Primary Human Fetal Lung Fibroblast Cells
Cat.No.: CSC-C4382X
Species: Human
Source: Lung
Cell Type: Fibroblast
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
These cells were originated using Complete Serum-Free Medium Kit With SuperFuel™, are available at <12 Cumulative Population Doublings (CPD) in vitro [Passage 3] and were cryopreserved in aliquots of ~1.5 X 10^6 cells. This vial will initiate a Passage 4 cell culture in a 75cm2 flask.
These cells are available in both cryopreserved vials as well as in 25cm2 and 75cm2 proliferating culture flasks.
Each vial or flask of cells is shipped to Customer with Bac-O (antibiotic) and SuperEnergy™ (animal derived growth factors) or SuperEnergy-R™ (human recombinant growth factors) at no additional cost.
Primary Human Fetal Lung Fibroblast Cells are spindle-shaped or stellate in appearance, grow adherently, have well-defined nuclei and plentiful cytoplasm. These cells demonstrate robust growth characteristics in vitro, maintaining proliferative capacity over extended periods during subculturing under standard conditions. They are involved in lung development, injury repair, and progression of lung disease. And they are the main cells responsible for producing extracellular matrix components and are involved in extracellular matrix synthesis, remodeling, and contraction. When the lungs are injured, fibroblasts receive injury signals and can proliferate and differentiate into myofibroblasts to repair lung tissue. In addition, they can also regulate the inflammatory and immune response. Human fetal lung fibroblasts can be used in research to model the pathogenesis of pulmonary diseases, drug screening, and cell therapy. For example, they can be used to study the pathogenesis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), as well as viral infection, tumor growth, and intercellular signaling studies.
Antimony(III) and bismuth(III) compounds have medical applications but their mechanisms are poorly understood. Ucar et al. synthesized four new complexes with imidazolidine-2-thione (IMT) and characterized them using spectroscopic, thermal, and X-ray diffraction methods.
The anticancer activity of compounds 1-4 and the free ligand (IMT) was measured on human breast adenocarcinoma (MCF-7) cell line after 48 h of incubation (Fig. 1). The IC50 values of 1-4 are >30 µM. They exhibited low activity towards MCF-7 cells, with cisplatin being much more active than complexes 1-4. The free ligand was found to be inactive as well. Moreover, the toxicity of 1-4 on normal human fetal lung fibroblast cells (MRC-5) was measured. The IC50 values of complexes 3 and 4 were >30 µM while the IC50 values of 1 and 2 were 5.4 ± 0.2 µM and 15.1 ± 0.9 µM, respectively. The therapeutic potency index (TPI) of antimony compounds (1 and 2) was lower than of bismuth compounds (3 and 4), which indicates the greater toxicity. TPI was calculated as IC50(normal cells)/IC50(tumor cells). Imidazolidine-2-thione complexes (1-4) were less active than dithiocarbamate complexes against cancer cells which can be related to their lower stability (Fig. 1).
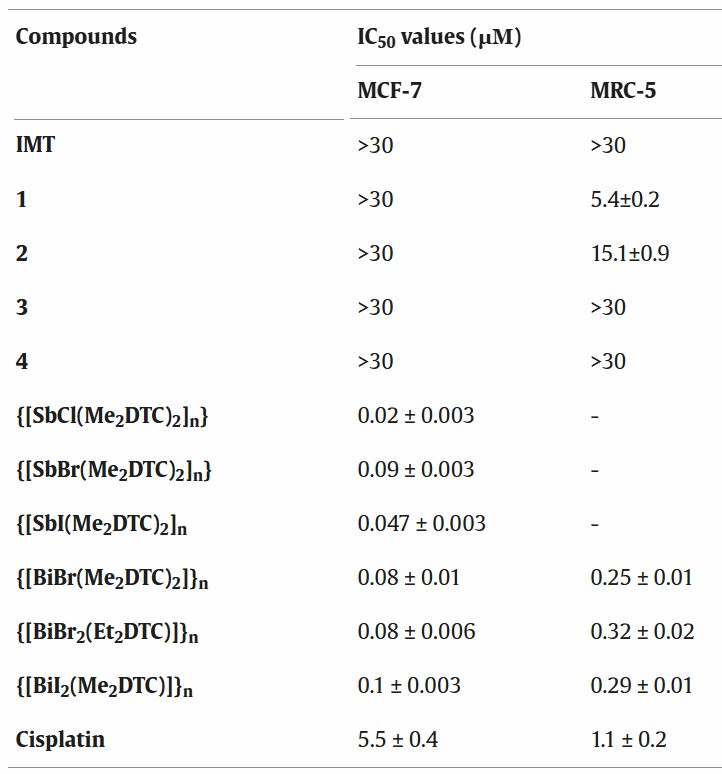 Fig. 1. IC50 values for cell viability found for complexes 1-4 and other Sb(III) and Bi(III) dithiocarbamate complexes against MCF-7 (breast) and MRC-5 cells (normal human fetal lung fibroblast cells) (Ucar O, Grześkiewicz A M, et al., 2021).
Fig. 1. IC50 values for cell viability found for complexes 1-4 and other Sb(III) and Bi(III) dithiocarbamate complexes against MCF-7 (breast) and MRC-5 cells (normal human fetal lung fibroblast cells) (Ucar O, Grześkiewicz A M, et al., 2021).
E2F Inhibitor Upregulates HO-1 mRNA and Protein Levels in Human Lung Fibroblasts
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is a progressive fibrotic and fatal lung disease of unknown etiology. HO-1, an anti-inflammatory enzyme, plays a role in IPF, but the mechanisms that control its expression are unknown. Ye's team investigated the regulation of HO-1 by E2F2 in lung fibroblasts using E2F2 inhibitors, siRNA, and overexpression techniques.
The E2F transcriptional inhibitor HLM006474 (HLM) was used to determine the role of E2Fs in primary human lung fibroblasts (HLF). HLM specifically binds to the E2F family of transcription factors and prevents their DNA binding activity, thus suppressing E2F transcriptional activity. HLF cells were treated with HLM (10 μM) for 24 h and then harvested for RNA extraction and RNA sequencing (RNA-seq). HO-1 mRNA was significantly upregulated in HLF cells treated with HLM (Fig. 2A). Real-time PCR analysis confirmed that HLM treatment resulted in increased HO-1 expression in HLF cells (Fig. 2B). Immunoblotting analysis showed that HLM treatment significantly induced HO-1 protein expression in a time-dependent manner in HLF cells (Fig. 3A) and in a time- and dose-dependent manner in normal human fetal lung fibroblast (IMR90) cells (Fig. 3B, C). Similar results were observed in another lung fibroblast cell line (Mrc5) (Fig. 3D). HLM also increased HO-1 protein expression in human lung small airway epithelial cells (HASEpC). Taken together, these data show that E2F transcription factors repress HO-1 expression.
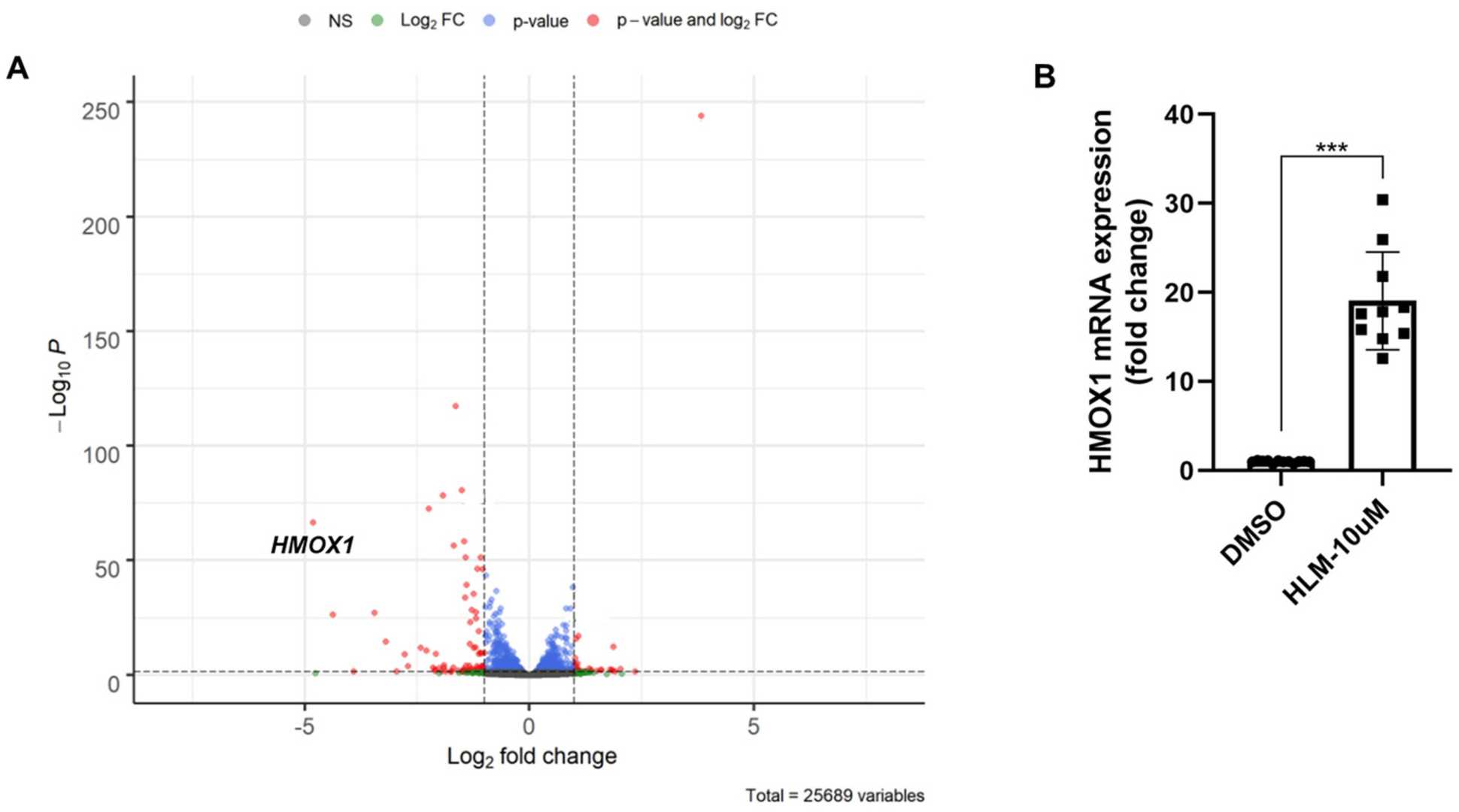 Fig. 2. E2F inhibitor upregulates HO-1 mRNA level (Ye Q, Taleb SJ, et al., 2022).
