Porcine Kidney Epithelial Cells
Cat.No.: CSC-C9246J
Species: Pig
Source: Kidney
Cell Type: Epithelial Cell
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
Porcine Kidney Epithelial Cells are primary or immortalized epithelial cells isolated from the kidney of healthy pigs (Sus scrofa). The cells exhibit morphology, physiology and molecular characteristics similar to human renal epithelial cells and provide an appropriate in vitro model system for studying renal biology and translational research. In many areas of translational research porcine derived renal epithelial cells have been used as a useful in vitro model where human relevance is of importance and primary human material is limited.
Porcine kidney epithelial cells have the expected morphology of epithelial cells being polygonal with prominent cell-cell junctions and contact inhibited adherent growth. In typical culture conditions, the cells will form cohesive monolayers and stable proliferation in appropriate renal epithelial cell media containing growth factors and serum. These cells express epithelial markers including cytokeratins, E-cadherin and tight junction proteins.
Functionally, porcine kidney epithelial cells also express a number of renal-specific characteristics including ion transport, solute reabsorption and metabolic activity in line with proximal or distal tubular epithelium depending on isolation protocol. Porcine kidney epithelial cells are often used to model renal physiology, nephrotoxicity, and drug transport, and for use in studies of host-pathogen interactions involving the kidney. Porcine kidney epithelial cells are also extensively used in virology, vaccine manufacture, and toxicology as they are easily susceptible to viral infection and provide a stable biological response.
UL13 Triggers FTO-Dependent Suppression of ISG Expression in Primary Porcine Epithelial Cells
FTO mediates RNA demethylation, influencing mRNA splicing, export, translation, and degradation. Here, Verhamme et al. studied FTO's role in antiviral responses using primary epithelial cells infected with PRV.
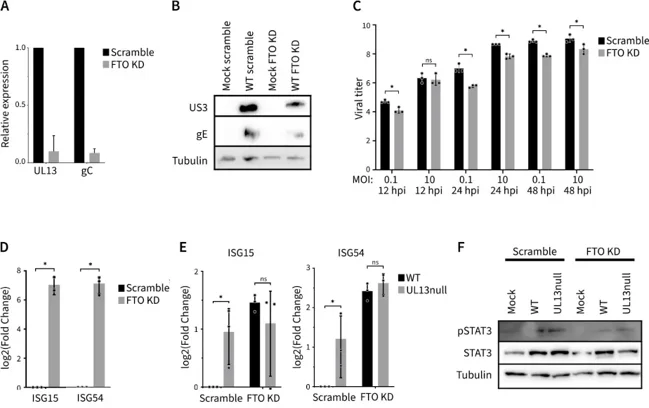
They found that PRV's UL13 kinase phosphorylates FTO in ST cells, leading to FTO-dependent suppression of antiviral interferon-stimulated genes (ISGs). Given that ST cells, like many immortalized cell lines, are defective in type I IFN production, the potential impact of FTO and/or its modulation by PRV on the production of type I IFN and ISGs cannot be readily evaluated in this cell type. Therefore, they examined the effects of FTO knockdown on PRV mRNA and protein production in IFN-competent primary porcine kidney epithelial cells (PPK). In PPK cells, FTO depletion significantly reduced viral RNA and protein production (Fig. 1A and B). Titration of progeny virus produced in PRV-infected PPK cells showed that FTO knockdown by siRNA resulted in lower virus titers compared to cells treated with scrambled siRNA (Fig. 1C). To investigate whether the impact of FTO knockdown on PRV protein production and virus titers in PPK cells correlates with differences in ISG expression, we assessed the effects of siRNA-mediated FTO knockdown on ISG expression in PPK cells. Specifically, they analyzed the expression of ISG15 and ISG54 using RT-qPCR. FTO knockdown increased the expression of these transcripts compared to cells treated with control scrambled siRNA, indicating that FTO is involved in suppressing ISG expression (Fig. 1D). This observation aligns with a recent report showing a suppressive effect of FTO on ISG expression.
Experiments have shown that heat-inactivated serum, properly treated, is not required for most cells. Serum treated in this way has only a minor promotion of cell growth, or no effect at all, even if the cell growth rate is usually reduced because the heat treatment affects the quality of the serum. The formation of precipitates is significantly increased in heat-treated sera, and these precipitates look like "black dots" when viewed under an inverted microscope, often leading researchers to believe that the sera are contaminated, while placing the sera in a 37°C environment increases the precipitates even more, leading researchers to believe that the microorganisms are dividing and amplifying.
Ask a Question
Average Rating: 5.0 | 1 Scientist has reviewed this product
Good quality and low price
In addition to helping us with our research, this cellular product is cost effective compared to similar products.
18 Apr 2023
Ease of use
After sales services
Value for money
Write your own review