Human Brain Vascular Adventitial Fibroblasts (HBVAF)
Cat.No.: CSC-7826W
Species: Human
Source: Brain
Cell Type: Fibroblast
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
Human Brain Vascular Adventitial Fibroblasts (HBVAFs) are the dominant cell type isolated from the human brain and are found in the adventitia, the outermost layer of the connective tissue surrounding cerebral vessels. The HBVAFs are spindle shaped, a common feature of fibroblasts, and positive for mesenchymal markers, such as fibronectin on immunofluorescence. The cells can attach to surfaces coated with poly-L-lysine and can grow in fibroblast optimized growth medium at 37 °C, 5% CO2 in an incubator. Functionally, adventitial fibroblasts (AFs) including HBVAFs are well known for their role in vessel wall homeostasis as well as in vascular diseases. Fibroblasts reside in the adventitia of blood vessels. Recent evidence suggests that AFs may not just be passive bystanders in the adventitia and may actively contribute to vascular remodeling. Stimuli such as mechanical injury, hypoxia, inflammation and endothelial cell damage can induce proliferation, migration, and secretion of matrix proteins and vasoactive factors by the AFs. Hence, HBVAF can be used as an in vitro model for studying aspects of vascular outer-wall remodeling in the cerebral vasculature. This includes cell-matrix interactions, oxidative stress, myofibroblast differentiation and paracrine signaling to the media and intima of the vessel wall.
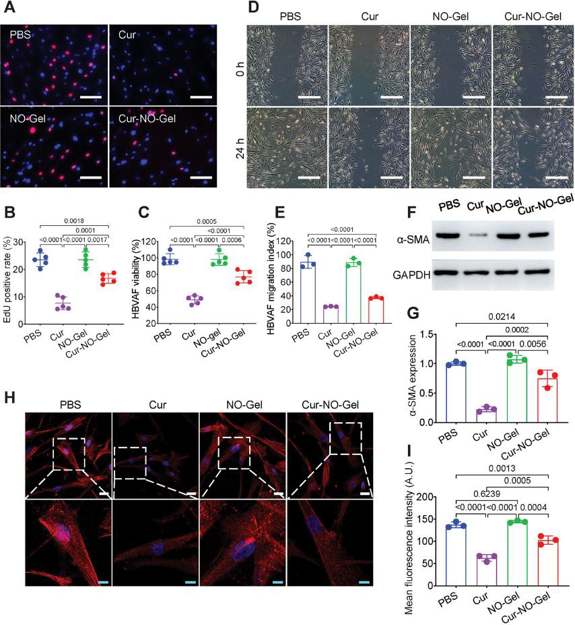
Cur-NO-Gel Suppresses the Activity of Vascular Fibroblasts and Inhibits Myofibroblast Transformation
Restenosis after angioplasty leads to recurrent coronary heart disease. Existing drug-eluting stents face limitations in function and safety. Here, Fu's team developed a stent-free anti-stenosis drug coating (Cur-NO-Gel) using a peptide hydrogel that releases nitric oxide (NO) and curcumin (Cur).
In vitro, they evaluated Cur-NO-Gel's effect on human brain vascular adventitial fibroblasts (HBVAFs). EdU assays showed Cur reduced proliferation from 23.52% to 7.63%, and Cur-NO-Gel to 16.7% (Fig. 1A, B). CCK-8 results were consistent. Scratch assays revealed Cur-NO-Gel reduced migration from 89.64% to 37.23% (Fig. 1C). These results indicate Cur-NO-Gel effectively inhibits vascular fibroblast activity. Activated fibroblasts (myofibroblasts) are characterized by high α-SMA expression. Western blot and immunofluorescence staining showed Cur-NO-Gel significantly reduced α-SMA expression in HBVAFs (Fig. 1D-I). These results prove Cur-NO-Gel inhibits the transformation of adventitial fibroblasts into myofibroblasts.
Receive the cells without opening the lid first, use alcohol to disinfect the entire cell bottle outer wall, placed in the incubator after a number of hours of static (depending on the density of the cells) in the inverted microscope to observe the growth of the cells, and take pictures of the cells at different magnifications (it is recommended to receive the cells when the media to take a picture, observe the color of the media and whether there is a leakage of the liquid situation, microscope to take pictures of the cells 100X, 200X each of the two), the cells should not be contaminated. Rule out contamination of the cells themselves.
Ask a Question
Average Rating: 5.0 | 1 Scientist has reviewed this product
Great
Creative Bioarray's cell products are great. The process is simple and it works perfectly.
10 Sep 2023
Ease of use
After sales services
Value for money
Write your own review