Human Cardiac Fibroblasts-adult ventrical (HCF-av)
Cat.No.: CSC-7816W
Species: Human
Source: Heart
Cell Type: Fibroblast
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
Human Cardiac Fibroblasts - Adult Ventricular (HCF-av) are primary fibroblast cells derived from the ventricular myocardium of adult human heart. Cardiac fibroblasts are the most prevalent non-myocyte cell type in the heart and are essential for the structural, mechanical, and extracellular matrix (ECM) homeostasis of the myocardium. In the adult ventricle, they are the primary effector cells for physiological and pathological tissue remodeling.
HCF-av display a typical fibroblast-like, spindle-shaped morphology and express fibroblast markers such as vimentin, fibroblast-specific protein-1 (FSP1), discoidin domain receptor 2 (DDR2) and ECM proteins such as collagen types I and III, and fibronectin. In response to mechanical stretch, inflammatory cytokines or profibrotic mediators such as transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β), HCF-av can differentiate into activated myofibroblasts characterized by increased expression of α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) and enhanced ECM deposition.
HCF-av are extensively employed for cardiovascular research including ventricular fibrosis, cardiac remodeling, and heart failure-associated structural remodeling. They serve as a physiologically relevant in vitro model to study fibroblast signaling pathways, cell-matrix crosstalk, and to assess antifibrotic drugs, cardiotoxicity and regenerative therapeutic strategies for adult human heart disease.
Long-Term Culture of Human Cardiac Fibroblasts Leads to Myofibroblast Transition
Activation of cardiac fibroblasts into myofibroblasts underlies pathological cardiac fibrosis, which can cause arrhythmias and heart failure. Hall et al. sought to determine if the myofibroblast phenotype is reversible in human cardiac fibroblasts cultured on soft substrates or with inhibition of TGF-β receptors.
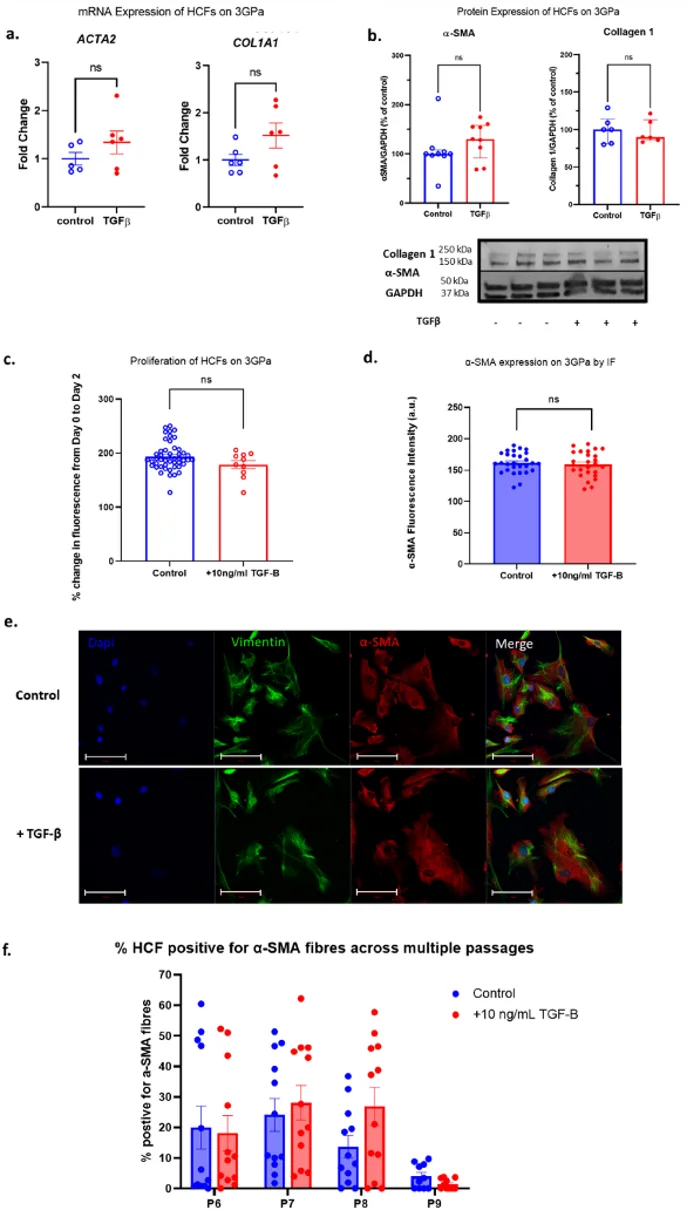
Human cardiac fibroblasts (HCFs) were cultured for up to 10 passages on stiff polystyrene plates (E = 3 GPa) to activate the myofibroblast phenotype. Cells were then treated with 10 ng/mL TGF-β for 2-4 days to induce further activation. Fibroblast activation was indicated by expression of α-SMA and collagen 1. HCFs cultured on stiff substrates for long term had baseline activation; α-SMA expression was confirmed by western blot and immunofluorescence (Fig. 1, panels b, d, e). However, when treated with TGF-β for 4 days, there was no significant increase in expression of α-SMA or collagen 1 at the mRNA (Fig. 1a) or protein level (Fig. 1b) compared to controls. TGF-β had no effect on proliferation (Fig. 1c) or cell size. Immunofluorescence also revealed that ~70% of HCFs were α-SMA positive. There was no significant difference in the percent of α-SMA positive cells with TGF-β treatment (Figs. 1d, f), and secondary antibody controls were used to rule out non-specific binding of the α-SMA antibody. Lack of response to TGF-β was confirmed in HCFs cultured for a range of passages p6-p9 (Fig. 1f). Both the total expression of α-SMA and the percent of α-SMA positive cells did not significantly change throughout long term culture (Fig. 1f). There was a non-significant decrease in α-SMA positive cells with time, which may indicate de-differentiation. This data shows that culturing human cardiac fibroblasts on stiff plastic substrates is sufficient to irreversibly transition into myofibroblasts and TGF-β stimulation is unable to upregulate fibroblast activation.
Check all containers for leakage or breakage. Directly and immediately transfer the cells from dry ice to liquid nitrogen and keep the cells in liquid nitrogen until they are needed for experiments.
Creative Bioarray's Primary Human Cardiac Fibroblasts are isolated from the ventricles of the adult heart.
Ask a Question
Average Rating: 5.0 | 1 Scientist has reviewed this product
Reliable products
I am confident in the integrity of my research data thanks to the reliable cells obtained from Creative Bioarray, and I plan to continue using their products in future projects.
18 Jan 2023
Ease of use
After sales services
Value for money
Write your own review
