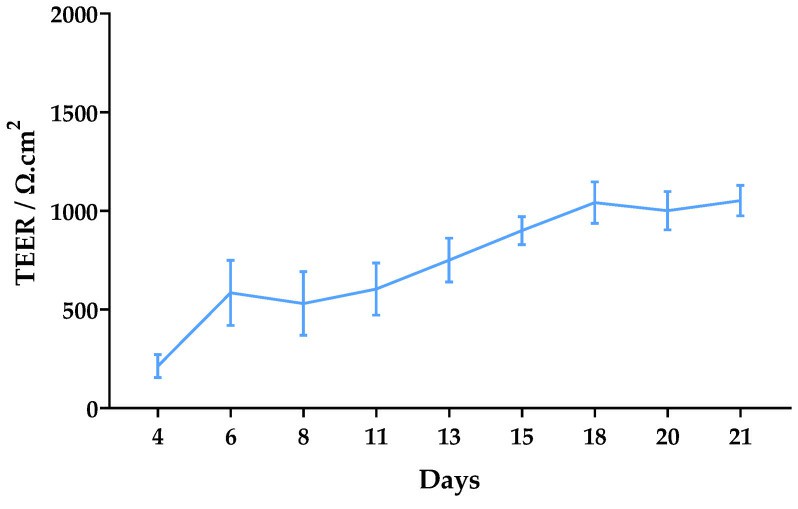
Fig. 1 Left: Cytotoxicity evaluation in Caco-2 cells exposed to racemic MDPV (0-1500 µM) for 24 h performed by the NR assay. Right: Monitoring of TEER values from day 4 to day 21 after seeding of Caco-2 cells.
- Cells were exposed to 300 µM of each enantiomer on day 22 after seeding. Samples were collected in the chosen time points (40, 60, 90, 120, 180, 240, and 300 min) from the receiver compartment. The results were expressed as the percentage of cumulative quantity in the initial quantity. A considerable percentage of passage was observed from the first time point (40 min) in both enantiomers for both directions, increasing significantly during the rest of the interval. No statistically significant difference was found between the enantiomers in any of the time points for both directions.
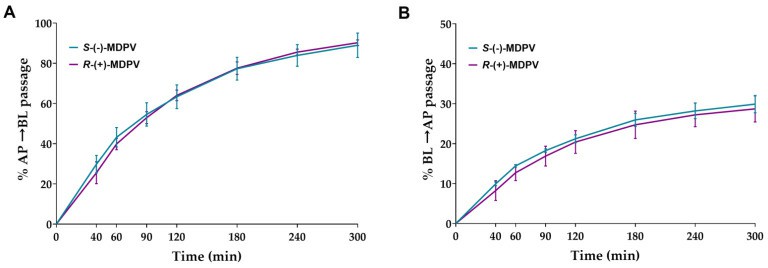 Fig. 2 Percentage of the cumulative quantity of the enantiomers of MDPV (S-(-)-MDPV and R-(+)-MDPV) transported through the Caco-2 monolayer in each time point for the AP to BL direction (A) and BL to AP direction (B).
Fig. 2 Percentage of the cumulative quantity of the enantiomers of MDPV (S-(-)-MDPV and R-(+)-MDPV) transported through the Caco-2 monolayer in each time point for the AP to BL direction (A) and BL to AP direction (B).
SUMMARY
A UHPLC-UV method was successfully validated for the detection and quantification of MDPV in the transport buffer of this study, HBSS (+/+). The results showed that the enantiomers of MDPV were highly permeable across the Caco-2 monolayer. Enantioselectivity was found between the enantiomers in the Papp values obtained for the BL to AP direction, suggesting the involvement of a transport protein. Efflux ratios indicate that a facilitated diffusion mechanism should be accepted for the efflux of the enantiomers of MDPV.
RELATED PRODUCTS & SERVICES
Reference
- Almeida AS, et al. (2023). "Assessment of the Permeability of 3,4-Methylenedioxypyrovalerone (MDPV) across the Caco-2 Monolayer for Estimation of Intestinal Absorption and Enantioselectivity." Int J Mol Sci. 24 (3): 2680.