Immortalized Human Pancreatic Stellate Cells-SV40
Cat.No.: CSC-I2291Z
Species: homo sapiens
Morphology: Polygonal
Culture Properties: Adherent
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
free from contaminations (bacteria incl. mycoplasma, fungi, HIV, HAV, HBV, HCV, Parvo-B19) and cross-contaminations
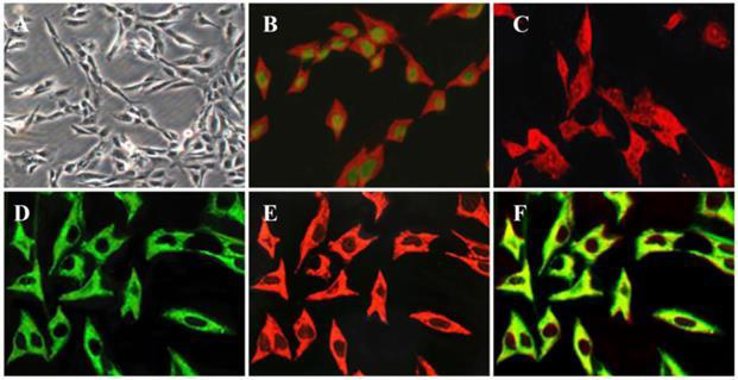
Pancreatic stellate cells (PSCs) play a key role in the pathogenesis of pancreatic fibrosis and the deposition of large amounts of insoluble extracellular matrix (ECM). In a normal pancreas, stellate cells are quiescent and, like their counterparts in the liver, store vitamin A in lipid droplets in their cytoplasm. When exposed to injury, inflammation or after prolonged cultivation in vitro, the cells transform to an activated myofibroblast-like state. In this activated state, PSCs begin to proliferate and synthesize ECM components like collagen type I and III (Col I and Col III), fibronectin (FN) and laminin. This state is accompanied by a gradual loss of lipid droplets and the expression of the proteins desmin, vimentin, αSMA and glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP).
Several methods for isolation of these cells have been published; however, these methods need fairly large amounts of tissue to obtain a sufficient number of cells. Furthermore, due to the finite lifespan of PSCs and the phenotypic changes observable with time in culture, researchers need to analyze different preparations of PSCs, making a direct comparison of results difficult. Immortalized Human Pancreatic Stellate Cells-SV40 retain key phenotypic features of primary pancreatic stellate cells while possessing the extended lifespan and reproducibility required for robust experimental studies. They are ideal for research in pancreatic biology, fibrosis, tumor-stroma interactions, and extracellular matrix regulation.
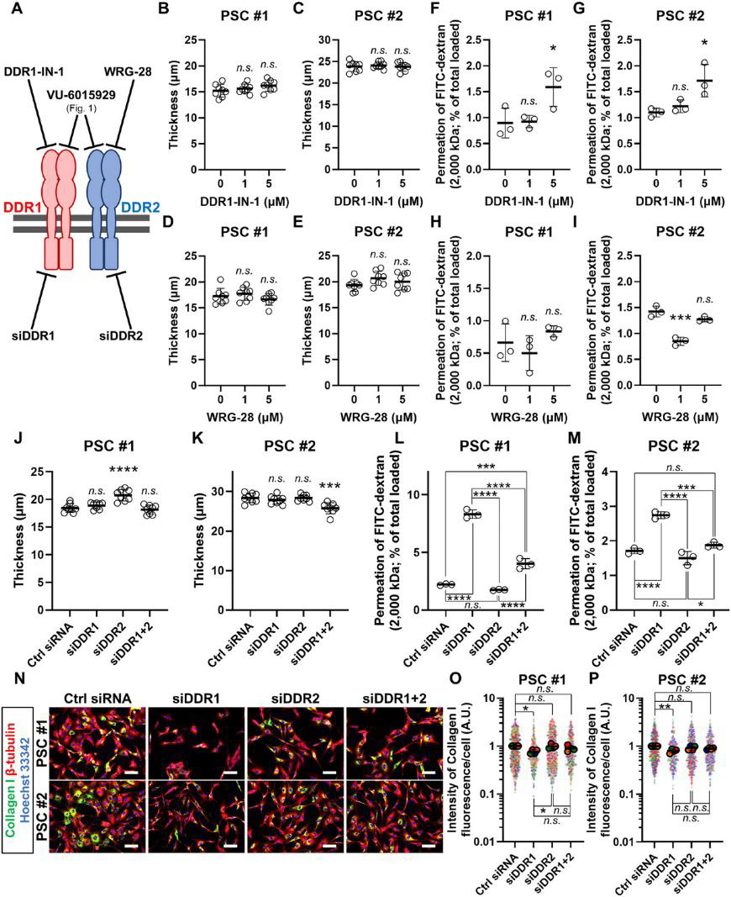
Collagen Signaling via DDR1 Exacerbates Barriers to Macromolecular Drug Delivery in a 3D Model of Pancreatic Cancer Fibrosis
Fibrosis is a significant barrier to drug delivery in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) and contributes to its dismal prognosis. Pancreatic stellate cells (PSCs) drive fibrosis by excessively secreting extracellular matrix proteins such as collagen I. Collagen I is thought to physically obstruct the delivery of macromolecules, such as albumin, antibodies, and nanomedicines. Apart from its structural role, collagen signals through dedicated cell surface receptors, such as the discoidin domain receptors (DDR) 1/2. However, whether and how collagen signaling contributes to fibrotic barrier generation remains uncharacterized.
Here, a 3D culture model of PDAC fibrosis constructed from patient PSCs is used to assess the contribution of DDR1/2-mediated collagen signaling. DDR1/2 inhibition diminishes collagen I expression in PSCs to enhance macromolecular delivery. Moreover, MEK inhibitors exacerbate the fibrotic barrier by up-regulating collagen I, an effect reversed by inhibiting DDR1/2. Through isoform-specific targeting, inhibiting DDR1, but not DDR2, is shown to be effective. Altogether, the results show in vitro that DDR1-mediated collagen signaling exacerbates the fibrotic barrier and may be targeted to enhance macromolecular drug delivery in PDAC.
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells
