Porcine Small Intestinal Epithelial Cells
Cat.No.: CSC-C9253J
Species: Pig
Source: Small Intestine; Intestine
Cell Type: Epithelial Cell
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
Porcine Small Intestinal Epithelial Cells are epithelial cells isolated from the small intestine of pig (Sus scrofa). They are a physiologically relevant in vitro model of gastrointestinal epithelium. A well-characterized representative of this cell type is IPEC-J2 cell line, originally isolated from mid-jejunum of neonatal, unsuckled piglet which is non-transformed and non-tumorigenic and has many characteristics of normal intestinal epithelium. These cells are epithelial in morphology, and form polarized monolayers with tight junctions and high transepithelial electrical resistance when grown on permeable supports. IPEC-J2 cells express innate immune receptors and cytokines and therefore, are a useful cell model for studying host-pathogen interactions and barrier function in vitro.
Porcine small intestinal epithelial cells are commonly used in studies of intestinal transport, permeability and barrier function, intestinal innate immunity, nutrient uptake, and enteric infection, as their properties are similar to those of primary intestinal epithelial cells, and they are more physiologically relevant to humans than are most rodent models. This cell line is commonly used for studies of bacterial and viral pathogen interactions including Salmonella, E. coli, and rotaviruses as well as for testing of probiotics, toxins and drug permeability across the intestinal epithelium.
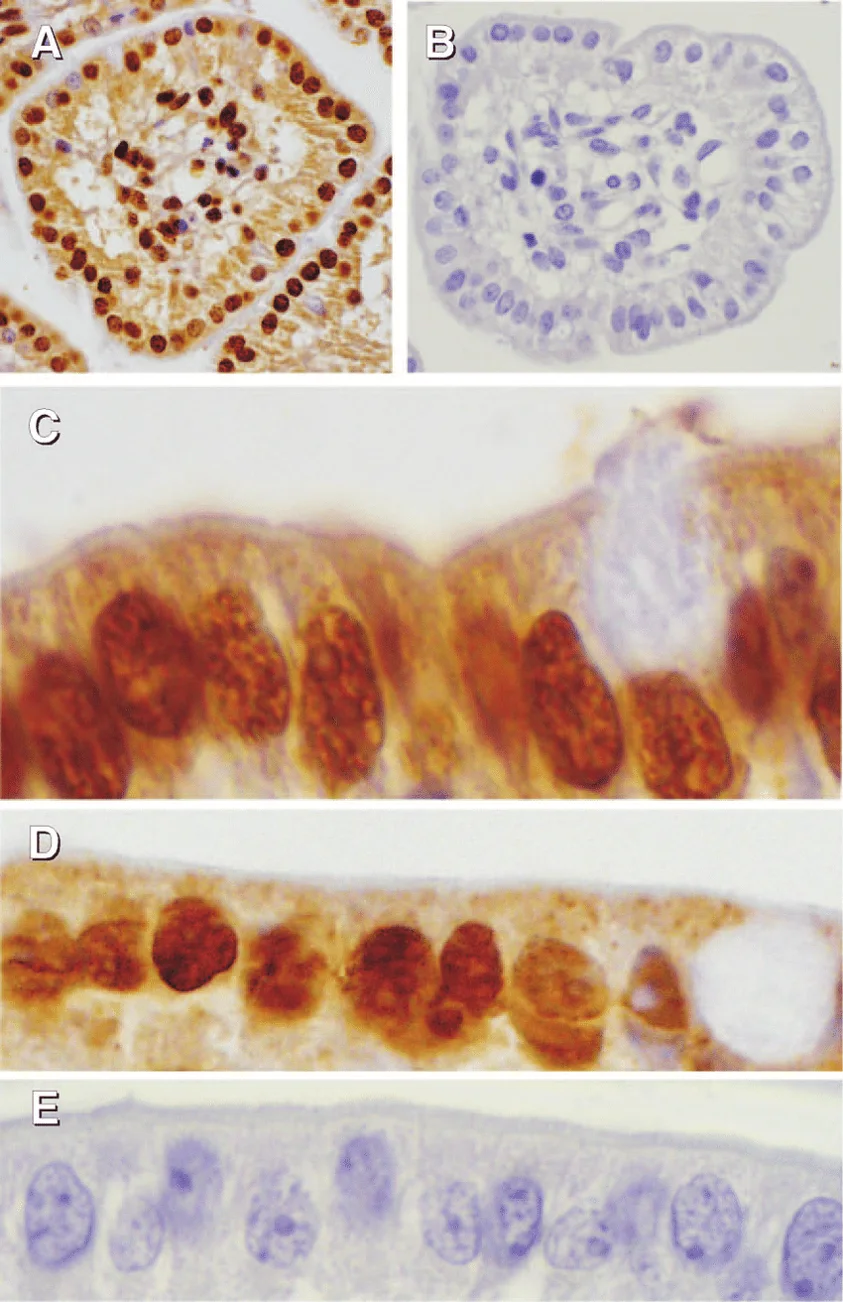
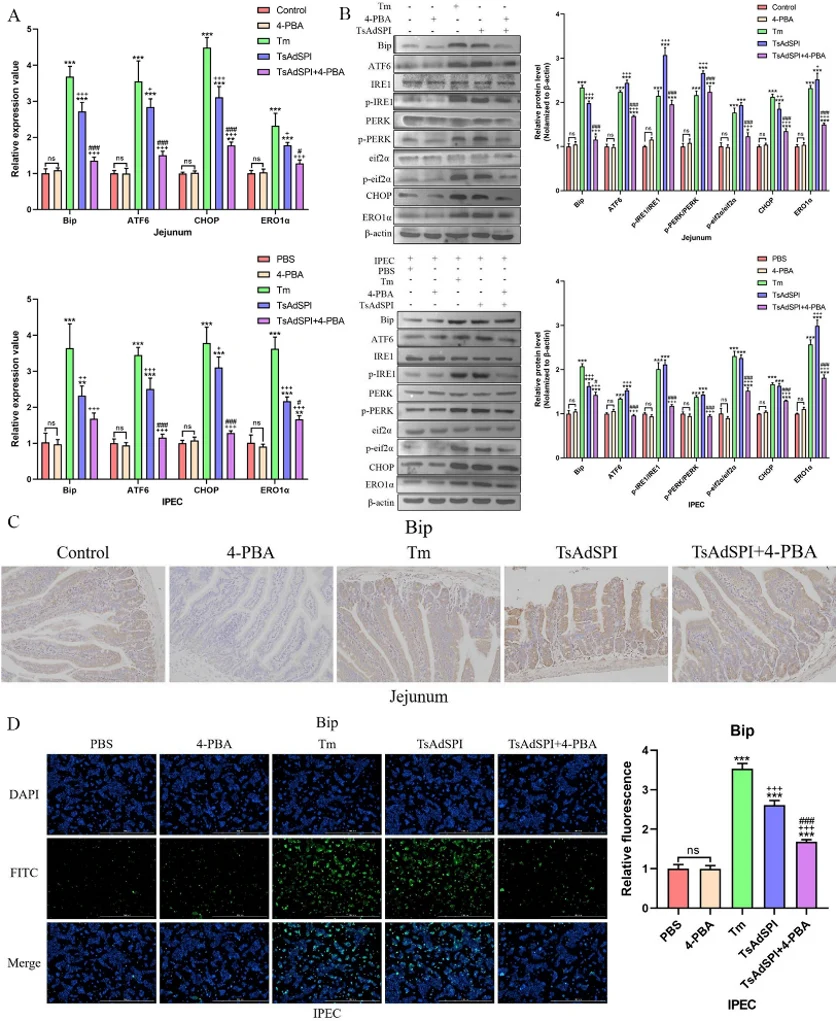
TsAdSPI Induced ERS in IECs
Endoplasmic reticulum stress (ERS) and oxidative stress (OS) are adaptive responses to stressors. While Trichinella spiralis is known to induce ERS and OS in hosts, their relationship remains unclear. Zhen's team investigated whether T. spiralis-secreted serpin-type serine protease inhibitor (TsAdSPI) regulates the relationship between ERS and OS in the host intestine.
In vivo and in vitro experiments were conducted with mice jejunum and porcine small intestinal epithelial cells (IECs) divided into 10 groups: control, PBS, 4-PBA, Tm, TsAdSPI, and TsAdSPI + 4-PBA. qPCR showed no significant difference in ERS-promoting gene expression (Bip, ATF6, CHOP, ERO1α) between the control, PBS, and 4-PBA groups (Fig. 1A). However, the Tm and TsAdSPI groups had significantly higher ERS-related transcription levels. The TsAdSPI + 4-PBA group showed inhibited ERS-related index expression compared to the TsAdSPI group. Western blot results indicated significantly higher expression of ERS-promoting proteins (Bip, ATF6, p-IRE1/IRE1, p-PERK/PERK, p-eif2α/eif2α, CHOP, ERO1α) in the TsAdSPI group than in the control, PBS, and 4-PBA groups (Fig. 1B). IHC showed that Bip was mainly expressed in IECs, with the highest expression in the TsAdSPI group (Fig. 1C). IF results also revealed significantly higher Bip expression in the TsAdSPI group compared to the PBS and 4-PBA groups (Fig. 1D). These findings suggest that TsAdSPI induces ERS in IECs.
When significant culture contamination occurs, the investigator may attempt to eliminate or control the contamination. First, determine whether the contaminant is bacterial, fungal, mycoplasma or yeast, isolate the contaminated cells from other cell lines, disinfect culture vessels and ultra-clean tables with laboratory disinfectant, and check HEPA filters. High concentrations of antibiotics and antimycotics may be toxic to some cell lines, and thus, dose-response experiments are done to determine the dose levels at which antibiotics and antimycotics produce toxicity. This is especially important when using antibiotics such as amphotericin B and antimycotics such as tylosin.
Ask a Question
Average Rating: 5.0 | 1 Scientist has reviewed this product
Subtlety
The goods we receive correspond to the list, and they have not made any mistakes in this regard.
12 Apr 2023
Ease of use
After sales services
Value for money
Write your own review