Cryopreserved Mammary Luminal Epithelial Cells
Cat.No.: CSC-7669W
Species: Human
Source: Breast
Cell Type: Epithelial Cell
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
Luminal cells line the apical surface of the normal breast duct and have secretory properties. Most breast cancers arise from luminal cells and are heterogeneous in their expression of hormone receptors and ERBB2 expression.
Human Mammary Luminal Epithelial Cells are primary epithelial cells isolated from the luminal compartment of the ducts and alveoli of the human mammary gland. Mammary luminal epithelial cells line the inner surface of the mammary epithelium and are involved in secretory and transport functions. They play an important role in normal breast development, lactation, and hormonal responsiveness. Luminal epithelial cells are a major cellular component of the mammary gland and are central to tissue organization and epithelial homeostasis.
Human mammary luminal epithelial cells have epithelial morphology and express epithelial lineage-specific markers including cytokeratins 8 and 18 (CK8/CK18), epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM), MUC1, and depending on donor status and culture conditions, hormone receptors including estrogen receptor (ER) and progesterone receptor (PR). They retain functional responsiveness to hormonal and growth factor signaling pathways and are highly relevant for mechanistic studies. The cell type is commonly used as an in vitro model for mammary gland biology, epithelial differentiation, cell polarity, and early events of breast tumorigenesis. Human mammary luminal epithelial cells have been used as a model system for hormone-driven signaling, breast cancer initiation, and drug response profiling. They are a physiologically relevant cell type for toxicology and preclinical evaluation of breast-targeted therapies.
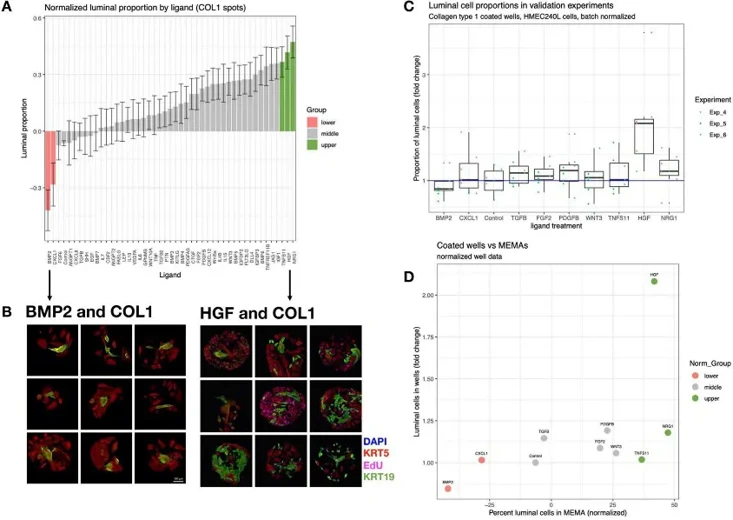
Microenvironment-Mediated Luminal Phenotypes that were Robust to Individual Variation
Microenvironment signals are crucial for cell fate and tissue homeostasis, but understanding their coordinated regulation of cellular phenotype is challenging. Jokela et al. uses a high-throughput microenvironment microarray to identify factors supporting proliferation and maintenance of primary human mammary luminal epithelial cells.
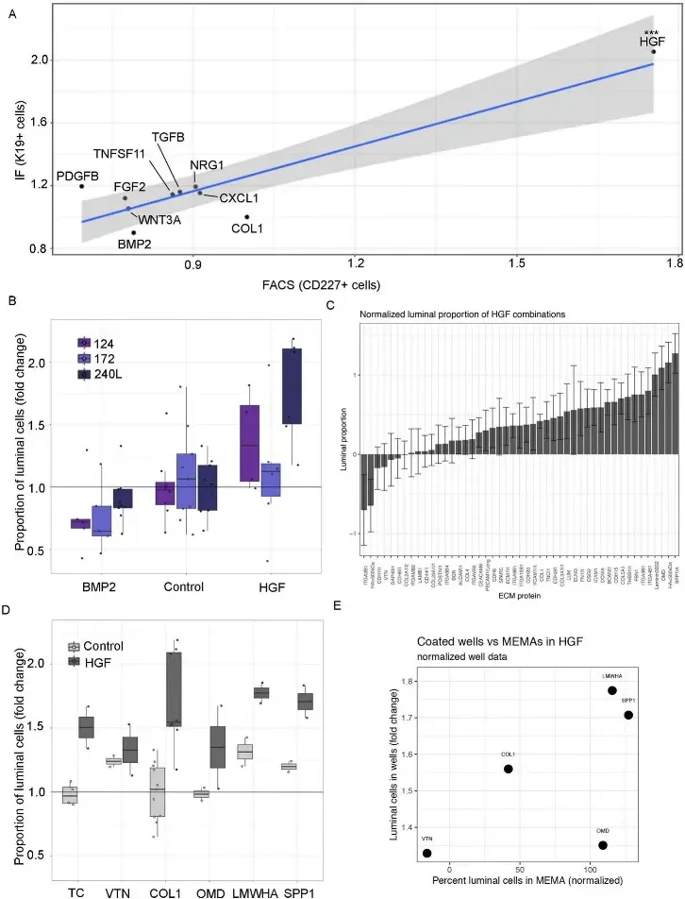
Here, they used a microarray with 2640 unique pairwise signals to identify factors influencing primary human mammary luminal epithelial cells. To replicate key findings from the MEMA screen, human mammary epithelial cells (HMEC) were cultured on collagen type 1 (COL1)-coated plates with significant luminal cell regulatory ligands (BMP2, CXCL1, TGFbeta, FGF2, PDGFbeta, Wnt3a, TNSF11, HGF, and NRG1) until 90% confluency (5-6 days). The proportion of KRT19+ cells generally matched MEMA results (Fig. 1C, D). Flow cytometry confirmed that BMP2 decreased and HGF increased luminal proportions (Fig. 2A). Three HMEC strains (240L, 124, and 172) were tested. BMP2 repressed and HGF promoted the growth of KRT19+ cells in all strains, though effect sizes varied (Fig. 2B). In summary, MEMA results were reproducible with 240L cells, but validation with additional strains showed some inter-individual variation. HGF and BMP2, which showed consistent effects across multiple strains, were selected for deeper functional studies.
Ask a Question
Write your own review