Fig. 2. E2F inhibitor upregulates HO-1 mRNA level (Ye Q, Taleb SJ, et al., 2022).
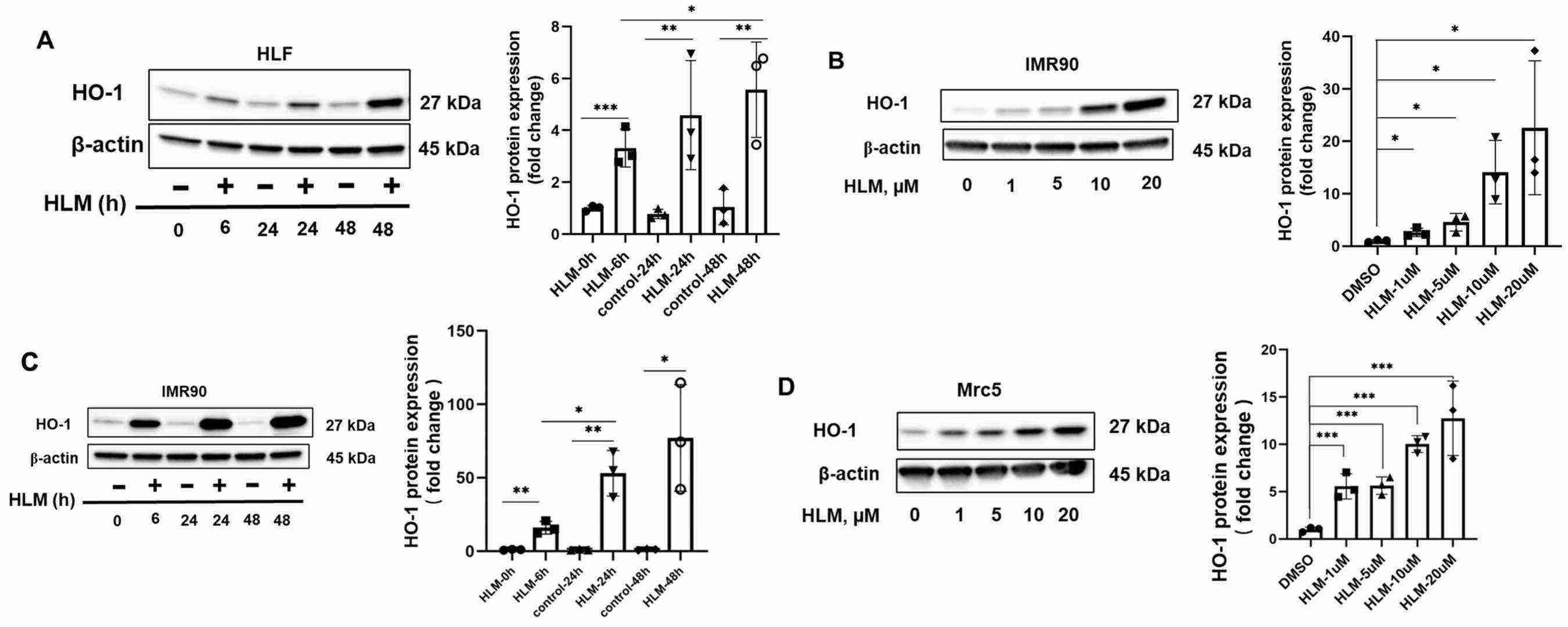 Fig. 3. HLM006474 increases HO-1 protein levels (Ye Q, Taleb SJ, et al., 2022).
Fig. 3. HLM006474 increases HO-1 protein levels (Ye Q, Taleb SJ, et al., 2022).
Ask a Question
Write your own review