Human Conjunctival Fibroblasts (HConF)
Cat.No.: CSC-7801W
Species: Human
Source: Conjunctiva; Eye
Cell Type: Fibroblast
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
Human conjunctival fibroblasts (HConF) are primary fibroblast cells isolated from the healthy conjunctival tissue of adult donors, typically from the bulbar and palpebral conjunctiva that line the ocular surface. Morphologically, HConF cells exhibit the classical spindle‑shaped, fibroblastic morphology in two‑dimensional culture and form an interlaced network upon confluence. They express canonical mesenchymal markers such as vimentin, fibronectin, collagen I and IV, and acquire α‑smooth muscle actin (α‑SMA) upon activation. Importantly, these cells lack epithelial cytokeratins, confirming their non‑epithelial lineage and origin.
Functionally, HConF are highly sensitive to various profibrotic stimuli. Transforming growth factor‑β (TGF‑β1/β2) robustly up‑regulates extracellular‑matrix components (collagen I/IV, fibronectin) and α‑SMA, recapitulating conjunctival fibrosis. HConF also respond to other fibrotic stimuli and signaling pathways including fibroblast growth factor‑2, Wnt/β‑catenin, and PLC‑γ to regulate proliferation, migration, and contractility. Metabolic profiling revealed modest changes in oxidative phosphorylation and glycolysis under fibrotic stimulation, particularly in three‑dimensional spheroid models.
Taken together, these characteristics make HConF an attractive and multipurpose platform for exploring ocular surface fibrosis, allergic conjunctivitis, and drug screening. HConF are used in 2D and 3D cultures, as well as co‑culture systems with epithelial or immune cells and in gene‑silencing studies to map out signaling networks and identify therapeutic targets. As such, HConF are invaluable in both basic ophthalmic research and translational studies aiming to address postoperative scarring and chronic inflammatory diseases of the eye.
The sGC Stimulator BAY 41-2272 Has No Effect on Cell Viability and Inhibits TGFβ1-Induced Proliferation of Human Conjunctival Fibroblasts
Conjunctival fibrosis is an important pathological outcome in a number of ocular diseases that is the result of chronic inflammation leading to aberrant wound healing and scar formation. Fioretto et al. assessed the in vitro impact of sGC stimulation with BAY 41-2272 on TGFβ1-mediated profibrotic activation of human conjunctival fibroblasts.
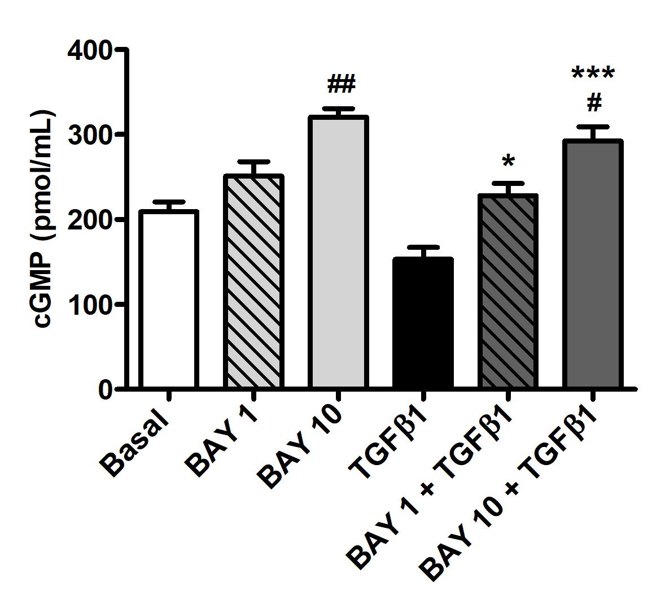
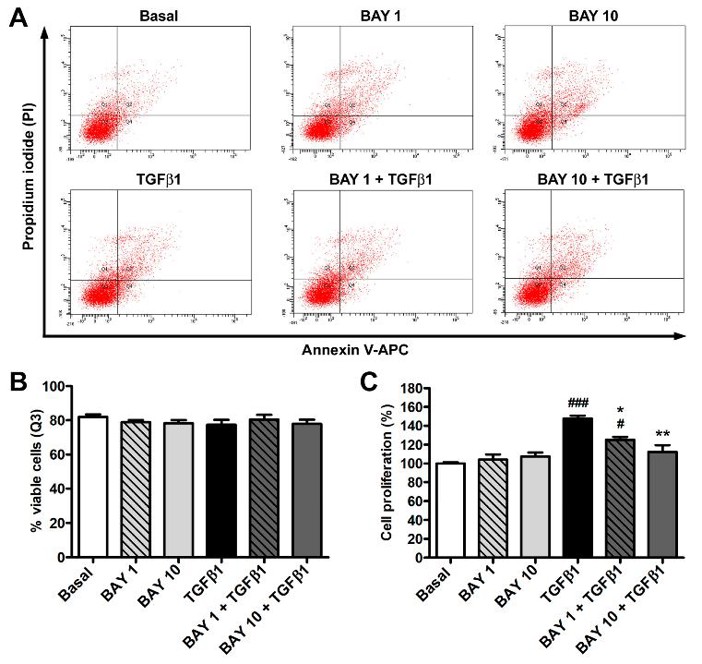
Figure 1 Stimulation of sGC with BAY 41-2272 robustly increased cGMP levels in human conjunctival fibroblasts. To exclude potential side effects of BAY 41-2272, they used Annexin V/PI flow cytometry to examine cell viability. They did not observe any significant differences in the number of viable, early apoptotic, late apoptotic, and necrotic cells in all conditions (Fig. 2A, B), suggesting that treatment with recombinant human TGFβ1, BAY 41-2272 (1 μM or 10 μM), alone or in combination, did not impact viability. The WST-1 assay demonstrated that TGFβ1 alone enhanced proliferation while BAY 41-2272 alone did not (Fig. 2C). In contrast, pre-treatment of fibroblasts with BAY 41-2272 before the TGFβ1 challenge blocked TGFβ1-induced proliferation, with only 10 μM BAY 41-2272 being sufficient to preserve basal rates of proliferation (Fig. 2C). Based on these data, they only used 10 μM BAY 41-2272 in thier subsequent experiments.
Ask a Question
Write your own review