BALB/c Mouse Aortic Endothelial Cells
Cat.No.: CSC-C4350X
Species: Mouse
Source: Aorta
Cell Type: Endothelial Cell
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
BALB/c Mouse Aortic Endothelial Cells (MOEA) are primary endothelial cells that are isolated from the aorta of BALB/c mice and are commonly used as an in vitro model that is physiologically relevant and genetically well-defined for studying vascular endothelial biology. MOEA cells display the classic cobblestone morphology of endothelial monolayers and express characteristic endothelial markers, such as CD31 (PECAM-1), VE-cadherin, von Willebrand factor (vWF), and endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS), indicating their vascular identity and phenotype.
MOEA cells are functionally significant for modeling vascular homeostasis, angiogenesis, inflammation, and endothelial barrier function. They are responsive to various stimuli, including pro-inflammatory cytokines, shear stress, and hypoxic conditions, and are thus well-suited for studying endothelial activation, leukocyte adhesion, oxidative stress, and nitric oxide signaling. These cells are also commonly used in research related to atherosclerosis, vascular remodeling, thrombosis, and metabolic or immune-mediated vascular diseases.
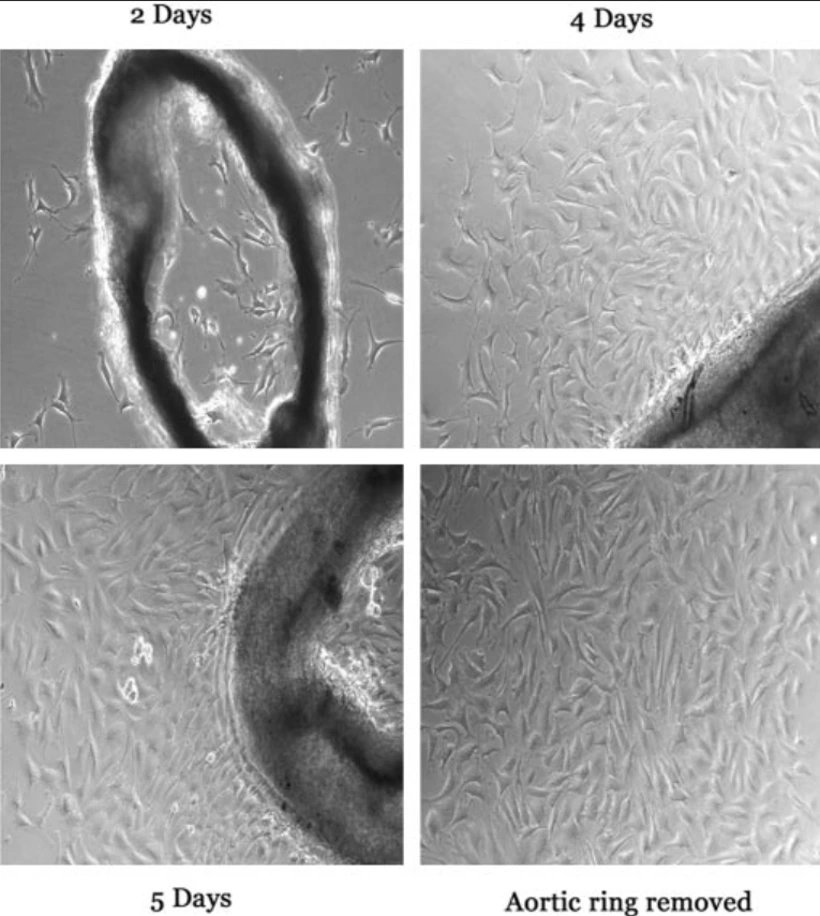
M1 Macrophage Polarization Induces EndMT Process
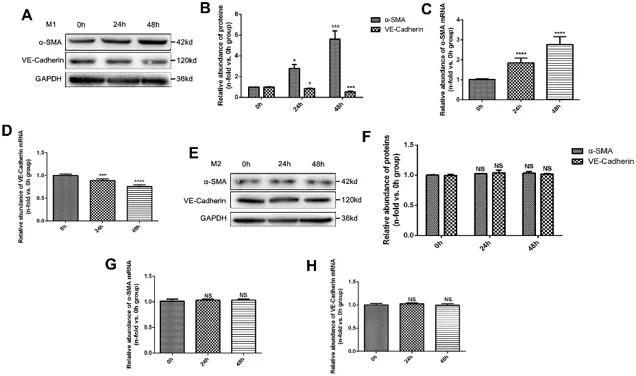
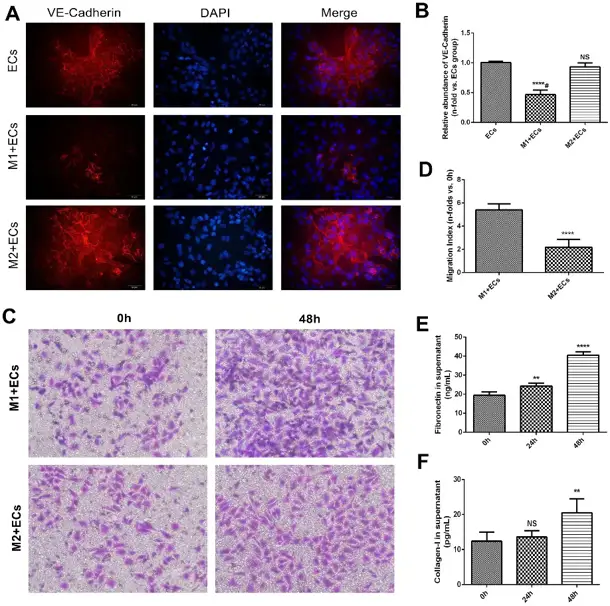
Chronic allograft dysfunction (CAD) is a progressive fibrosing process with obvious macrophage infiltration. Gui's team analyzed whether M1 macrophage polarization promoted endothelium-to-myofibroblast transition (EndMT) and contributed to the progression of CAD, and tried to explore the potential mechanism.
M1 and M2 macrophages were polarized in vitro and then co-cultured with mouse aortic endothelial cells (MAECs). M1 macrophages significantly increased α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) protein expression and decreased VE-Cadherin protein expression in MAECs in a time-dependent manner (Fig. 1A and B). PCR assay showed consistent results at the mRNA level (Fig. 1C and D). Co-culture with M2 macrophages did not significantly alter α-SMA or VE-Cadherin protein expression (Fig. 1E and F) or treatment with M2 macrophages (Fig. 1G and H). VE-Cadherin protein expression in endothelial cells treated with M1 macrophages was significantly lower than in endothelial cells co-cultured with M2 macrophages according to cell immunofluorescence assay (Fig. 2A and B). Transwell assay showed that the number of migrated endothelial cells was significantly higher in M1 macrophages than in M2 macrophages (Fig. 2C and D). Collagen-I and Fibronectin levels in supernatant of endothelial cells treated with M1 macrophages were significantly upregulated (Fig. 2E and F).
Ask a Question
Write your own review