Porcine Skeletal Muscle cells
Cat.No.: CSC-C0523Z
Species: Pig
Source: Skeletal Muscle
Morphology: Polygonal
Culture Properties: Adherent
Cell Type: Skeletal Muscle Cell
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
Note: Never can cells be kept at -20°C.
Porcine skeletal muscle cells (myoblasts and myotubes), derived from the muscle tissue of domestic pigs, are primary cells characterized by their capacity to proliferate, differentiate, and fuse into multinucleated myotubes that exhibit contractile properties. These cells share significant physiological, metabolic, and anatomical similarities with human skeletal muscle, making them a highly relevant model system. In current research, they are widely used in two main areas: biomedicine and cellular agriculture. In biomedicine, they serve as a critical in vitro platform for studying muscle physiology, metabolic diseases like insulin resistance, and for testing therapeutic compounds, offering a more human-relevant alternative to rodent models. Simultaneously, they are the fundamental building blocks for cultivated pork production, where they are cultured and structured to manufacture meat products, aiming to address sustainability and ethical concerns of conventional livestock farming.
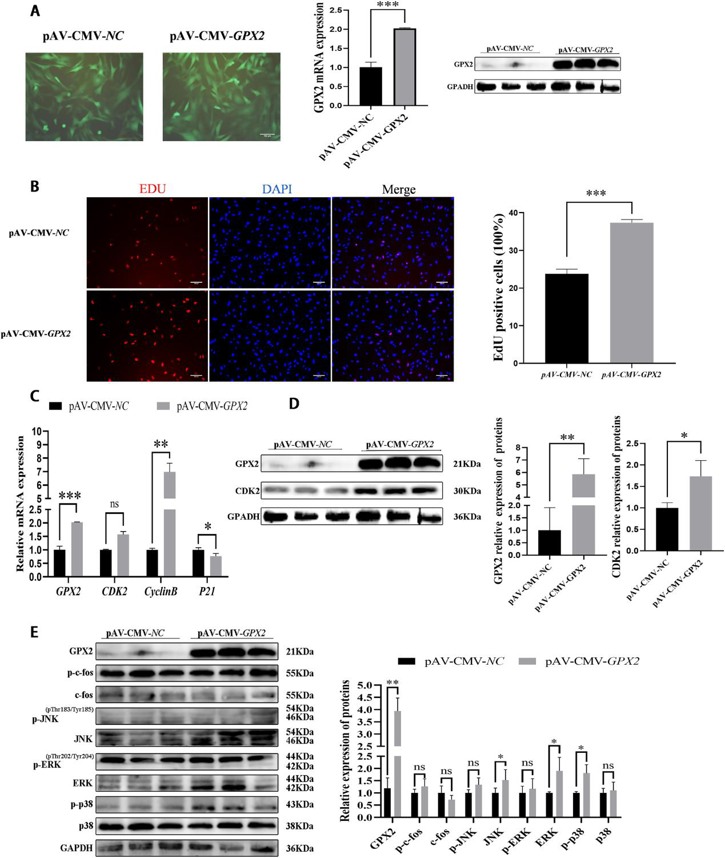
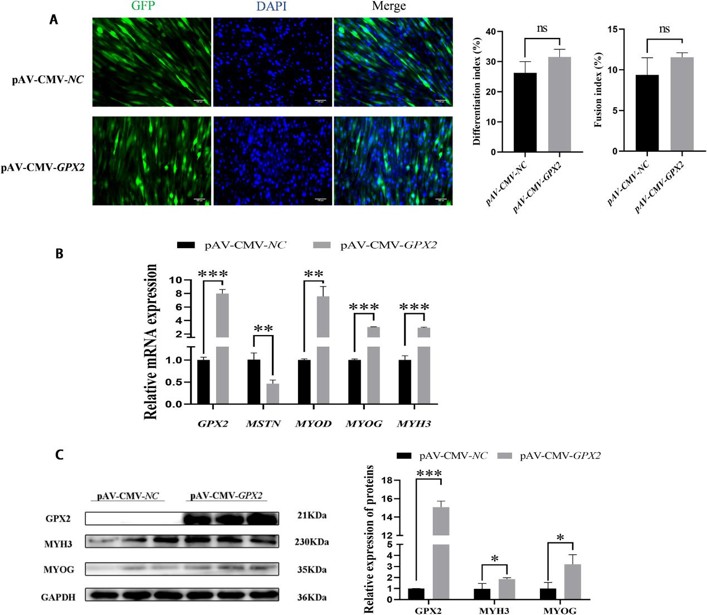
Overexpression of GPX2 Gene Regulates the Development of Porcine Preadipocytes and Skeletal Muscle Cells
Glutathione peroxidase 2 (GPX2) is a selenium-dependent enzyme and protects cells against oxidative damage. Recently, GPX2 has been identified as a candidate gene for backfat and feed efficiency in pigs. However, it is unclear whether GPX2 regulates the development of porcine preadipocytes and skeletal muscle cells. In this study, adenoviral gene transfer was used to overexpress GPX2. The findings suggest that overexpression of GPX2 gene inhibited proliferation of porcine preadipocytes. And the process is accompanied by the reduction of the p-p38. GPX2 inhibited adipogenic differentiation and promoted lipid degradation, while ERK1/2 was reduced and p-p38 was increased. Proliferation of porcine skeletal muscle cells was induced after GPX2 overexpression, was accompanied by activation in JNK, ERK1/2, and p-p38. Overexpression methods confirmed that GPX2 has a promoting function in myoblastic differentiation. ERK1/2 pathway was activated and p38 was suppressed during the process. This study lays a foundation for the functional study of GPX2 and provides theoretical support for promoting subcutaneous fat reduction and muscle growth.
Heat inactivates the complement system. Activated complement is involved in lysing cellular events, stimulating smooth muscle contraction, histamine release from cells and platelets, and activation of lymphocytes and macrophages. Heat inactivated serum is recommended for immunological studies, culturing ES cells, insect cells and smooth muscle cells.
Ask a Question
Average Rating: 4.0 | 1 Scientist has reviewed this product
Efficient process
I had a great experience with cell culture products. The process was easy to understand and very efficient.
02 Aug 2023
Ease of use
After sales services
Value for money
Write your own review